Service Entities
Page 46 7210 SAS M Services Guide
Overview of G.8032 Operation
R-APS messages that carry the G.8032 protocol are sent on dedicated protocol VLAN called ERP
VLAN (or Ring Control Instance). In a revertive case, G.8032 Protocol ensures that one Ring
Protection Link (RPL) owner blocks the RPL link. R-APS messages are periodically sent around
in both directions to inform other nodes in the Ring about the blocked port in the RPL owner node.
In non-revertive mode any link may be the RPL link.Y.1731 Ethernet OAM CC is the basis of the
RAPs messages. Y.1731 CC messages are typically used by nodes in the ring to monitor the health
of each link in the ring in both directions. However CC messages are not mandatory. Other link
layer mechanisms could be considered – for example LOS (Loss of Signal) when the nodes are
directly connected.
Initially each Ring Node blocks one of its links and notifies other nodes in the ring about the
blocked link. Once a ring node in the ring learns that another link is blocked, the node unblocks its
blocked link possibly causing FDB flush in all links of the ring for the affected service VLANs,
controlled by the ring control instance. This procedure results in unblocking all links but the one
link and the ring normal (or idle) state is reached. In revertive mode the RPL link will be the link
that is blocked when all links are operable after the revert time. In non-revertive mode the RPL
link is no different that other ring links. Revertive mode offers predictability particularly when
there are multiple ring instances and the operator can control which links are block on the different
instances. Each time there is a topology change that affects Reachability, the nodes may flush the
FDB and MAC learning takes place for the affected service VLANs, allowing forwarding of
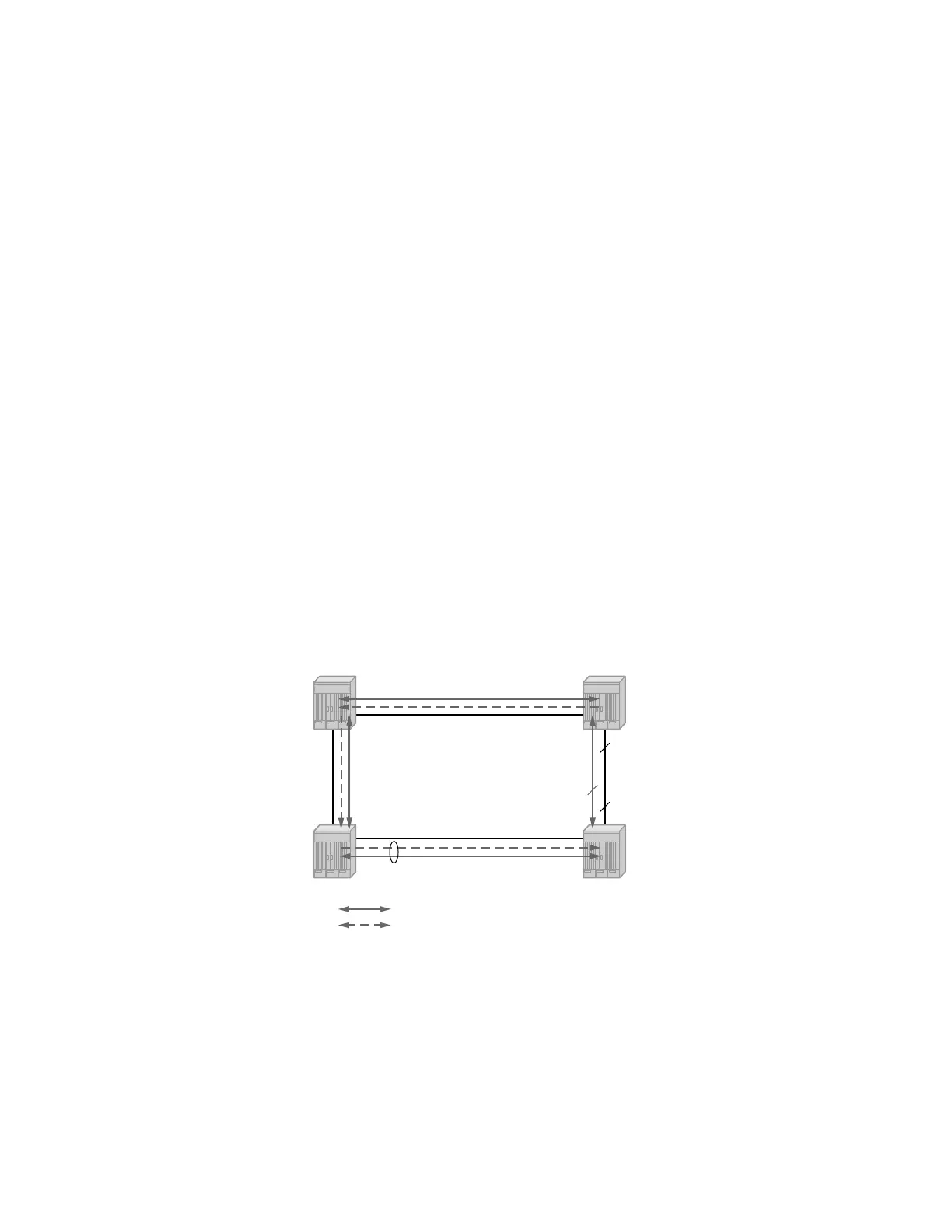
packets to continue. Figure 6 depicts this operational state:
Figure 6: G.8032 Ring in the Initial State
When a ring failure occurs, a node or nodes detecting the failure (enabled by Y.1731 OAM CC
monitoring) send R-APS message in both directions. This allows the nodes at both ends of the
failed link to block forwarding to the failed link preventing it from becoming active. In revertive
mode, the RPL Owner then unblocks the previously blocked RPL and triggers FDB flush for all
Ring Link
Ring Link
Ring Instance
Ring Link
Ring Link
Optional Blocking
Mandatory Blocking
Ring APS - ERP - Control Channel
Ring Data Channel
7210
7210
7210
7210
Ring Node
Ring Node
Ring Node
“RPL Neighbor”
RPL Owner Node

 Loading...
Loading...















