Version 7.2 749 Mediant 1000B Gateway & E-SBC
User's Manual 43. Software Upgrade
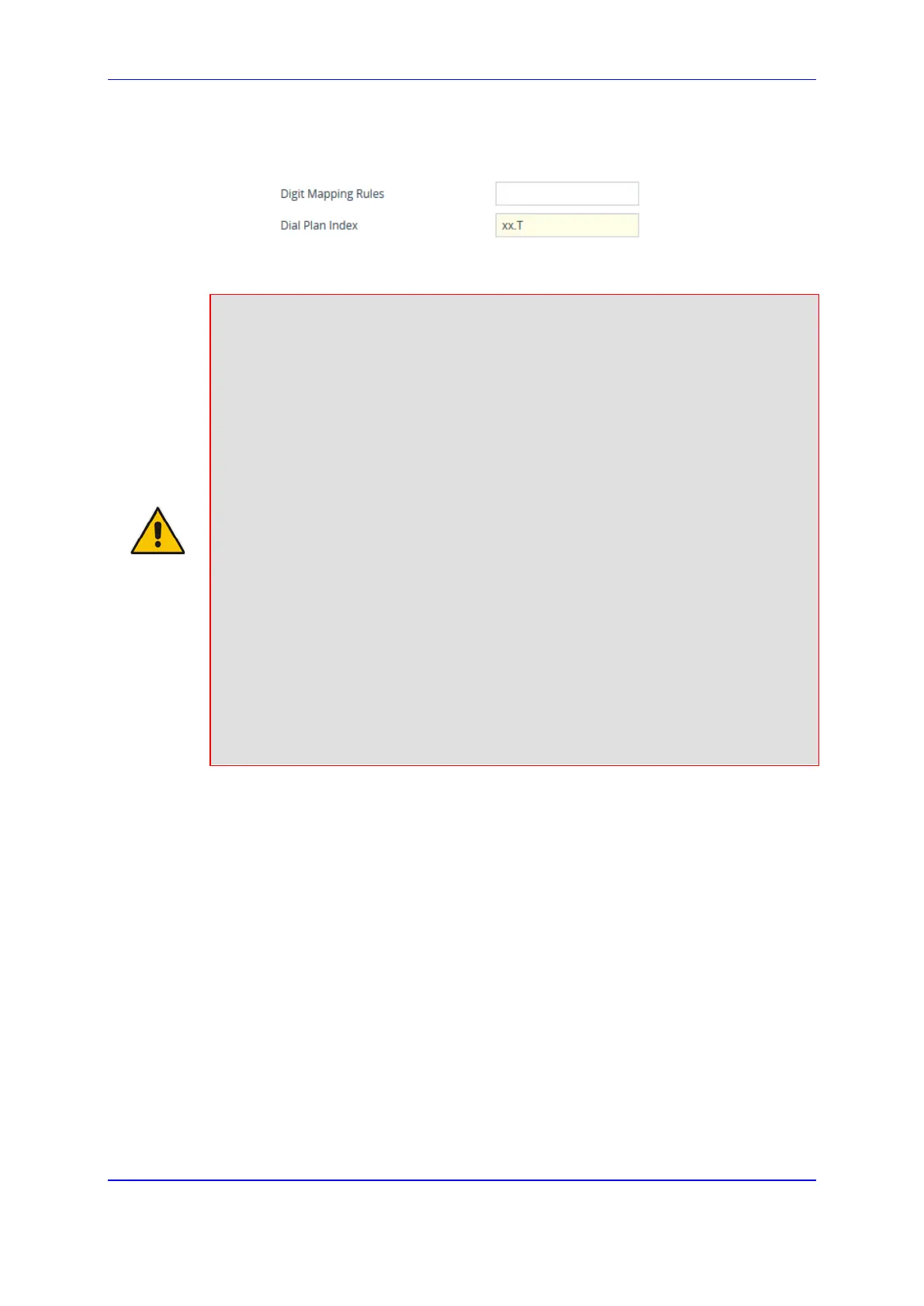
c. In the 'Digit Mapping Rules' field, enter the digit map.
Figure 43-2: Configuring Digit Map and Dial Plan
6. Click Apply.
Note:
• The Dial Plan file must not contain overlapping prefixes. Attempting to process an
overlapping configuration by the DConvert utility results in an error message
specifying the problematic line.
• The Dial Plan index can be selected globally for all calls (as described in the
previous procedure), or per specific calls using Tel Profiles.
• It may be useful to configure both Dial Plan file and Digit Maps. For example, the
Digit Map can be used for complex digit patterns (which are not supported by the
Dial Plan file) and the Dial Plan can be used for long lists of relatively simple digit
patterns. In addition, as timeout between digits is not supported by the Dial Plan,
the Digit Map can be used to configure digit patterns that are shorter than those
defined in the Dial Plan or left at default (MaxDigits parameter). For example, the
“xx.T” digit map instructs the device to use the Dial Plan and if no matching digit
pattern is found, it waits for two more digits and then after a timeout
(TimeBetweenDigits parameter), it sends the collected digits. Therefore, this
ensures that calls are not rejected as a result of their digit pattern not been
completed in the Dial Plan.
• By default, if no matching digit pattern is found in both the Dial Plan and Digit Map,
the device rejects the call. However, if you set the DisableStrictDialPlan parameter
to 1, the device attempts to complete the call using the MaxDigits and
TimeBetweenDigits parameters. In such a setup, it collects the number of digits
configured by the MaxDigits parameters. If more digits are received, it ignores the
settings of the parameter and collects the digits until the inter-digit timeout
configured by the TimeBetweenDigits parameter is exceeded.
43.1.7.3 Dial Plan Prefix Tags for IP-to-Tel Routing
For deployments requiring many IP-to-Tel routing rules that exceed the maximum number
of rules that can be configured in the IP-to-Tel Routing table, you can employ user-defined
string labels (tags) to represent the many different prefix calling (source) and called
(destination) numbers. The prefix tags are used in the IP-to-Tel Routing table (see
''Configuring IP-to-Tel Routing Rules'' on page 484) as source and destination number
matching characteristics for the routing rule. Prefix tags are typically implemented when
you have calls of many different called or calling numbers that need to be routed to the
same destination. Thus, instead of configuring a routing rule for each prefix number, you
need to configure only one routing rule using the prefix tag.
For example, this feature is useful in deployments that need to handle hundreds of call
routing scenarios such as for a large geographical area (a state in the US). Such an area
could consist of hundreds of local area codes as well as codes for international calls. The
local calls and international calls would need to be routed to different SIP trunks. Thus,
instead of configuring many routing rules for each call destination type, you can simply
configure two routing rules, one with a unique prefix tag representing the different local
area codes and the other with a prefix tag representing international calls.

 Loading...
Loading...



















