4.11.5 Functional Description
Two different ways to apply target positions to a drive are supported by this device profile.
Set of setpoints:
After reaching the target_position, the drive device immediately processes the next
target position, which results in a move where the velocity of the drive normally is not
reduced to zero after achieving a setpoint. With S300/S700, this is
only possible if trapezoidal ramps are used.
Single setpoints:
After reaching the target_position, the drive device signals this status to a host
computer and then receives a new setpoint. After reaching a target_position, the
velocity is normally reduced to zero before starting a move to the next setpoint.
The two modes are controlled by the timing of the bits for new_setpoint and change_set_immedi
-
ately in the control word, and setpoint_acknowledge in the status word. These bits allow the setting
up of a request-response mechanism in order to prepare a set of setpoints while another set is still
being processed in the drive unit. This minimizes reaction times within a control program on a host
computer.
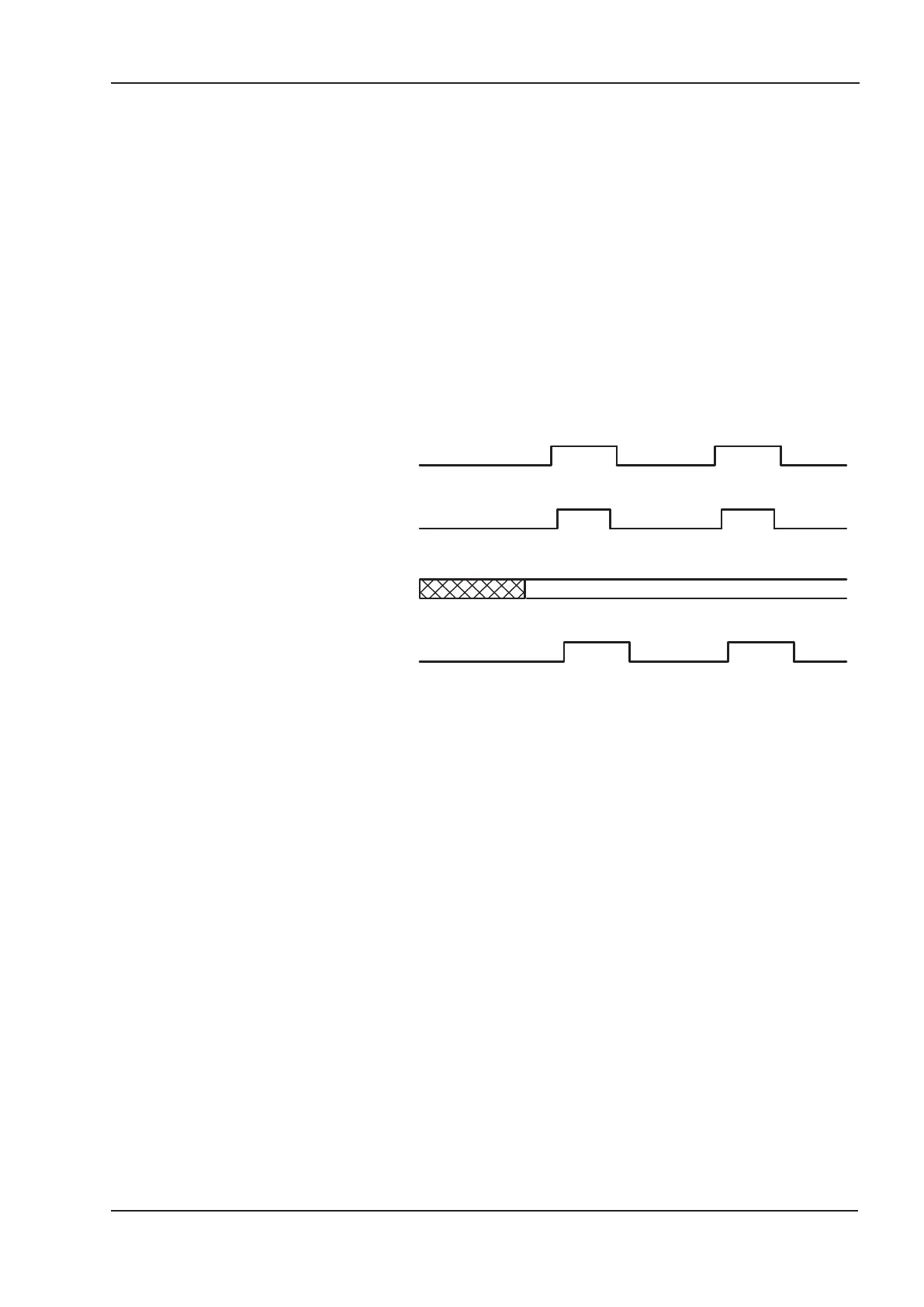
The figures show the difference between the set_of_setpoints mode and the single setpoint mode.
The initial status of the bit change_set_immediately in the control word determines which mode is
used. To keep these examples simple, only trapezoidal moves are used.
CANopen for S300/S700 89
Kollmorgen 11/2018 CANopen Drive Profile
(2)
(4)
(6)
(3)
(5)
(1)
data
new_setpoint
change_set_immediately
setpoint_acknowledge

 Loading...
Loading...



