Setting up Compax3 C3I22T11
262 192-120114 N5 C3I22T11 June 2008
Non-linearities and their effects
In this chapter you can read about:
Attenuation of the excitation amplitude............................................................................ 262
Shifting the working point into a linear ran
ge................................................................... 263
Non-linearities in mechanical systems are for example due to friction, backlash or
position-dependent transmissions (cams and crankshaft drives). In general, the
frequency response is only defined for linear systems (see
Linear Systems 7.2
(see page 280)). What happens in the frequency ra
nge in the event of a non-linear
system, is shown below.
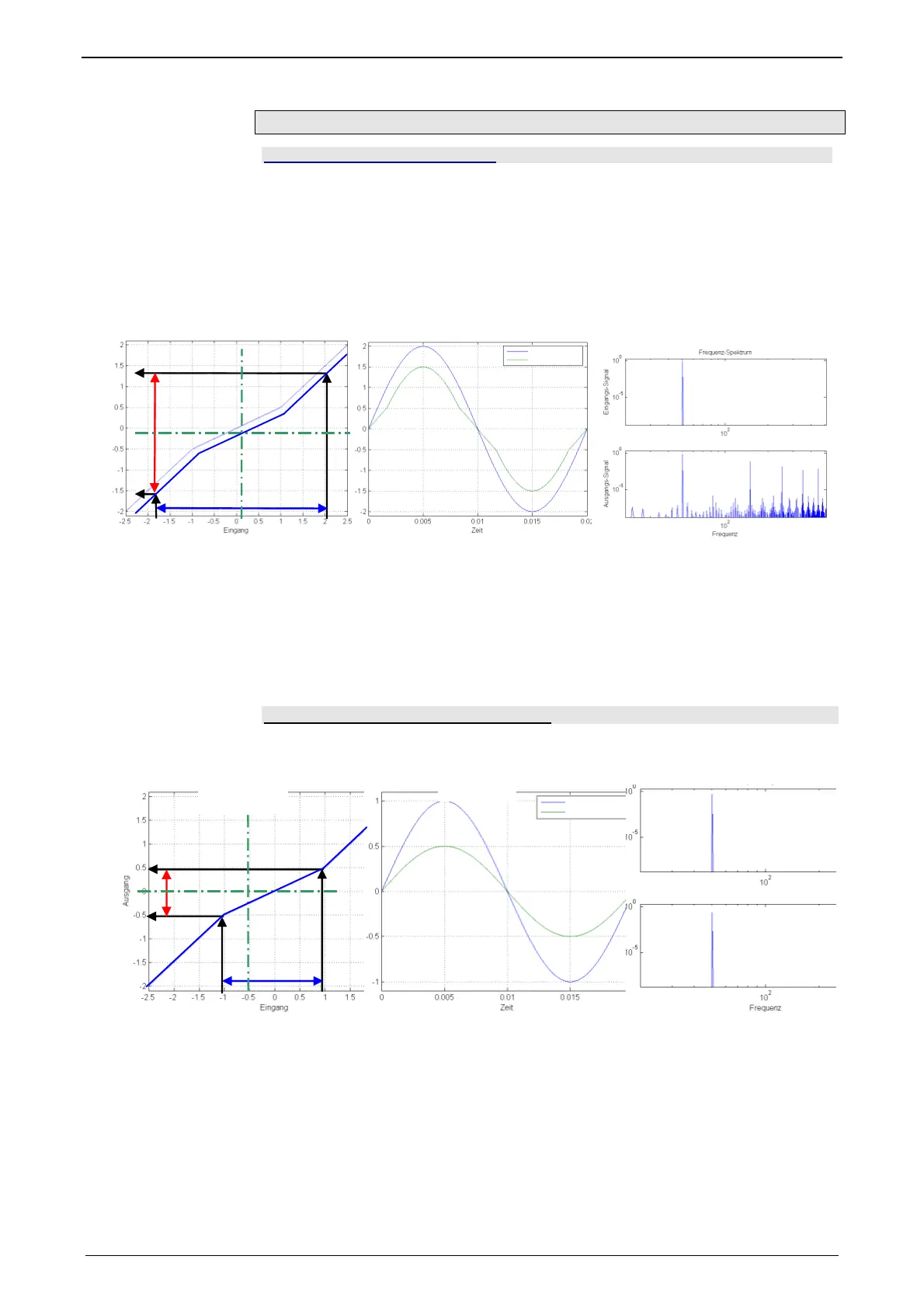
Signal amplitude too high => non-linearity in the signal range
Signals
Spectrum
Output Signal
Input Signal
S
stem
Input Signal
Output Signal
Input Signal
Output Signal
Due to the non-linear transmission behavior of the system, many "new" frequencies
were generated in the output signal. In the frequency response, only one change of
the frequency present in the input signal can be displayed meaningfully.
=> The frequencies generated in the spectre of the output signal lead to a deterio-
ration of the measured frequency response.
There are however two possibilities to make successful measurements of fre-
quency responses in spite of non-linearities present:
Attenuation of the excitation amplitude
Signal amplitude too small => no non-linearity in the signal range
Signals
Spectrum
Output
Signal
Input
Signal
System
Input Signal
Output Signal
Input Signal
Output Signal

 Loading...
Loading...