TI-83, TI-83 Plus, TI-84 Plus Guide
Chapter 2 Describing Change: Rates
As you calculate average and other rates of change, remember that every numerical answer in
a context should be accompanied by units telling how the quantity is measured. You should
also be able to interpret each numerical answer. It is only through their interpretations that the
results of your calculations will be useful in real-world situations.
FINDING AVERAGE RATE OF CHANGE Finding an average rate of change using a
function is just a matter of evaluating the equation at two different values of the input variable
and dividing by the difference of those input values.
We illustrate this concept using the function describing the temperature on a typical day in
May in a certain Midwestern city that is given in Example 3 of Section 2.1 of Calculus
Concepts.
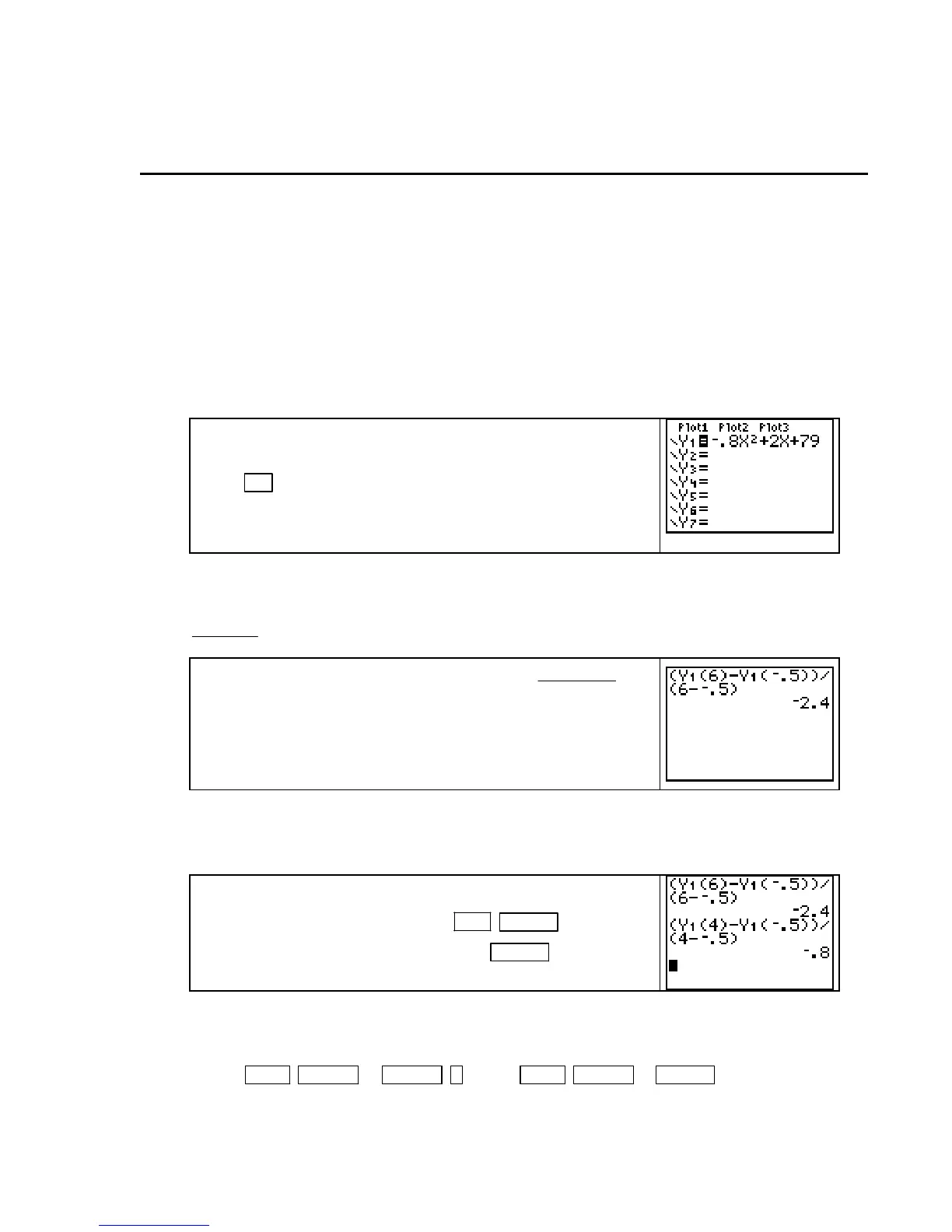
The temperature referred to above is given by the function T(t)
=
where t is the number of hours after noon.
Press
Y=
2
0.8 2 79 F−++tt
o
, clear any functions, turn Plot 1 off, and enter this
function in
Y1 using X as the input variable.
To find the average rate of change of the temperature between 11:30 A.M. and 6 P.M., first
realize that 11:30
A.M. corresponds to t = -0.5 and 6 P.M. corresponds to t = 6. Then, recall
that the average rate of change of T between 11:30
A.M. and 6 P.M. is given by the quotient
(6) ( 0.5)
6(0.5)
−−
−−
TT
.
Return to the home screen and type the quotient
Y1(6) Y1( 0.5)
6(0.5)
−−
−−
.
Remember to enclose both the numerator and denominator of
the fraction in parentheses.
Finding this quotient in a single step avoids having to round
intermediate calculation results.
Recall that rate of change units are output units per input units. On average, the temperature
on a typical day in May in a certain Midwestern city decreased about 2.4
o
per hour between
11:30
A.M. and 6 P.M.
F
To find the average rate of change between 11:30 A.M. and 4
P.
M., recall the last expression with 2ND ENTER (ENTRY)
and replace 6 with 4 in two places. Press
ENTER .
NOTE: If you have many average rates of change to calculate, you could put the average rate
of change formula in the graphing list:
Y2 = ( Y1(B) – Y1(A) )/(B – A). Of course, you need to
have a function in
Y1. Then, on the home screen, store the inputs of the two points in A and B
with
80 STO` ALPHA A ALPHA . ( : ) 100 STO` ALPHA B ENTER . All you need do
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
43

 Loading...
Loading...

















