30-4
Catalyst 3750 Metro Switch Software Configuration Guide
78-15870-01
Chapter 30 Configuring MPLS and EoMPLS
Understanding MPLS VPNs
• Flexible addressing—Customers can continue to use their present address spaces without network
address translation (NAT) because the MPLS VPN provides a public and private view of the address.
A NAT is required only if two VPNs with overlapping address spaces want to communicate.
• Straightforward migration—You can build MPLS VPNs over multiple network architectures.
Migration for the end customer is simplified because the CE router is not required to support MPLS,
so no customer's intranet modifications are needed.
• MPLS VPN also provides increased BGP functionality.
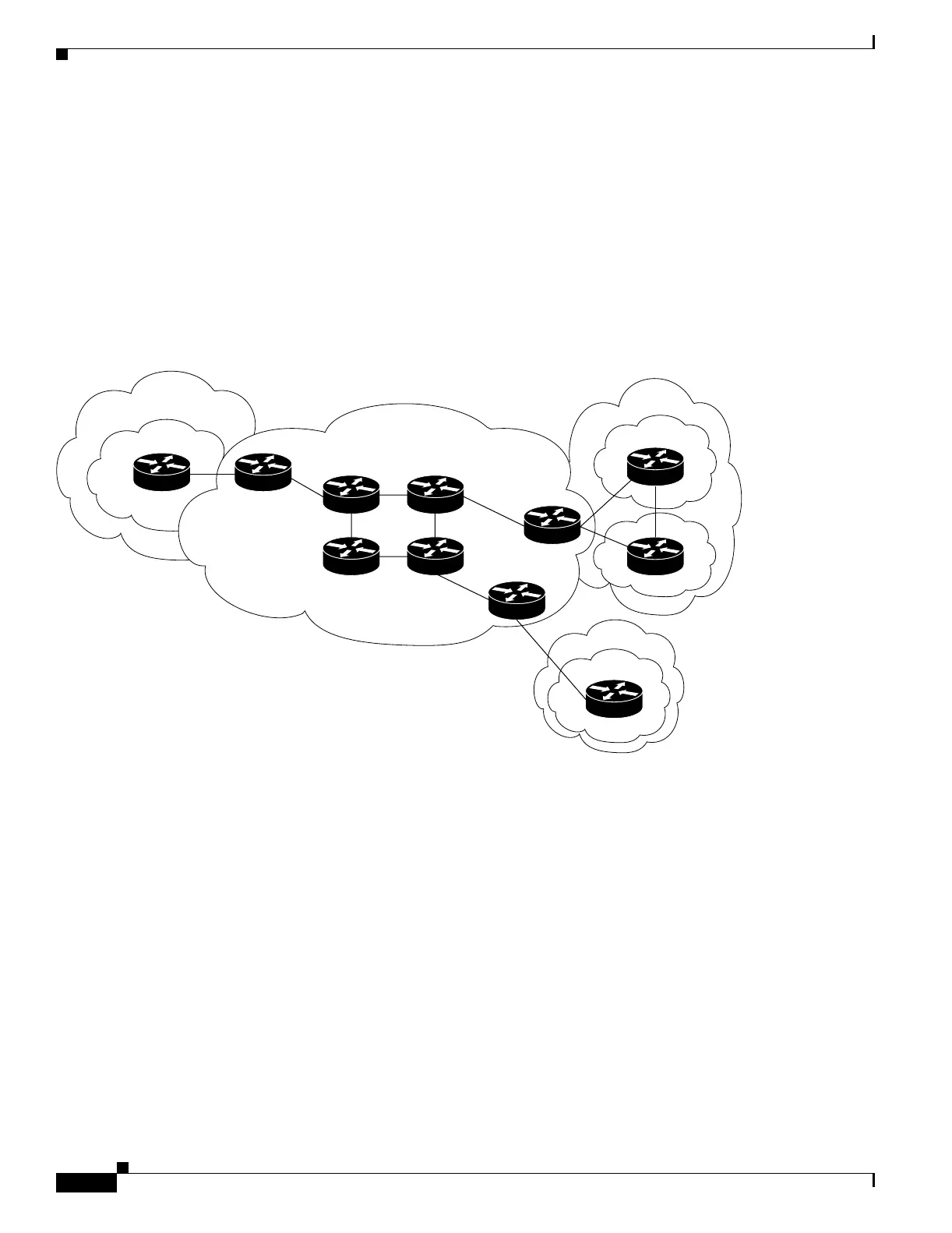
Figure 30-1 shows an example of a VPN with a service-provider backbone network, PE routers, and CE
devices.
Figure 30-1 VPNs with a Service-Provider Backbone
Each VPN contains customer devices attached to the CE devices. The customer devices use VPNs to
exchange information between devices, and the provider routers (P) are not aware of the VPNs.
Figure 30-2 shows five customer sites communicating within three VPNs. The VPNs can communicate
with these sites:
VPN1: Sites 2 and 4
VPN2: Sites 1, 3, and 4
VPN3: Sites 1, 3, and 5
CE
PE
PE
CE
PE
CE
CE
P
Service provider
backbone
Site 1
Site 3
Site 2
VPN 1
VPN 1
VPN 2
VPN 2
P
P
P
101819

 Loading...
Loading...











