9 Heat Run – Cooling Curve
9.1 Theory
The purpose of this test is to establish the top oil temperature rise in steady-state condition with
dissipation of total losses and to establish the average winding temperature rise at rated current
and with the top oil temperature rise specified before.
This target is achieved in two main steps:
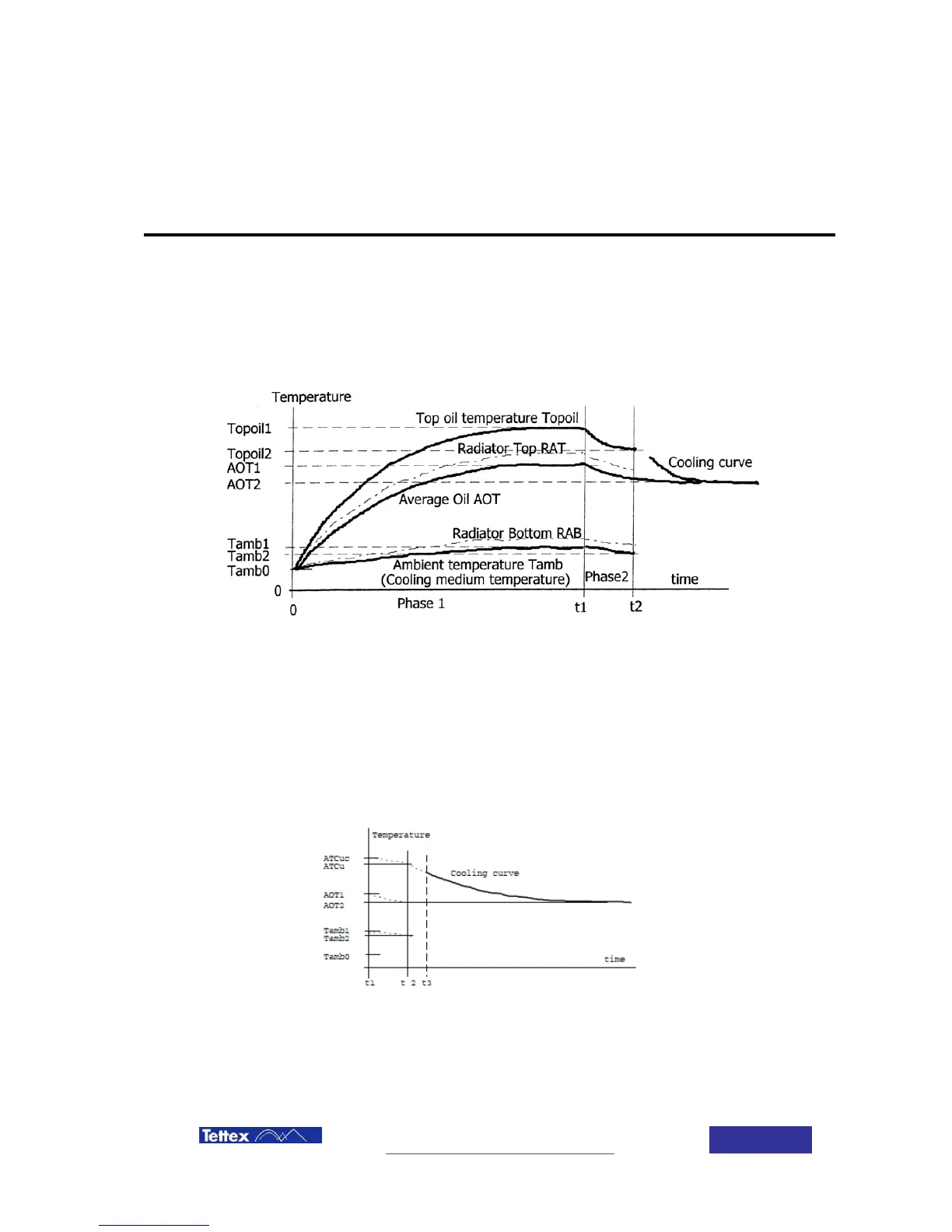
First the top oil and average oil temperature rises are established when the transformer is
subjected to a test voltage such that the measured active power is equal to the total losses of the
transformer. The oil temperature and the cooling medium temperature are monitored, and the test
is continued until a steady-state oil temperature is reached. When the top oil temperature has
been established, the test shall immediately continue with the test current reduced to the rated
current for the connected winding. This condition is maintained for a certain time (normally 1h).
Following the first part of the procedure (heating), resistance has to be measured after a quick
disconnection of the power supply. The values of average temperature of the two windings are
determined from the resistances change along the time, known as cooling curve.
 Loading...
Loading...