Cut with the Machine Torch
108 809240 Operator Manual Powermax45 XP
Expanded metal cutting
Expanded metal has a slotted or mesh pattern. Cutting expanded metal wears out
consumables more quickly because it requires a continuous pilot arc. A pilot arc occurs
when the torch is fired but the plasma arc is not in contact with the workpiece.
Incorrect consumables for output current and mode
To optimize consumable life, make sure the consumables installed on the torch match
the selected mode and output current. For example:
Do not use gouging consumables when the system is set to Cut mode. See
page 51.
Do not set the output current between 26 A and 45 A with the Marking
consumables or the Precision gouging consumables installed.
Understand and optimize cut quality
Several factors affect cut quality:
Cut angle – The degree of angularity of the cut edge.
Dross – The molten material that solidifies on the top or bottom of the workpiece.
Straightness of the cut surface – The cut surface can be concave or convex.
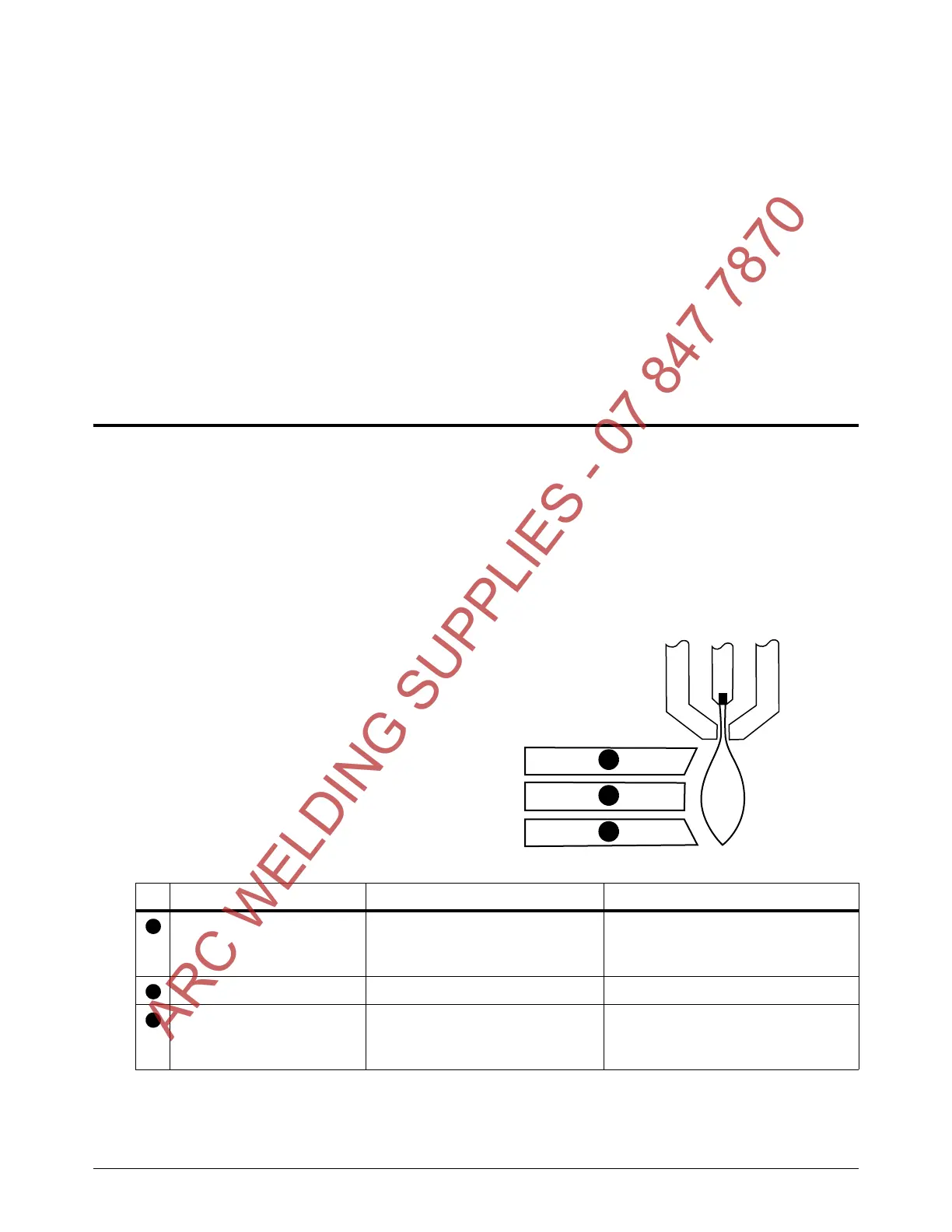
Cut or bevel angle
A positive cut angle results when
more material is removed from
the top of the cut than from the
bottom.
A negative cut angle results when
more material is removed from
the bottom of the cut.
The squarest cut angle is on the right side with respect to the forward
motion of the torch. The left side always has some degree of cut angle.
Problem Cause Solution
Negative cut angle The torch is too low. Raise the torch; or if you are using a
torch height control, increase the
arc voltage.
Square cut
Positive cut angle The torch is too high. Lower the torch; or if you are using
a torch height control, decrease the
arc voltage.
ARC WELDING SUPPLIES - 07 847 7870

 Loading...
Loading...











