Engineering Manual Introduction
17
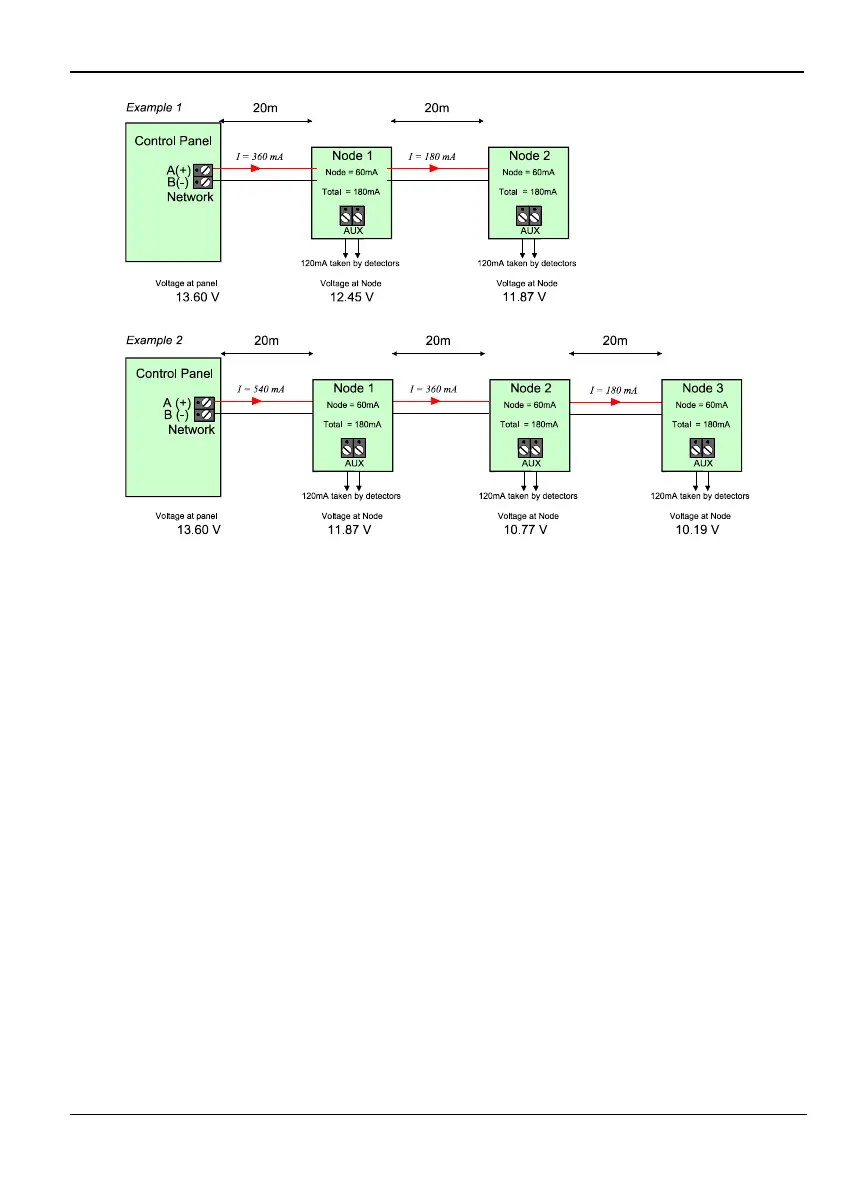
Figure 6. Voltage Drop Examples 1 & 2
Reducing Voltage Drop - Method 1
The simplest way to reduce voltage drop is to double up the supply connections (A & B), which
will halve the resistance on each core and therefore halve the voltage drop. When using the
voltage drop table to calculate the expected voltage drop, simply divide the voltage drop by
two. Figure 7 shows the same three nodes used in the previous example. The A and B network
connections have been doubled up; in order to do so the network cable must have two spare
cores. This method shows that voltage levels at all nodes is at a sufficient level.
Reducing Voltage Drop - Method 2
The second method to reduce voltage drop is to supply the detection devices from separate
cores. This is the preferred method of reducing voltage drop as detectors generally operate at
lower voltages (9.5V). When using this method, the network cable must have two spare cores.
This method shows that voltage levels at all nodes is at a sufficient level.

 Loading...
Loading...