10
General Instruction Characteristics Section 1-1
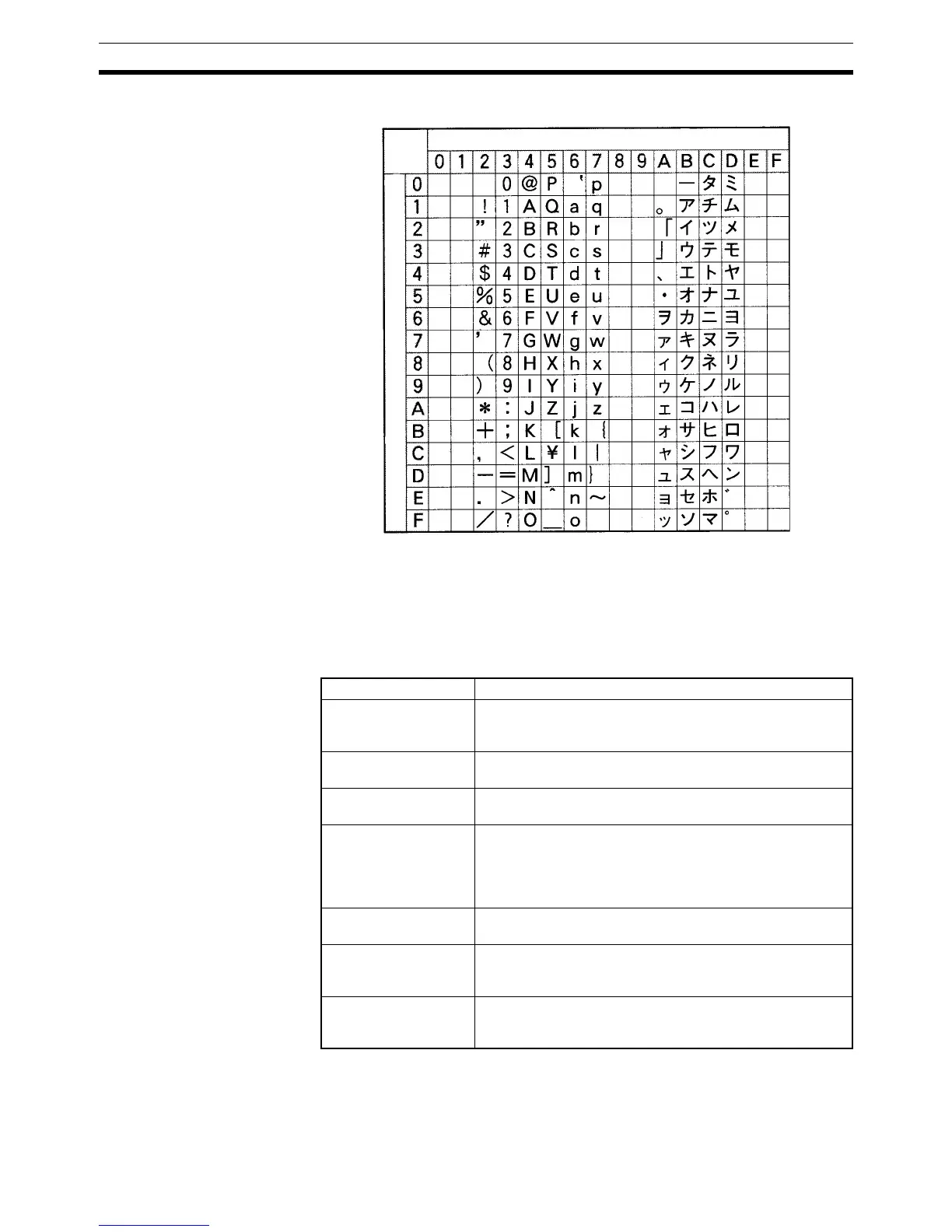
The following diagram shows the characters that can be expressed in ASCII.
Note The following instructions are executed even when the input conditions are
OFF. Therefore, when indirect memory addresses are specified using auto-
incrementing or auto-decrementing (,IR+ or ,IR-) in an operand of any of
these instructions, the value in the Index Register (IR) is refreshed each cycle
regardless of the input condition (increases or decreases one every cycle).
This must be considered when writing a program.
S
P
Rightmost bit
Leftmost bit
Classification Instructions
Sequence input
instructions
LD, LD NOT, AND, AND NOT, OR, OR NOT, LD TST(350),
LD TSTN(351), AND TST(350), AND TSTN(351), OR
TST(350), OR TSTN(351)
Sequence output
instructions
OUT, OUT NOT, DIFU(013), DIFD(014)
Sequence control
instructions
JMP(004), FOR(512)
Timer and counter
instructions
TIM/TIMX(550), TIMH(015)/TIMHX(551), TMHH(540)/
TMHHX(552), TIMU(541)/TIMUX(556), TMUH(544)/
TMUHX(557), TTIM(087)/TTIMX(555), TIML(542)/
TIMLX(553), MTIM(533)/MTIMX(554), CNT/CNTX(546),
CNTR(012)/CNTRX(548)
Comparison instruc-
tions
Symbol comparison instructions (LD, AND, OR =, etc.(func-
tion codes: 300, 305, 310, 320, and 325))
Single-precision float-
ing-point math instruc-
tions
Single-precision floating-point data comparison (LD, AND,
OR = F, etc.(function codes: 329 to 334))
Double-precision float-
ing-point math instruc-
tions
Double-precision floating-point data comparison (LD, AND,
OR = D, etc.(function codes: 335 to 340))
 Loading...
Loading...











