Reverse-Power Protection Application with Flexible Protection
Function
Functional Description
General
General By means of the flexible protection functions a single-element or multi-element reverse power protec-
tion can be realized. Each reverse power element can be operated in single-phase or three-phase. Depending
on the chosen option, the elements can evaluate active power forward, active power reverse, reactive power
forward or reactive power reverse as measured value. The pickup by the protection elements can occur on
exceeding or undershooting of the threshold. Possible applications for reverse power protection are set out in
Table 2-19.
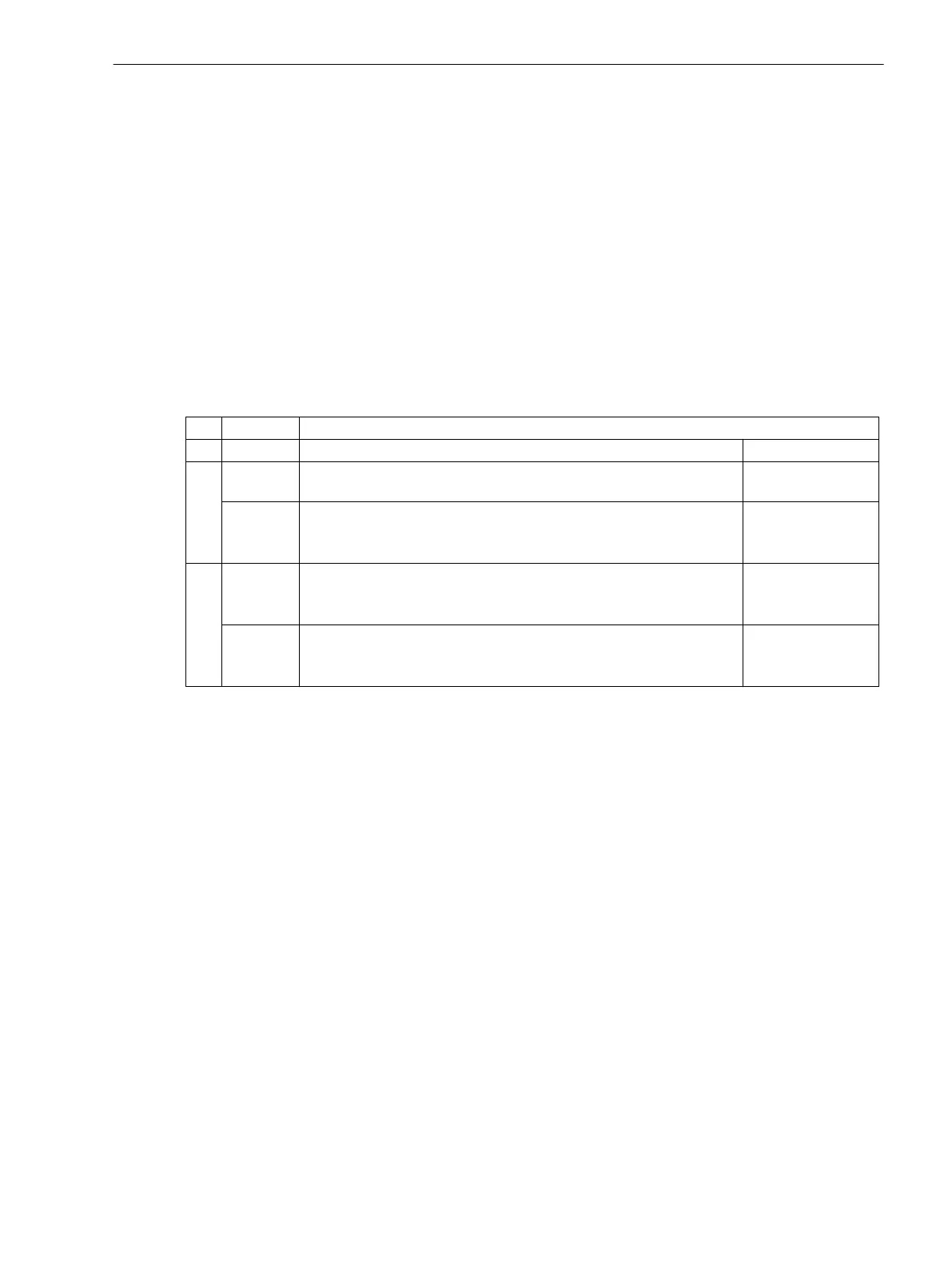
Table 2-19 Overview of reverse power protection applications
Type of Evaluation
Direction Overshooting Undershooting
P forward Monitoring of the forward power limits of operational equipment Detection of idling
motors
reverse Protection of a local industrial network against reversed feeding into
the energy supply network
Detection of reversed feeding by motors
Q forward Monitoring of the reactive power limits of operational equipment
(transformers, lines)
Connection of a capacitor bank for reactive power compensation
reverse Monitoring of the reactive power limits of operational equipment
(transformers, lines)
Connection of a capacitor bank
The following example depicts a typical application where the flexible function acts as reverse power protec-
tion.
Disconnection Facility
The following fugure gives an example of an industrial control system with internal supply by the illustrated
generator. All illustrated lines and the busbar are indicated in three-phase (excluding the ground connections
and the connection to the voltage measurement at the generator). Both feeders 1 and 2 supply the consumers
of the customer. Usually the industrial customer receives his current from the energy supplier. The generator
runs in synchronism, without feeding power. If the power supply company can no longer guarantee the
required supply, the control system is separated from the system of the power supply company and the gener-
ator is taking over the internal supply. In this example the control system is disconnected from the system of
the power supply company as soon as the frequency leaves the nominal range (e.g. 1 - 2% deviation from the
nominal frequency), the voltage exceeds or undershoots a set value, or the generator's active power is fed to
the system of the power supply company. Depending on the user's philosophy, some of these criteria may be
combined. This would be realized via the CFC.
The example illustrates how a reverse power protection is implemented by means of the flexible protection
functions. Frequency protection and voltage protection are described in Sections 2.8 Frequency Protection 81
O/U and 2.6 Voltage Protection 27, 59.
2.19
2.19.1
Functions
2.19 Reverse-Power Protection Application with Flexible Protection Function
SIPROTEC 4, 7SJ80, Manual 253
E50417-G1140-C343-A8, Edition 12.2017

 Loading...
Loading...











