Directional Overcurrent Protection 67, 67N
The directional time overcurrent protection comprises three elements each for phase currents and the ground
current that can operate directional or non-directional. All elements are independent of each other and can be
combined as desired.
High current element 67-2 and overcurrent element 67-1 always operate with a definite tripping time, the
third element 67-TOC always operates with inverse tripping time.
Applications
•
The directional overcurrent protection allows the application of multifunctional protection devices 7SJ80
also in systems where protection coordination depends on knowing both the magnitude of the fault
current and the direction of power flow to the fault location.
•
The non-directional overcurrent protection described in Section 2.2 Overcurrent Protection 50, 51, 50N,
51N may operate as overlapping backup protection or may be disabled. Additionally, individual elements
(e.g. 67-2 and/or 67N-2) may be interconnected with the directional overcurrent protection.
•
For parallel lines or transformers supplied from a single source, only directional overcurrent protection
allows selective fault detection.
•
For line sections supplied from two sources or in ring-operated lines, the overcurrent protection has to be
supplemented by the element-specific directional criterion.
General
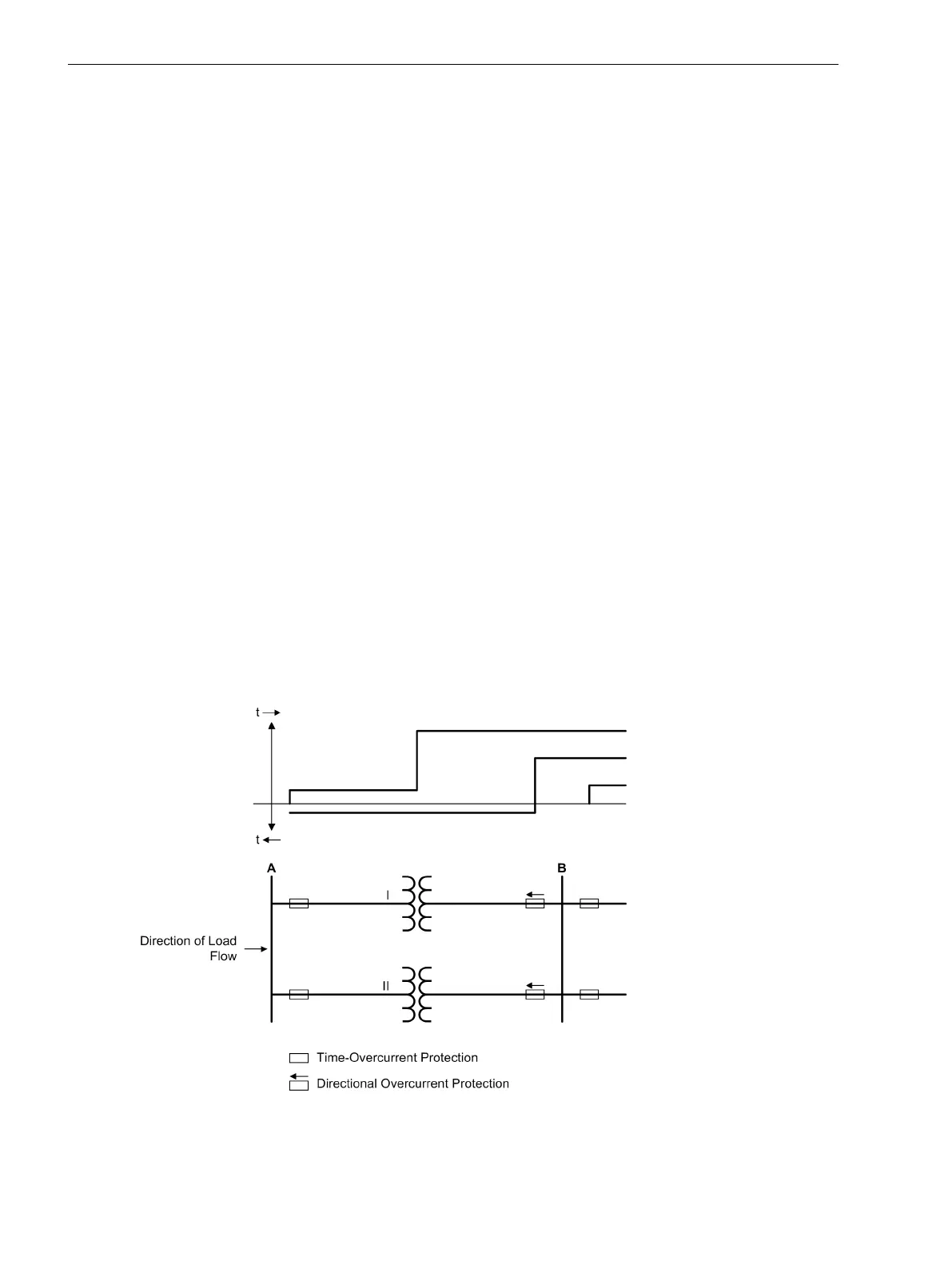
For parallel lines or transformers supplied from a single source (see Figure 2-19), the second feeder (II) is
opened on occurrence of a fault in the first feeder (I) if tripping of the breaker in the parallel feeder is not
prevented by a directional measuring element (at B). Therefore, where indicated with an arrow (Figure 2-19),
directional overcurrent protection is applied. Please ensure that the "forward" direction of the protection
element is in the direction of the line (or object to be protected). This is not necessarily identical with the
direction of the normal load flow, as shown in Figure 2-19.
[ueberstromzeitschutz-bei-paralleltransformatoren-020626-kn, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-19 Overcurrent protection for parallel transformers
2.3
2.3.1
Functions
2.3 Directional Overcurrent Protection 67, 67N
82 SIPROTEC 4, 7SJ80, Manual
E50417-G1140-C343-A8, Edition 12.2017

 Loading...
Loading...











