RUN MED: Service & Maintenance Manual - rev. 1.0
Page 3.6
3.2. TREAD BELT MOTOR DRIVE
3.2.1. MECHANICS
The tread belt is actuated by the motor through a linkage consisting of the motor pulley, the driving
roller and the belt which connects them. In this way, a given belt motor speed corresponds to a
predetermined linear tread belt speed.
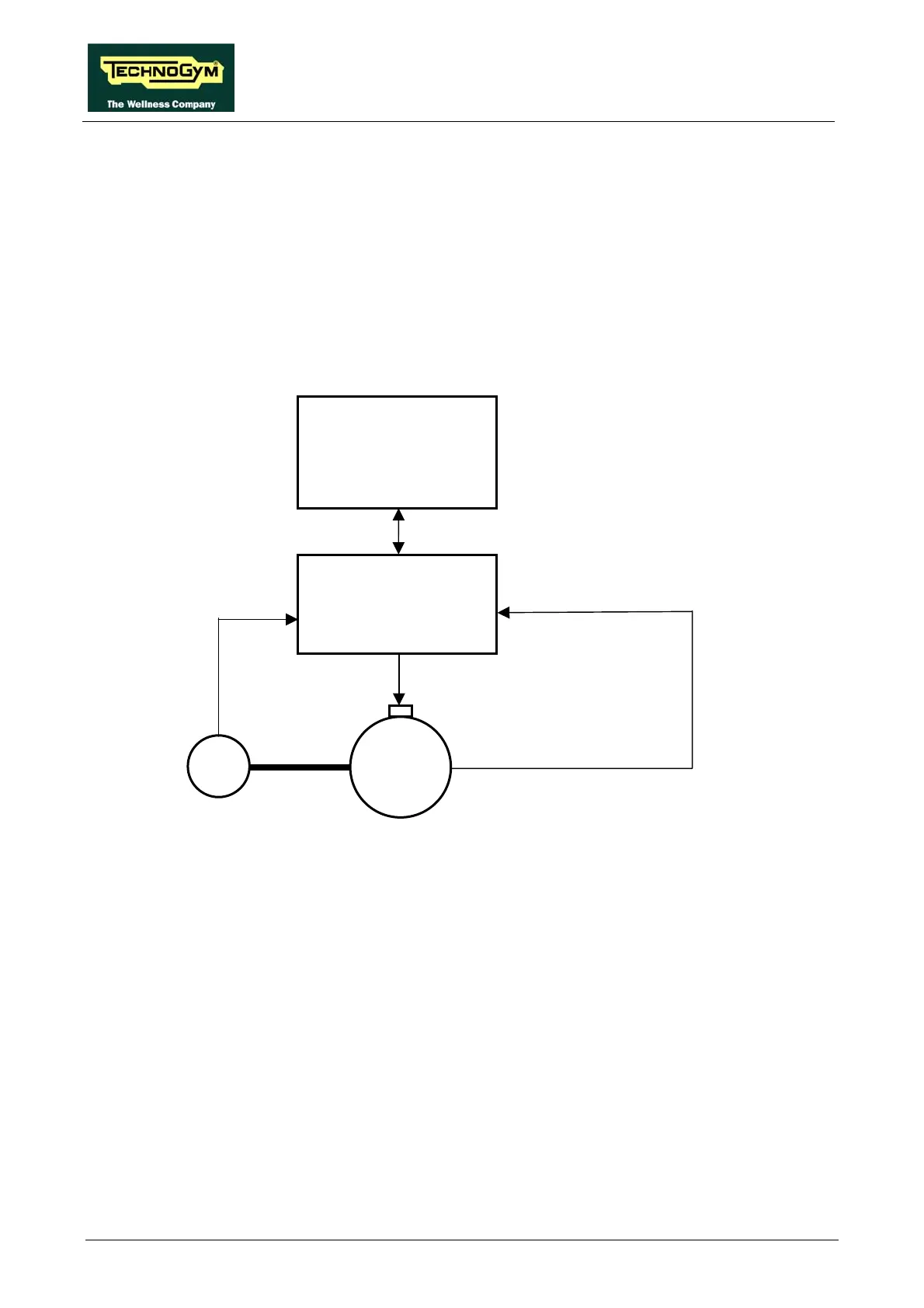
3.2.2. CONTROLS
The control block diagram is as follows:
Display Board
AT driver
RS-485
CN2
J4
1-2-3/J5
M
Cut-out
4-5/J5
VAC
with variable frequency
Encoder
1-2/J6
4-2/J6
Pulses
To actuate the motor, the display board communicates with the AT driver via the RS-485 serial
link. Based on the commands received, the AT driver drives the motor by applying a variable
frequency sinusoidal voltage: the frequency determines the speed of rotation of the motor and hence
the linear tread belt speed. The control may happen in 2 modalities:
• Close loop: When the motor turns, the AT driver receives the pulses produced by the encoder
that are representing the real speed at which the motor is turning and it uses these pulses to
adjust the frequency of the sinusoidal voltage in order to have the motor running at the selected
speed.
• Open loop: If, due to an error on the tread belt motor, the P13 parameter changes to 1, the
encoder is not more considered for the tread belt motor management. Since there is no encoder
to measure the motor speed, the AT driver provides to the motor a sinusoidal voltage at a
frequency that theoretically set the motor running at the selected speed.
During its movement, the AT driver continually checks the motor by monitoring its current draw as
well as the encoder signals, where available. If any problems are detected (low voltage, overcurrent,
 Loading...
Loading...











