Chapter 7 Fastening Instructions
PAGE 7-20
•
Fastener Slip Check
This selection enables fastener slip detection during the fastening process.
(Example: A fastener with a nut on opposite side starts to rotate or ‘slip’ while torque
is being applied)
Once the torque reaches Snug Torque, the system monitors the torque drop from
peak torque and starts to count angle if the torque drop value is more than D-No.121
[Fastener Slip Torque]. If torque does not recover within D-No.215 [Fastener Slip
Angle], the fastening is aborted and reported as Fastener Slip Reject.
The system outputs Rate 1 Low Reject, Rate 2 Low Reject, and Rate 3 Low Reject
signals together (PLC output signals) for this reject condition.
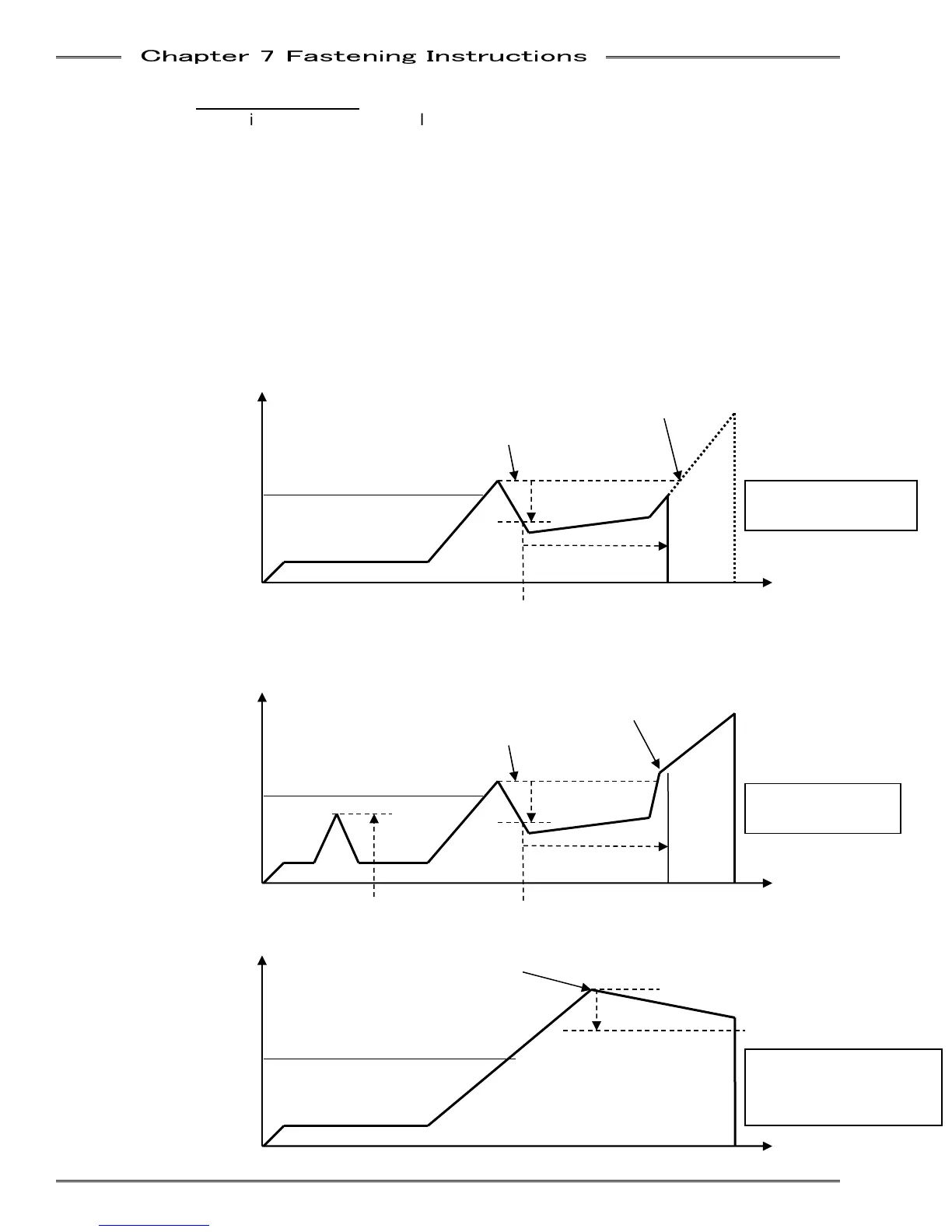
o Example of Fastener Slip detection
Snug Torque = 30Nm, Fastener Slip Torque = 10Nm, Fastener Slip Angle = 50 Degree
o Example of Fastener Slip not detected
Torque
Snug
30Nm
Angle
Slip Start Point
D-No.215 50 Deg.
Fastener Slip Reject
Standard Torque
Peak Torque of fastening
Torque recover point
Torque
Snug
30Nm
Angle
Slip Start Point
D-No.215 50 Deg.
Torque recovered
within (50deg) limit.
Standard Torque
Peak Torque of fastening
Torque recover point
Torque
Snug
30Nm
Angle
Not enough torque drop to
be detected as fastener
slip.
Standard Angle
Peak Torque of fastening
Ignore below Snug Torque
Torque not recovered
within (50deg) limit.
 Loading...
Loading...