VoIP and SIP SIP support
FortiGate Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
506 01-410-89802-20090903
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
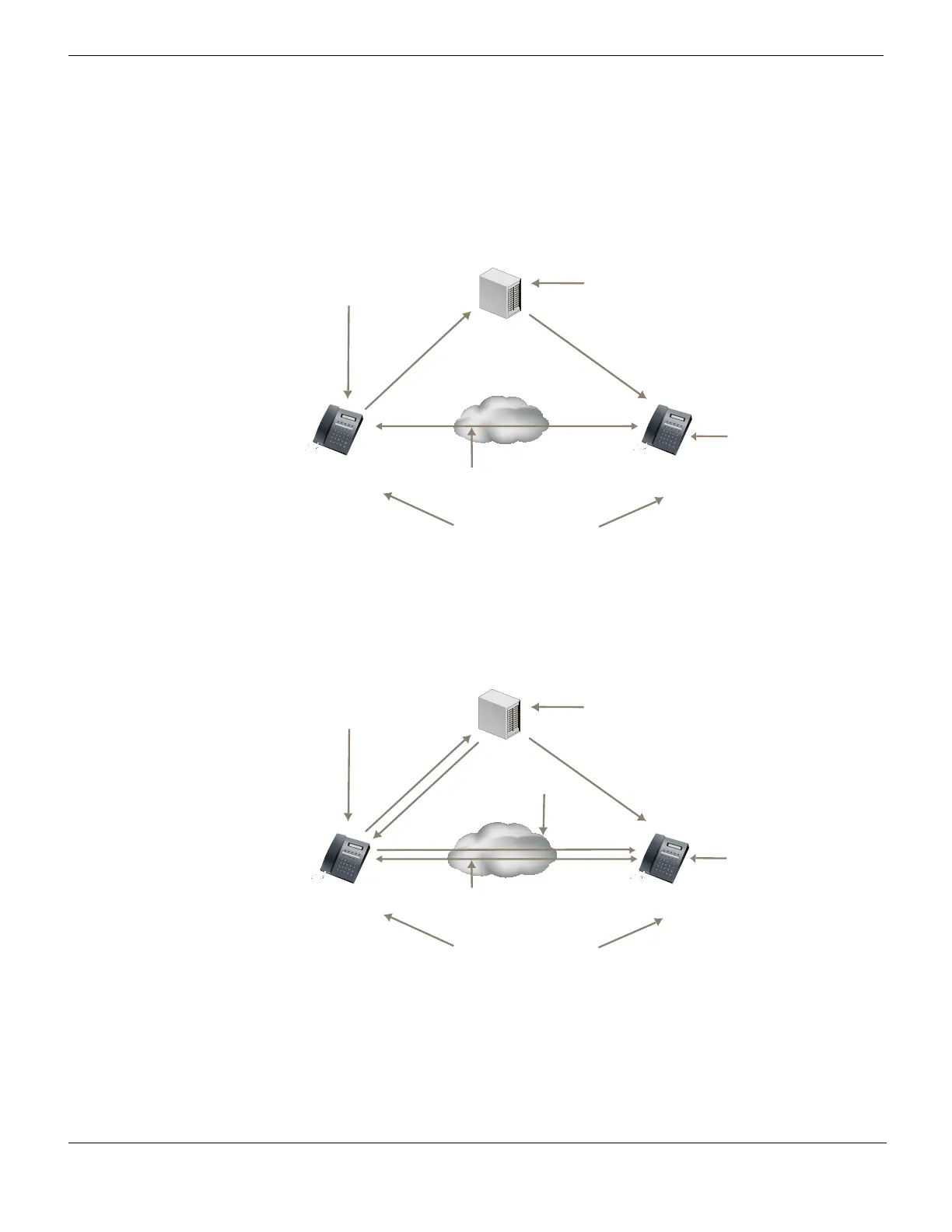
In proxy mode (shown in Figure 294), SIP clients send requests to the proxy server. The
proxy server either handles the requests or forwards them to other SIP servers. Proxy
servers can insulate and hide SIP users by proxying the signaling messages. To the other
users on the VoIP network, the signaling invitations look as if they come from the SIP
proxy server.
Figure 294: SIP in proxy mode
When the SIP server operates in redirect mode (shown in Figure 295), the SIP client
sends its signaling request to a SIP server, which then looks up the destination address.
The SIP server returns the destination address to the originator of the call, who uses it to
signal the destination SIP client.
Figure 295: SIP in redirect mode
SIP Client A
SIP Client B
SIP Proxy Server
IP Network
(b@example.com)
(a@example.com)
RTP Session
1. SIP clients register with SIP server
5. RTP session opens when
Client B answers
2. Client A dials Client B
and a request is sent to the SIP proxy server
3. Proxy server looks up phone number
or URL of destination client (Client B) and sends
invite to Client B
4. Client B is
notified of incoming
call by proxy server
– phone rings
SIP Client A
SIP Client B
IP Network
(b@example.com)
(a@example.com)
RTP Session
1. SIP clients register with SIP server
6. RTP session opens when
Client B answers
SIP Redirect Server
2. Client A dials Client B and
request is sent to SIP redirect server
3. Redirect server looks up phone number
or URL of destination client (Client B) and sends
address back to the caller (Client A)
5. Client B is
notified of incoming
call by redirect server
– phone rings
4. Client A sends invitation
to Client B

 Loading...
Loading...











