12.4 Formulae
209
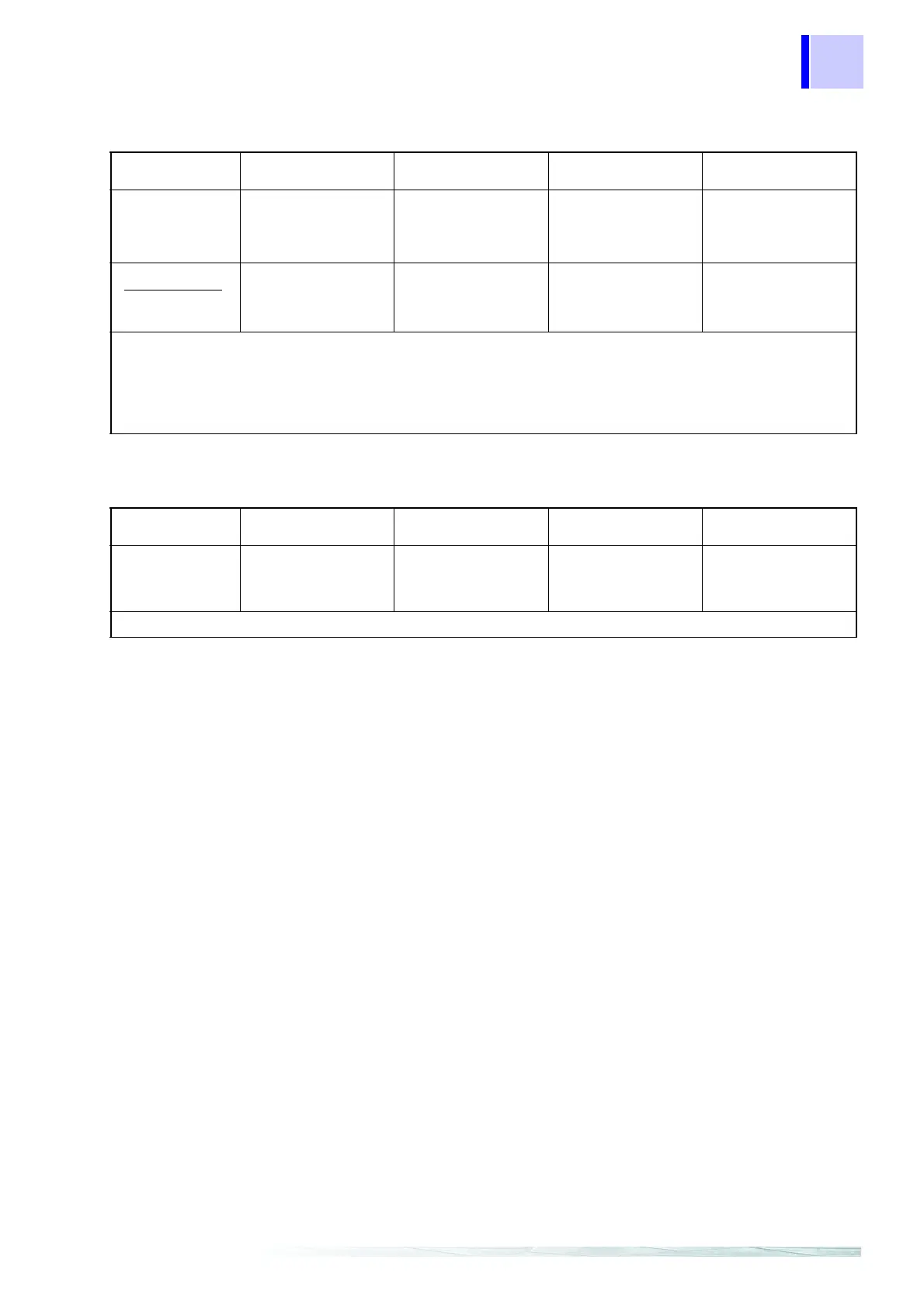
Harmonic voltage-current phase difference θk (deg)
Single-phase 2-wire
1P2W
Single-phase 3-wire
1P3W
Three-phase 3-wire
3P3W2M
Three-phase 3-wire
3P3W3M
Three-phase 4-wire
3P4W
θ
1k
θ
ck=
θ
cIk-
θ
cUk
θ
1k
θ
2k
θ
1k
θ
2k
θ
1k
θ
2k
θ
3k
θ
1k
θ
2k
θ
3k
• Calculate harmonic power at 2048 points for voltage and current (about once every 10 cycles at 50 Hz or
every 12 cycles at 60 Hz).
• When Psumk=Qsumk=0,
θ
k=0°.
• Psumk indicates the total harmonic power. (See the harmonic power formula.)
• Qsumk indicates the total harmonic reactive power. (See the harmonic reactive power formula.)
c: measured channel, k: order for analysis, r: resistance after FFT, i: reactance after FFT
θsum
Qsumk
Psumk
----------------
⎩⎭
⎨⎬
⎧⎫
1–
tan= θsum
Qsumk
Psumk
----------------
⎩⎭
⎨⎬
⎧⎫
1–
tan=
θsum
Qsumk
Psumk
----------------
⎩⎭
⎨⎬
⎧⎫
1–
tan=
θsum
Qsumk
Psumk
----------------
⎩⎭
⎨⎬
⎧⎫
1–
tan=
Voltage fluctuation ΔU (Vrms)
Single-phase 2-wire
1P2W
Single-phase 3-wire
1P3W
Three-phase 3-wire
3P3W2M
Three-phase 3-wire
3P3W3M
Three-phase 4-wire
3P4W
Δ
U(c)=Uc-Ur
Δ
U(1)
Δ
U(2)
Δ
U(12)
Δ
U(32)
Δ
U(12)
Δ
U(23)
Δ
U(31)
Δ
U(1)
Δ
U(2)
Δ
U(3)
“Ur” is the same value as the nominal voltage for standard voltage with respect to voltage fluctuations.
c: measured channel, r: resistance after FFT
 Loading...
Loading...