2 Concepts of 2D-LC
Active Solvent Modulation (ASM)
2D-LC User Guide 42
Understanding the ASM Factor
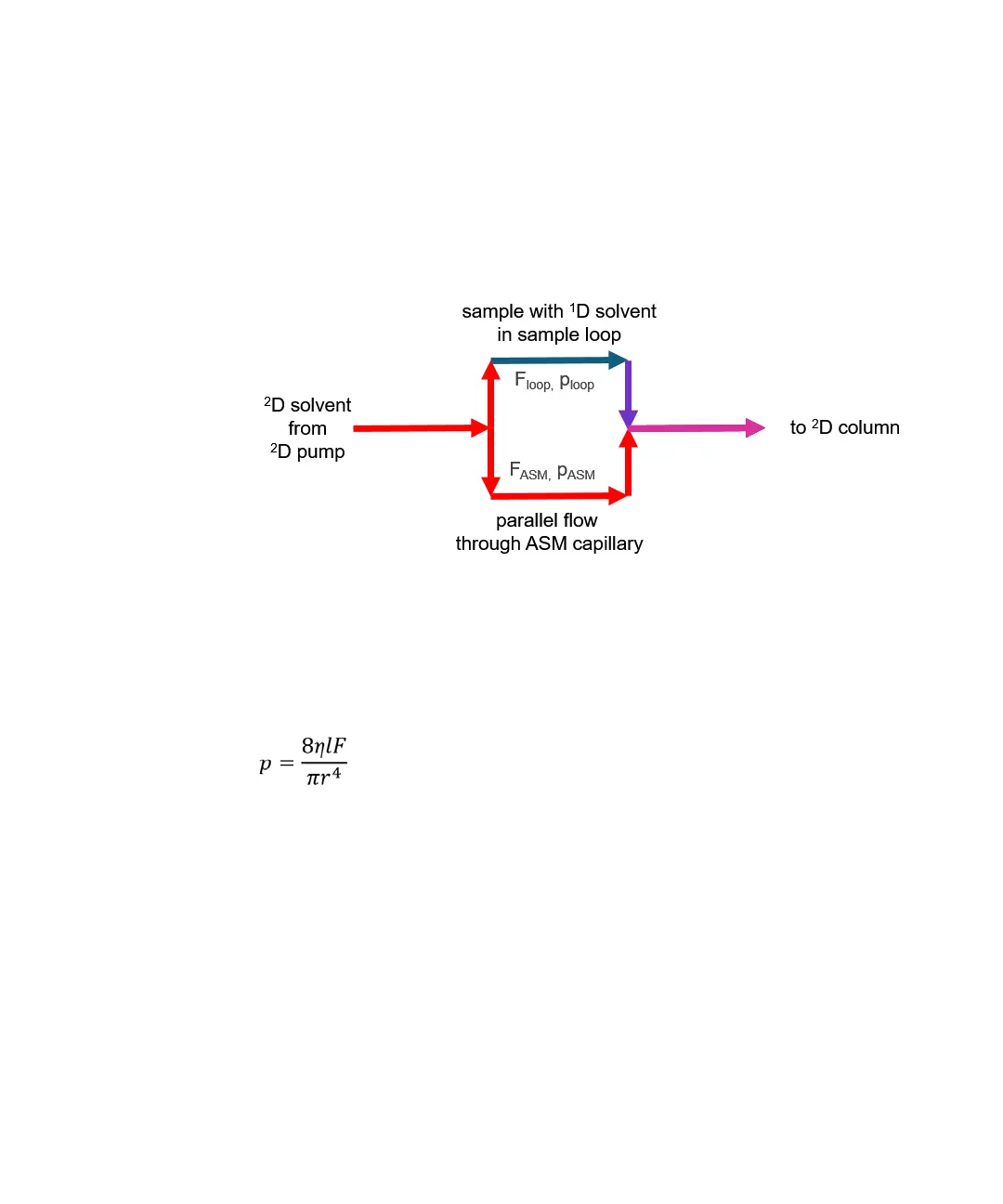
The principle of ASM is diluting
1
D sample loop solvent with
2
D solvent.
The ASM solution achieves this dilution by a parallel flow of solvents via sample
loop and ASM capillary.
Figure 23 Principle of active solvent modulation (schematic view)
The flow rates F through these parallel capillaries depend on the different
backpressures p of the capillaries in use. The backpressure of a capillary
depends on the capillary length l, radius r to the power of 4, and the viscosity of
the solvent.
The Hagen-Poiseuille equation describes the relation of these parameters.
Hagen-Poiseuille equation
Different ASM capillary lengths have an effect on
the following parameters:
• Capillary back pressure
• Dilution factor
• Optimum dilution for different applications

 Loading...
Loading...