6-10 Range, Digits, Speed, and Filters Models 2500 and 2502 User’s Manual
Moving filter
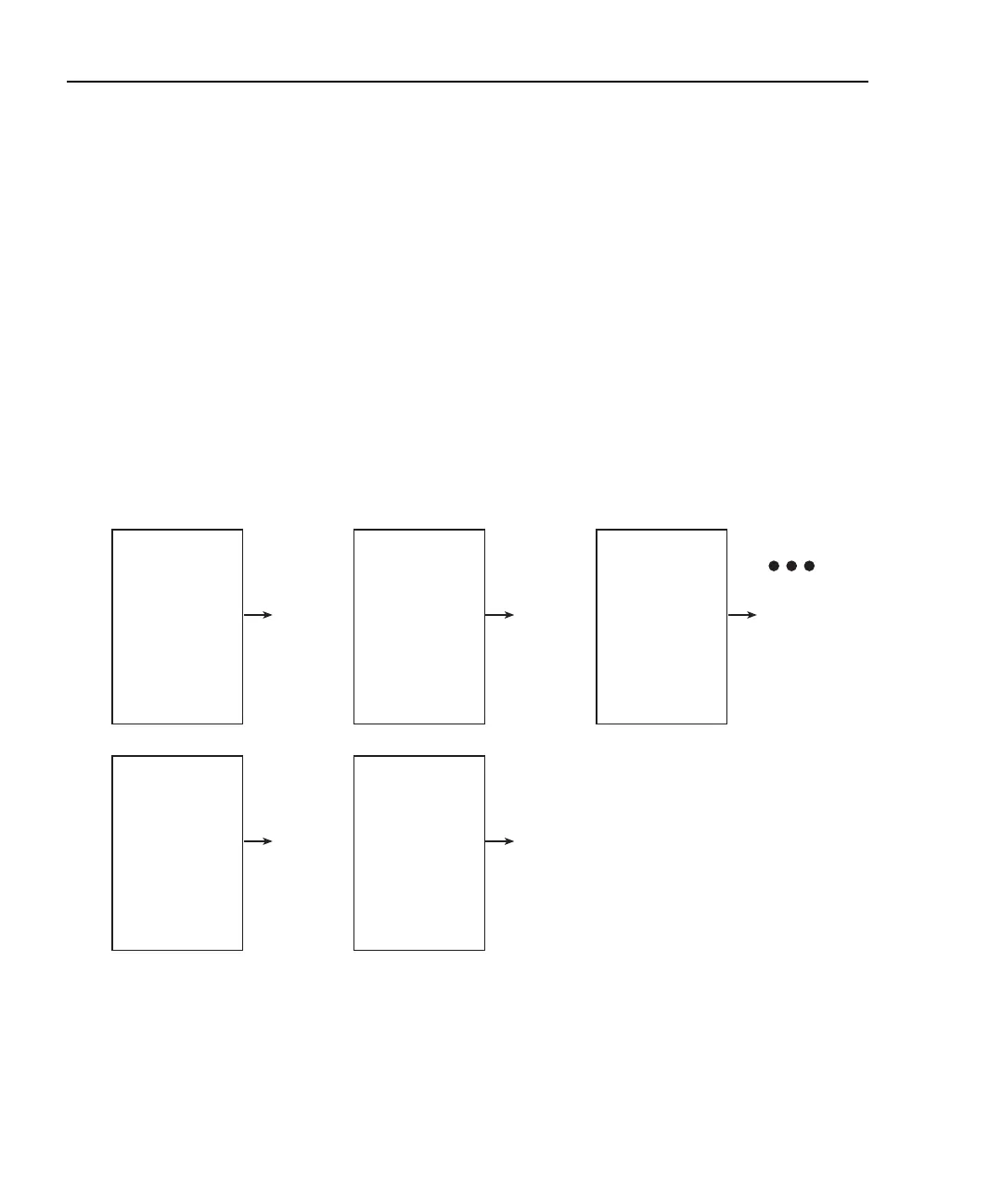
The moving average filter uses a first-in, first-out stack. When the stack (filter count)
becomes full, the readings are averaged, yielding a filtered reading. For each subsequent
reading placed into the stack, the oldest reading is discarded. The stack is reaveraged,
yielding a new reading.
When the filter is first enabled, the stack is empty. Keep in mind that a Moving Filter read-
ing is not yielded until the stack is full. The first reading is placed in the stack and is then
copied to the other stack locations in order to fill it. Therefore, the first filtered reading is
the same as the first reading that entered the stack. Now the normal moving average filter
process can continue. Note that a true average is not yielded until the stack is filled with
new readings (no copies in stack). For example, in Figure 6-5, it takes ten filtered readings
to fill the stack with new readings. The first nine filtered readings are calculated using cop-
ied readings.
Figure 6-5
Moving filter (count 10)
Reading #1
#1
#1
#1
#1
#1
#1
#1
#1
Reading #1
Moving
Reading
#1
•
•
•
Reading #2
#1
#1
#1
#1
#1
#1
#1
#1
Reading #1
Moving
Reading
#2
•
•
•
Reading #3
#2
#1
#1
#1
#1
#1
#1
#1
Reading #1
Moving
Reading
#3
•
•
•
Reading #10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
#2
Reading #1
Moving
Reading
#10
•
•
•
Reading #11
#10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
Reading #1
Moving
Reading
#11
•
•
•
Test Equipment Depot - 800.517.8431 - 99 Washington Street Melrose, MA 02176
TestEquipmentDepot.com
 Loading...
Loading...