ComBricks User Manual v6.4.0 | January 18| © PROCENTEC 134/219
12.5.5 Voltage at the end of the segment
The resistance of the cable causes a lower voltage at the end of the cable. At least 9V should be available for
the last device at the end of the cable. The following calculation is a ‘worst case’ scenario where all devices are
connected at the end of the cable:
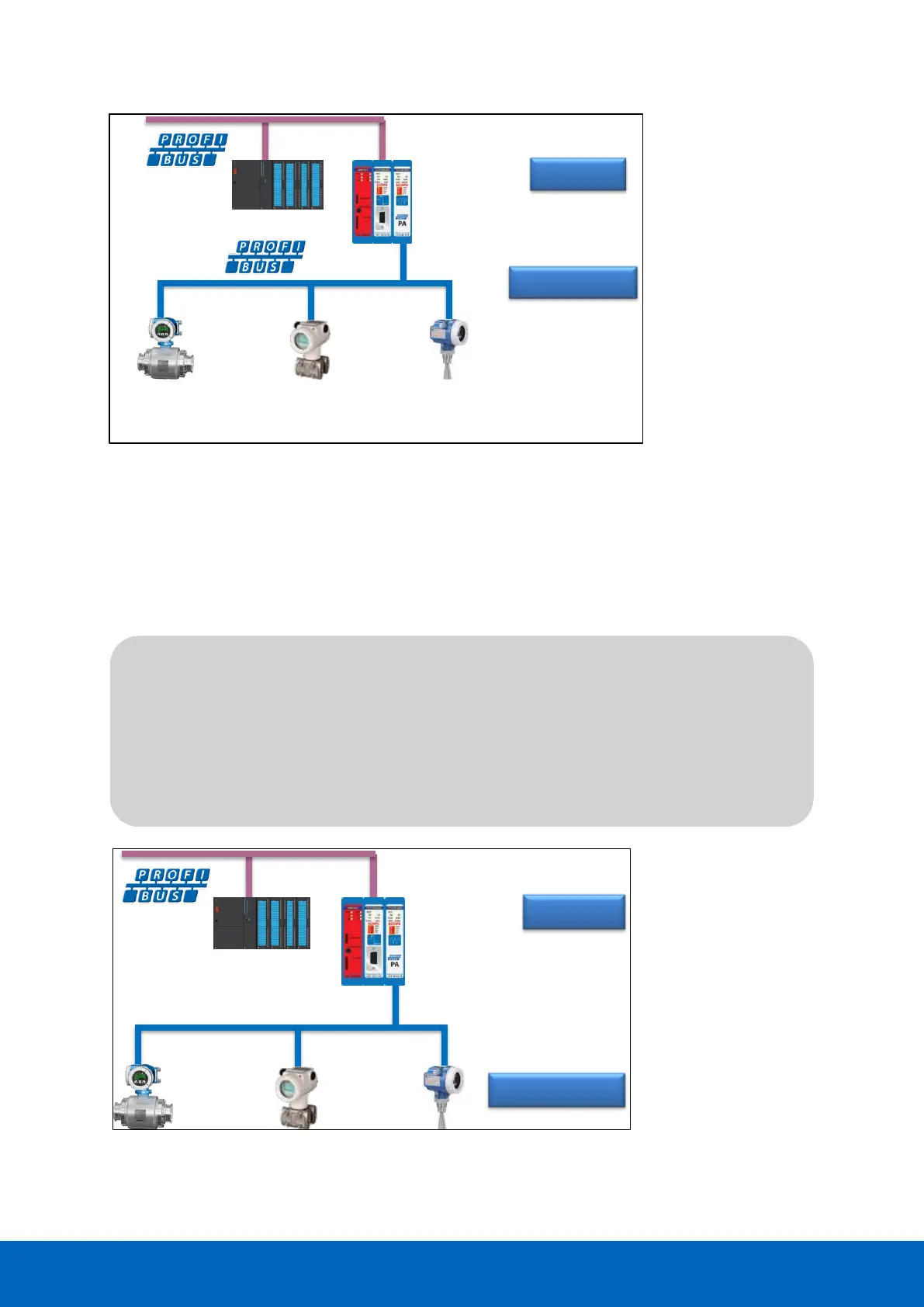
Fig. 89 - Example of voltage calculation at the end of the cable
In this example the voltage at the end of the cable is 24 V - (0.05A * 44 * 1.5) = 20.7 V
U
B
= U
S
– (I
SEG
* R
CABLE
* L
SEG
) (where U
B
> U
min
)
U
B
= Bus voltage at the last device (V)
U
S
= Voltage of the segment coupler (V)
I
SEG
= Total current In a segment (A)
R
CABLE
= Resistance per unit length of the cable (Ω/km)
L
SEG
= Length of all cables in the segment, including stubs (km)
U
min
= Minimal specified operating voltage of the last device (V)
 Loading...
Loading...