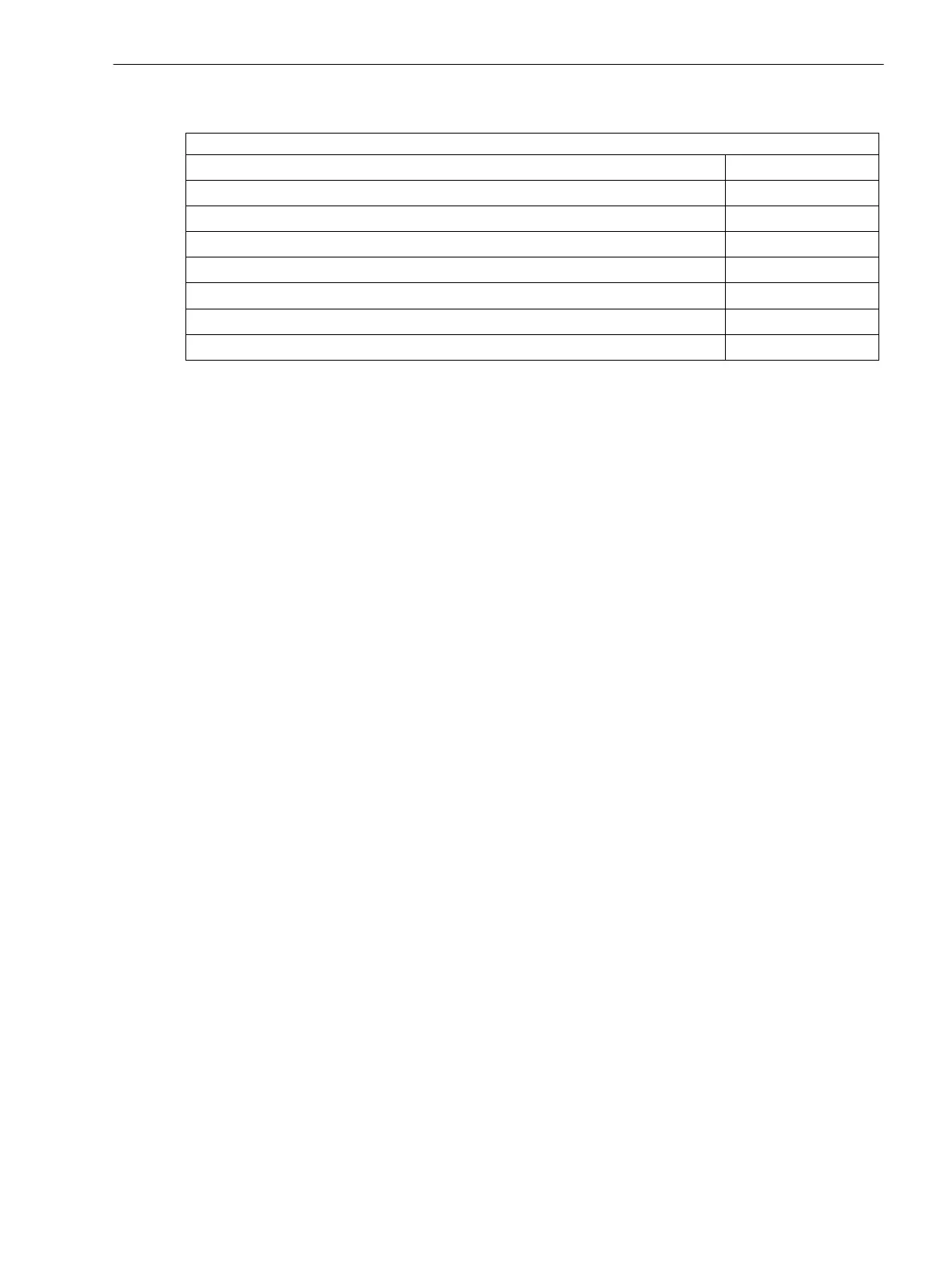
Table 2-20 System data for the application example
Power System Data
Generator nominal power S
Nom,Gen
= 38.1 MVA
Transformer nominal power S
Nom,Trafo
= 38.1 MVA
Nominal voltage of high-voltage side U
Nom
= 110 kV
Nominal voltage of busbar side U
Nom
= 11 kV
Nominal primary CT current on busbar side
Ι
Nom,prim
= 2000 A
Nominal secondary CT current on busbar side
Ι
Nom,sek
= 1 A
Nominal primary VT voltage on busbar side U
Nom,prim
= 11 kV
Nominal secondary VT voltage on busbar side U
Nom,sek
= 100 V
Protective Functionality
With protection device 7SJ80, the control system is disconnected from the generator upon the generator's
reversed feeding into the power supply company's power system (protection function P reverse>). This func-
tionality is realized by means of a flexible protection function. Additionally, the disconnection is effected by
fluctuations in frequency or voltage in the power supply company's power system (protection function f<, f>,
27-1 PICKUP, 59-1 PICKUP, 67-1 PICKUP, , 67N-1 PICKUP).
The protection receives the measured values via a three-phase current and voltage transformer set.
In case of disconnection, the circuit breaker CB2 is triggered.
The transformer is protected by a differential protection and inverse or definite time overcurrent protection
functions for the phase-to-phase currents. In the event of a fault, the circuit-breaker CB1 in the power supply
company's system is activated via a remote link. In addition, the circuit breaker CB2 is activated.
Overcurrent protection functions protect the feeders 1 and 2 against short circuits and overload caused by the
connected consumers. The phase-to-phase currents and the zero currents of the feeders can be protected by
inverse and definite time overcurrent protection elements. In the event of a fault, the circuit breakers CB4 and
CB5 are activated.
In addition, the busbar could be equipped with the 7UT635 differential protective relay for multiple ends. The
current transformers required to this end are already included in the example above.
Wiring Diagram, Power Direction
The following figure shows the wiring of the device for reverse power protection. The power flow in positive
or forward direction occurs from the high-voltage busbar (not shown) via the transformer to the lowvoltage
busbar.
Functions
2.19 Reverse-Power Protection Application with Flexible Protection Function
SIPROTEC 4, 7SJ80, Manual 255
E50417-G1140-C343-A8, Edition 12.2017

 Loading...
Loading...











