8-2 Set-Up SYNAX200 Ring SYNAX200
DOK-SYNAX*-SY*-07VRS**-PR01-EN-P
Constructing the Transmission Path
A transmission path starts at a transmitter output and ends at a receiver
input.
The transmission path is made up of fibre-optics cables and fibre-optics
cable leadthroughs. These serve as, for example, coupling units for wall
leadthroughs.
The plug-in connectors correspond to FSMA standards (IEC 874-2).
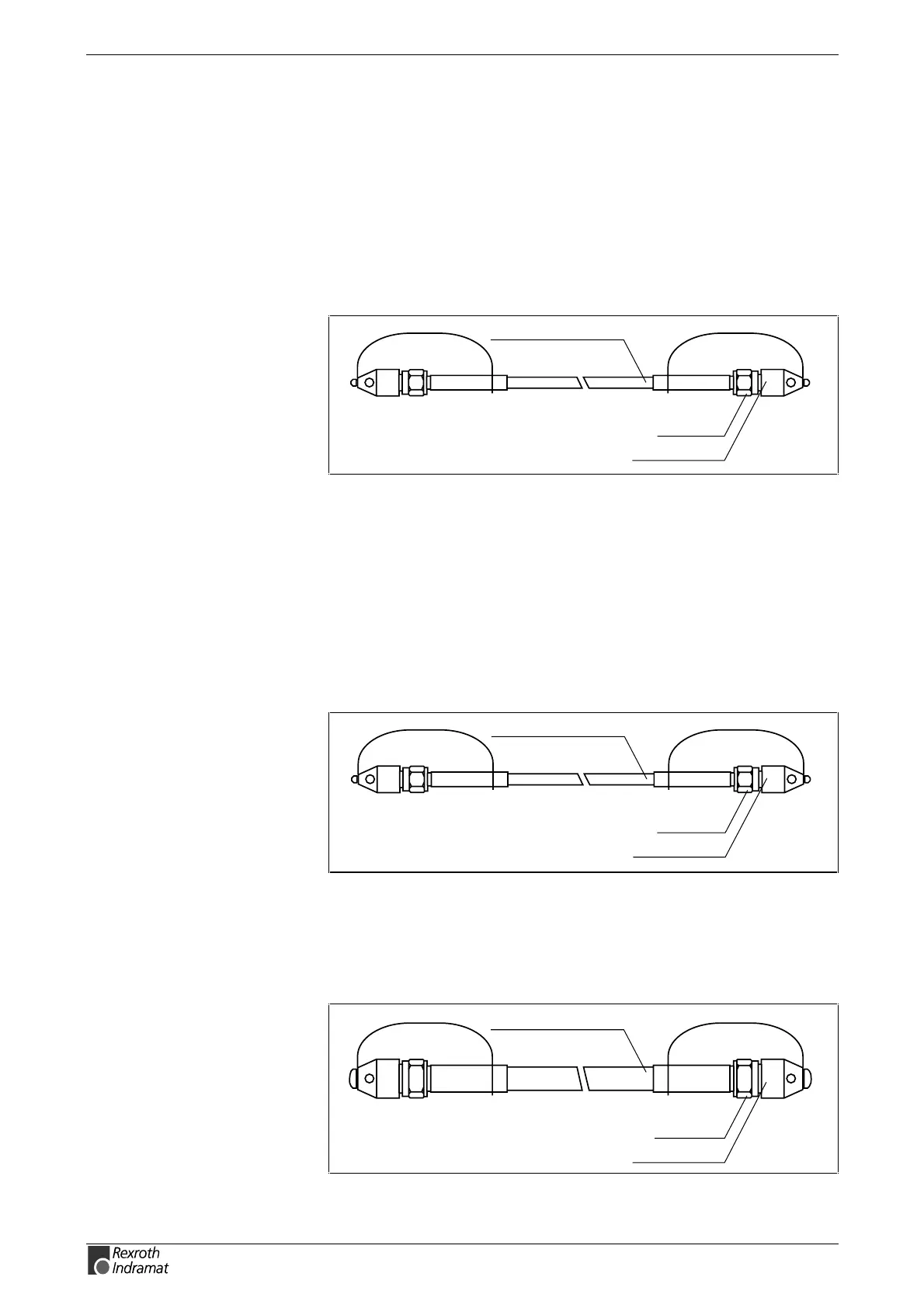
LWL cable ø 2,2 mm
connector
protective cap
SY6PR022.FH7
Fig. 8-2: Structure of a transmission path
Types of Fibre-Optics Cables
Plastic fibre-optics cables can be used for transmission length of up to 50
m and glass fibre-optics cables for lengths up to 500 m.
There are three different types of fibre-optics cables:
Plastic fibre-optics cables for internal control cabinet use with a diameter
of 2.2 mm.
LWL cable ø 2,2 mm
connector
protective cap
SY6PR023.FH7
Fig. 8-3: Plastic fibre-optics cable 2.2 mm (IKO 982)
Plastic fibre-optics cables for internal and external control cabinet use
with reinforced casings. The diameter of this fibre-optics cable equals 6
mm.
LWL cable ø 6,0 mm
connector
protective cap
SY6PR024.FH7
Fig. 8-4: Plastic fibre-optics cable 6 mm (IKO 985)
Fibre-optics cable isolating
points
FSMA standard (IEC 874-2)
Plastic fibre-optics cable 2.2mm
Plastic fibre-optics cable 6 mm

 Loading...
Loading...