7914DS3KPlanning_090710.fm Draft Document for Review March 28, 2011 12:24 pm
46 IBM System Storage DS3500: Introduction and Implementation Guide
Queue depth
There are a number of locations in the SAN solution that can have queue depth settings
within their control. The queue depth is the maximum number of IO commands that can be
queued for processing at the system, SAN network or the storage at one point in time.
For the host this value might be adjustable at the device level and HBA level. Some host
operating systems only use the HBA level setting. Care should be taken when setting these
levels as response time performance can be impacted by too high a value, as well as
device
busy
status being returned by the storage when its capabilities are exceeded.
For QLogic based HBAs, the queue depth is known as
execution throttle, which can be set
with either QLogic SANsurfer or in the BIOS of the QLogic-based HBA by pressing Ctl+Q
during the boot process.
For the storage there are values at the controller as well as drive level. These values can
varied between code levels and performance enhancement features.
For the latest firmware for the DS3500 controller, see the following Web site:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/storage/disk/
3.2.6 Disk expansion enclosures
The DS3500 Storage Systems offer the EXP3500 expansion enclosures for expanding the
subsystem beyond the internal drive count of the DS3500. There are two models of
expansions to chose from; the EXP3512 and the EXP3524. These expansions connect to the
DS3500 storage system through the 6 Gbps SAS expansion ports on the controller modules.
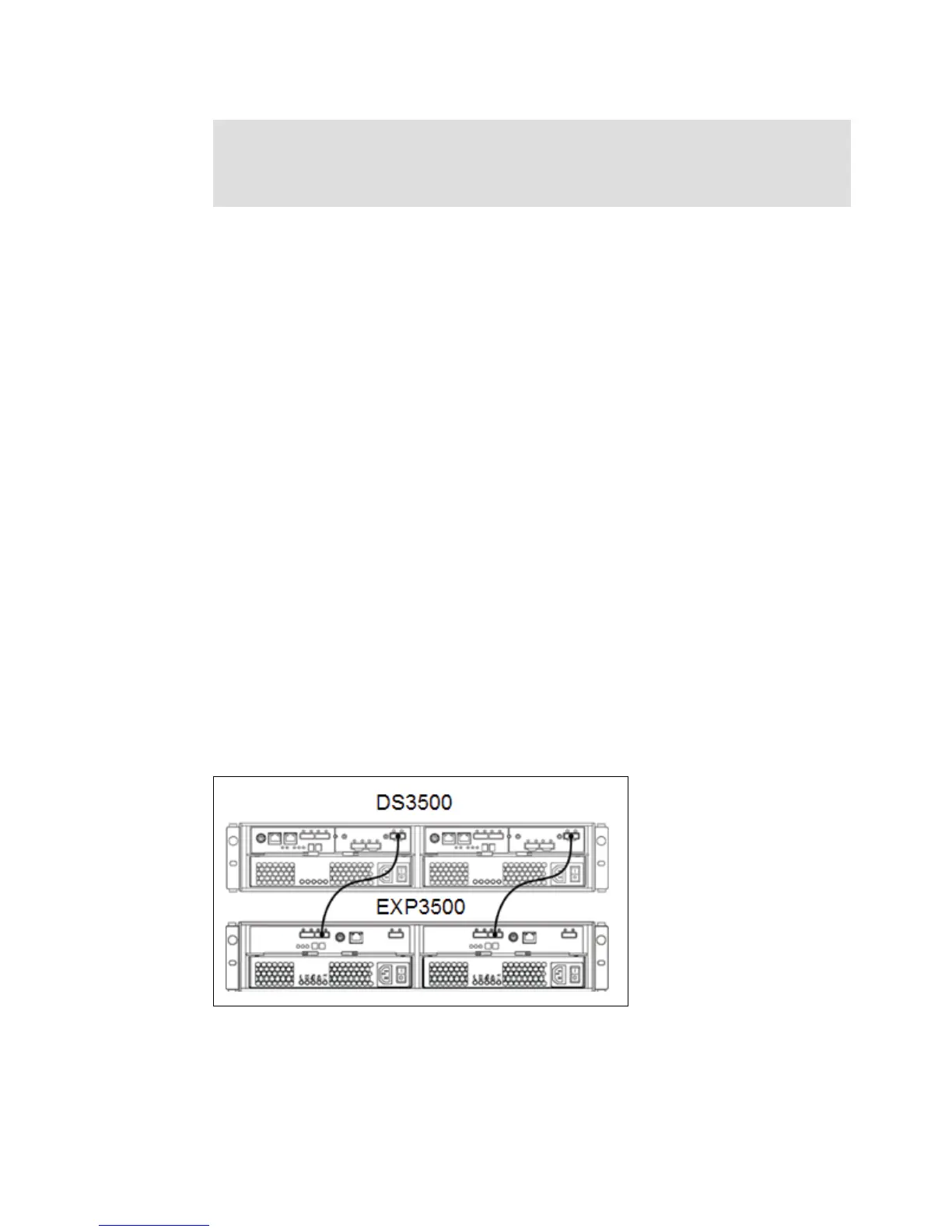
Figure 3-11 and Fig are examples of the cable connections needed to attach the DS3500 with
dual controllers to an EXP3500.
Figure 3-11 DS3500 and EXP3500 cable attachments for dual controllers
Note: In a cluster environment, you need a single path to the each of the controllers (A and
B) of the DS3500 Storage System. However, if the cluster software and host application
can do persistent reservations, you can keep multiple paths and the multipath driver will
route the I/O request using the appropriate path to the reserved logical drive.

 Loading...
Loading...











