STwrench User Guide Pset
9836 4134 01 Edition 2.9 133 (326)
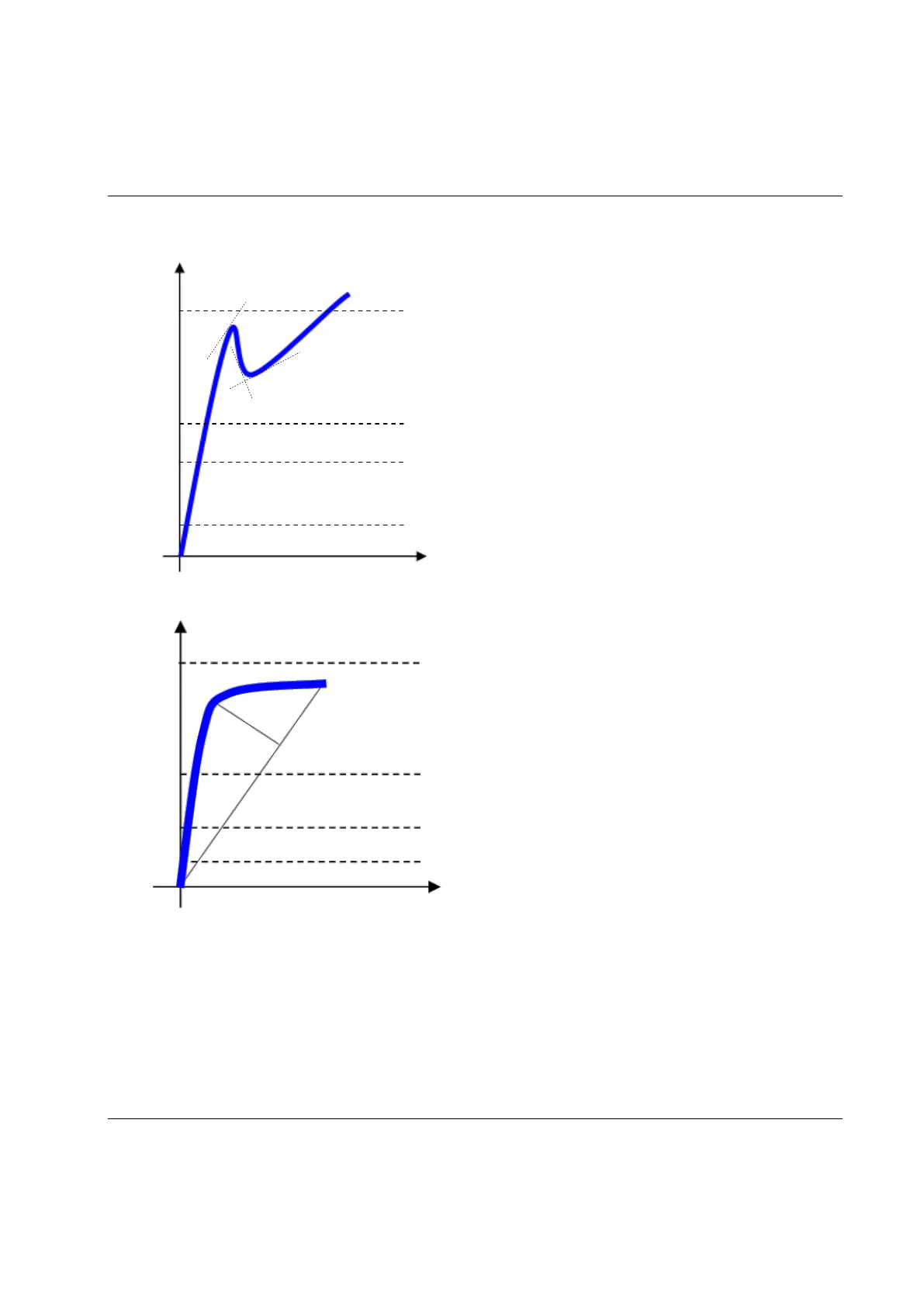
CASE A:
Sometimes very high static friction is built into the joint
(for instance, for no lubrication, conical seat). In that
case, as soon as the bolt moves, the torque decreases and
the real residual torque is lower than the peak torque
necessary to overcome the static friction.
The STwrench algorithm monitors the α
average
; if it goes
to a negative value, it waits until the α
average
goes back to
a positive value.
The point in which the α
average
goes back to a positive
value is considered to be the residual torque.
CASE B:
Normally, during breakaway there is a rapid change of
the gradient of the torque/angle function when the bolt
starts moving.
The STwrench algorithm takes as the breakaway point
the point of maximum distance “d” between the
torque/angle trace and the straight line from the start to
the actual point of the trace. This distance must be
greater than a threshold and must be consistent for
more samples. Moreover, the average slope of the
second part of the trace (after the breakaway point)
must be less than 60% of the average slope of the first
part of the trace. Once all these conditions are verified,
the test ends and the breakaway/residual point is
detected.
How to set the parameters:
- Cycle start: This is the point from where the torque is measured. Set to a low value, but
greater than the wrench minimum load.
- Start final angle: Set this value between Cycle Start and Torque Min.
- Torque min: Minimum residual value for achieving result OK.
- Torque max: Maximum residual value for achieving result OK.
average
> 0
average
> 0
average
< 0
Cycle start
Start final angle
 Loading...
Loading...