M-Series Operator’s Manual 4/9/15
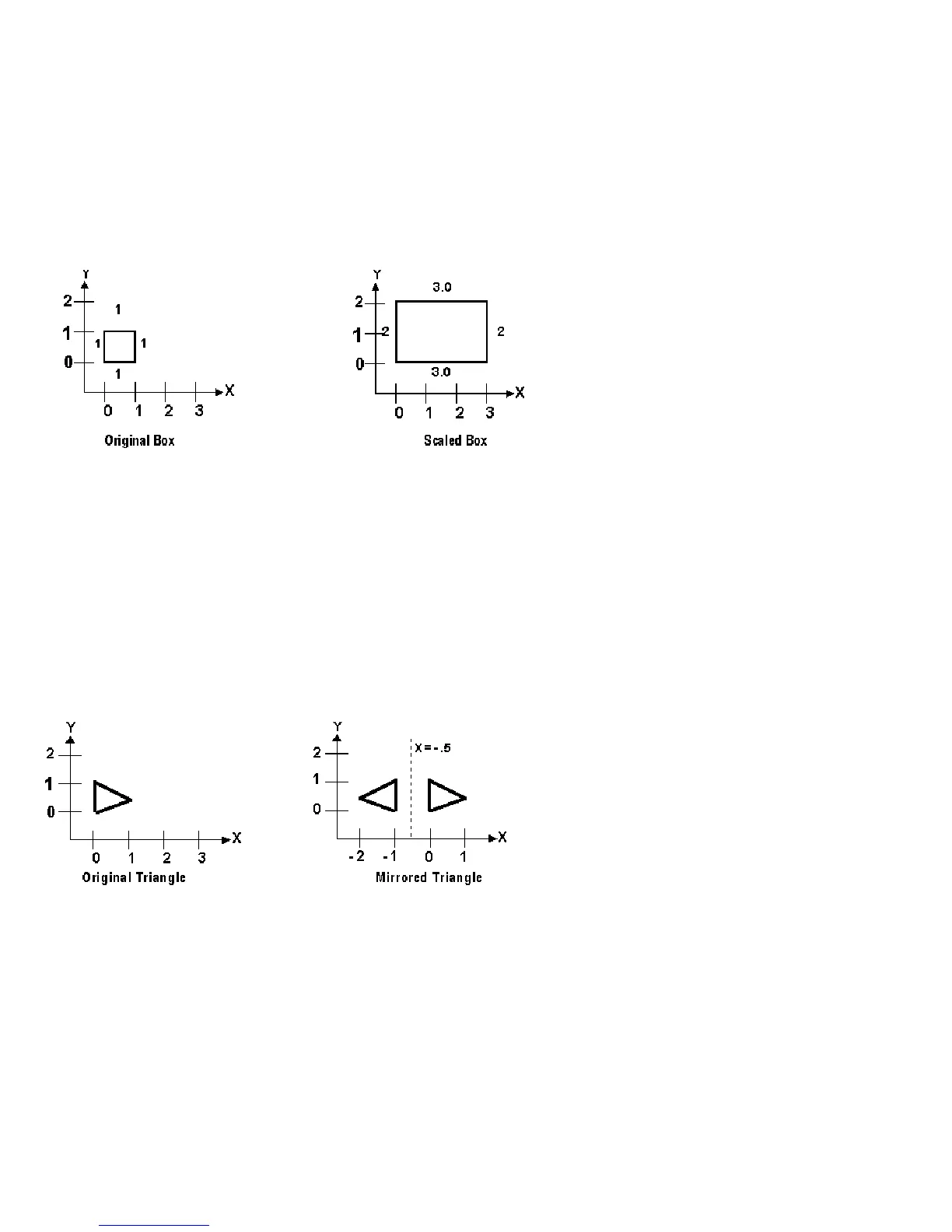
Example, Scaling:
G51 X0.0 Y0.0 Z0.0 I3.0 J2 K1 ; turn scaling on
G00 X0.0 Y0.0 Z1.0 ; rapid to X0, Y0, Z1
G01 X1.0 Y0.0 Z1.0 ; line to X1, Y0, Z1
G01 X1.0 Y1.0 Z1.0 ; line to X1, Y1, Z1
G01 X0.0 Y1.0 Z1.0 ; line to X0, Y1, Z1
G01 X0.0 Y0.0 Z1.0 ; line to X0, Y0, Z1
G01 X0.0 Y0.0 Z0.0 ; line to X0, Y0, Z0
G50 ; cancel scale
For this G51, the following program lines were scaled 3:1 in the X direction, 2:1 in the Y direction, and 1:1 in the Z
direction. If no scale factor is specified, the default is 1:1 for all axes.
Example, Mirroring:
G51 X-0.5 Y0.0 Z.0 I-1 J1 K1 ; turn mirror on (x axis -0.5 mirror
; line)
G00 X0.0 Y0.0 Z1.0 ; rapid traverse to X0, Y0, Z1
G01 X1.0 Y0.5 Z1.0 ; line to X1, Y.5, Z1
G01 X0.0 Y1.0 Z1.0 ; line to X0, Y1, Z1
G01 X0.0 Y0.0 Z1.0 ; line to X0, Y0, Z1
G50 ; cancel mirror
If scaling factors are the same for all the axes, parameter P can be used.
Example:
G51 X1.0 Y2.0 Z0.0 P2.5 ; scale all axes a factor of 2.5.
If an arc is scaled with uneven scaling factors, the result will depend on how the arc center and radius were
specified:
1. If the arc radius was specified with R, the radius will be scaled by the larger of the two circular plane scale
factors. The result will be a circular arc between the scaled arc start and the scaled arc end.
2. If the arc center was specified with I, J, and/or K, the centers will be scaled by the appropriate axis scale factors.
The result will be a circular arc from the scaled arc start, around the scaled center, and usually with a line from the
end of the circular arc to the scaled arc end.
3. In no case can an ellipse be generated using scaling.
 Loading...
Loading...