1-5
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7931G Administration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 8.0 (SCCP and SIP)
OL-20798-01
Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco Unified IP Phone
What Networking Protocols Are Used?
What Networking Protocols Are Used?
Cisco Unified IP Phones support several industry-standard and Cisco networking protocols required for
voice communication. Table 1-2 provides an overview of the networking protocols that the
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7931G supports.
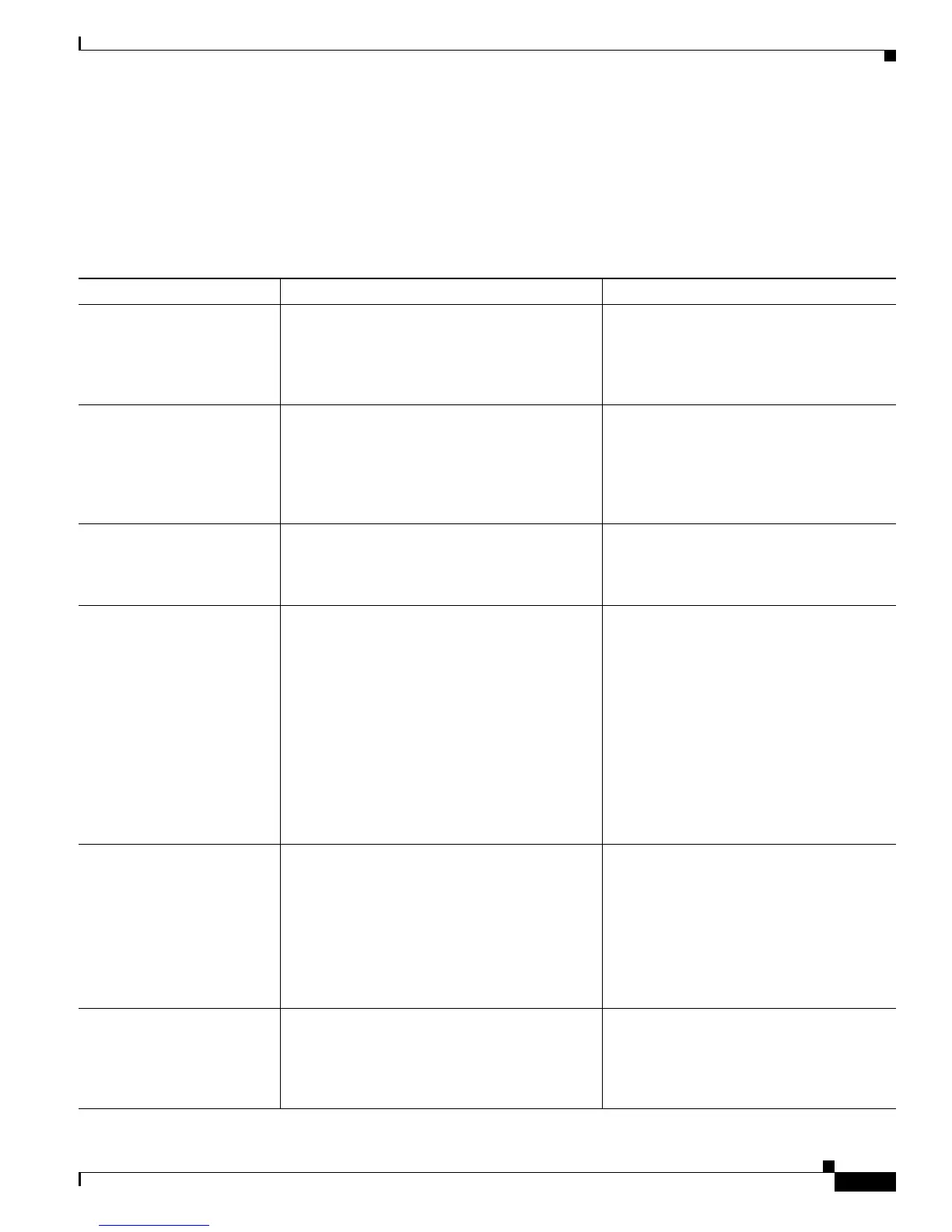
Table 1-2 Supported Networking Protocols on the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Networking Protocol Purpose Usage Notes
Bootstrap Protocol (BootP) BootP enables a network device such as the
Cisco Unified IP Phone to discover certain
startup information, such as its IP address.
If you are using BootP to assign IP
addresses to the Cisco Unified IP Phone,
the BOOTP Server option shows “Yes”
in the network configuration settings on
the phone.
Cisco Discovery Protocol
(CDP)
CDP is a device-discovery protocol that runs on
all Cisco-manufactured equipment.
Using CDP, a device can advertise its existence
to other devices and receive information about
other devices in the network.
The Cisco Unified IP Phone uses CDP to
communicate information such as auxiliary
VLAN ID, per port power management
details, and Quality of Service (QoS)
configuration information with the Cisco
Catalyst switch.
Cisco Peer-to-Peer
Distribution Protocol
(CPPDP)
CPPDP is a Cisco proprietary protocol that is
used to form a peer-to-peer hierarchy of devices.
CPPDP also is used to copy firmware or other
files from peer devices to neighboring devices.
CPPDP is used by the Peer Firmware
Sharing feature.
Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP)
DHCP dynamically allocates and assigns an IP
address to network devices.
DHCP enables you to connect an IP phone into
the network and have the phone become
operational without your needing to manually
assign an IP address or to configure additional
network parameters.
DHCP is enabled by default. If disabled,
you must manually configure the IP
address, subnet mask, gateway, and a TFTP
server on each phone locally.
Cisco recommends that you use DHCP
custom option 150. With this method, you
configure the TFTP server IP address as the
option value. For additional supported
DHCP configurations, see the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager
System Guide, Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol and Cisco TFTP.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
(HTTP)
HTTP is the standard way of transferring
information and moving documents across the
Internet and the web.
Cisco Unified IP Phones use HTTP for the
XML services and for troubleshooting
purposes.
Cisco Unified IP Phones do not support
the use of IPv6 addresses in the URL. You
cannot use literal IPv6 addresses in the
URL or hostname which maps to a
IPv6 address.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
Secure (HTTPS)
HTTPS is a combination of HTTP and the
SSL/TLS protocol to provide encryption and
secure identification of servers.
Web applications with both HTTP and
HTTPS support have two URLs configured.
Cisco Unified IP Phones that support
HTTPS choose the HTTPS URL out of the
two URLs.

 Loading...
Loading...





