Version 7.2 775 Mediant 1000B Gateway & E-SBC
User's Manual 45. Automatic Provisioning
45 Automatic Provisioning
This chapter describes the device's automatic provisioning mechanisms.
45.1 Automatic Configuration Methods
The table below summarizes the automatic provisioning methods supported by the device:
Table 45-1: Automatic Provisioning Methods
BootP / TFTP DHCP Automatic Update Methods SNMP
(EMS)
67 66 HTTP/S TFTP FTP NFS
No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes
45.1.1 DHCP-based Provisioning
A third-party DHCP server can be configured to automatically provide each device, acting
as a DHCP client, with a temporary IP address so that individual MAC addresses are not
required. The DHCP server can provide additional networking parameters such as subnet
mask, default gateway, primary and secondary DNS server, and two SIP server addresses.
These network parameters have a time limit, after which the device must 'renew' its lease
from the DHCP server.
The device can use a host name in the DHCP request. The host name is set to acl_nnnnn,
where nnnnn denotes the device's serial number. The serial number is the last six digits of
the MAC address converted to decimal representation. In networks that support this feature
and if the DHCP server registers this host name to a DNS server, you can access the
device (through a Web browser) using the URL, http://acl_<serial number> (instead of
using the device's IP address). For example, if the device's MAC address is 00908f010280,
the DNS name is acl_66176.
Note:
• When using DHCP to acquire an IP address, the IP Interfaces table, VLANs and
other advanced configuration options are disabled.
• For additional DHCP parameters, see ''DHCP Parameters'' on page 948.
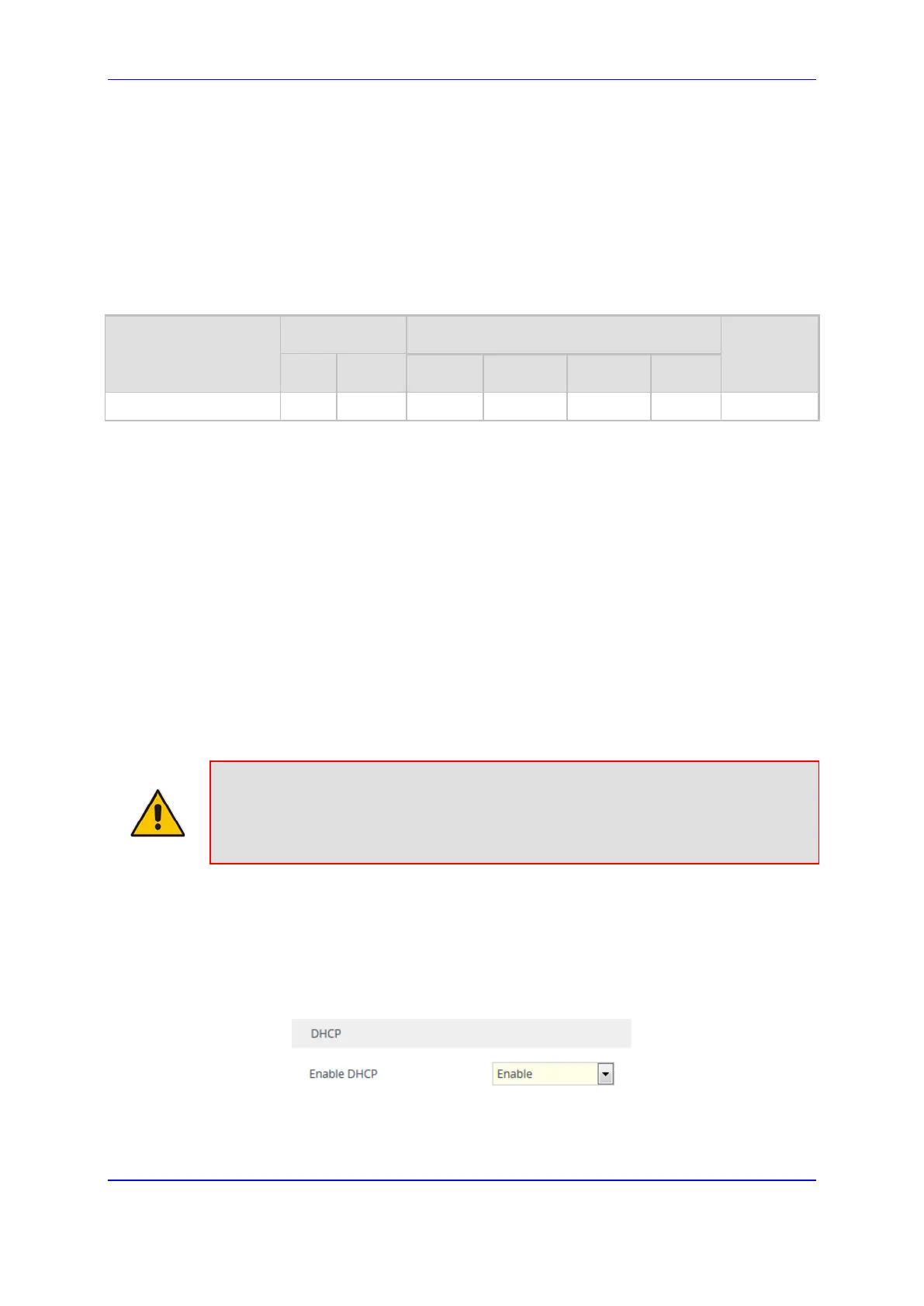
To enable the device as a DHCP client:
1. Open the Network Settings page (Setup menu > IP Network tab > Advanced folder >
Network Settings).
2. From the 'Enable DHCP" drop-down list, select Enable.
Figure 45-1: Enabling DHCP Client Functionality
3. Click Apply.
4. To activate the DHCP process, reset the device.

 Loading...
Loading...



















