Product description
18 MCS100E Operating Instructions 8009504/VYWA7/V3-1/2018-01 © SICK AG
Subject to change without notice
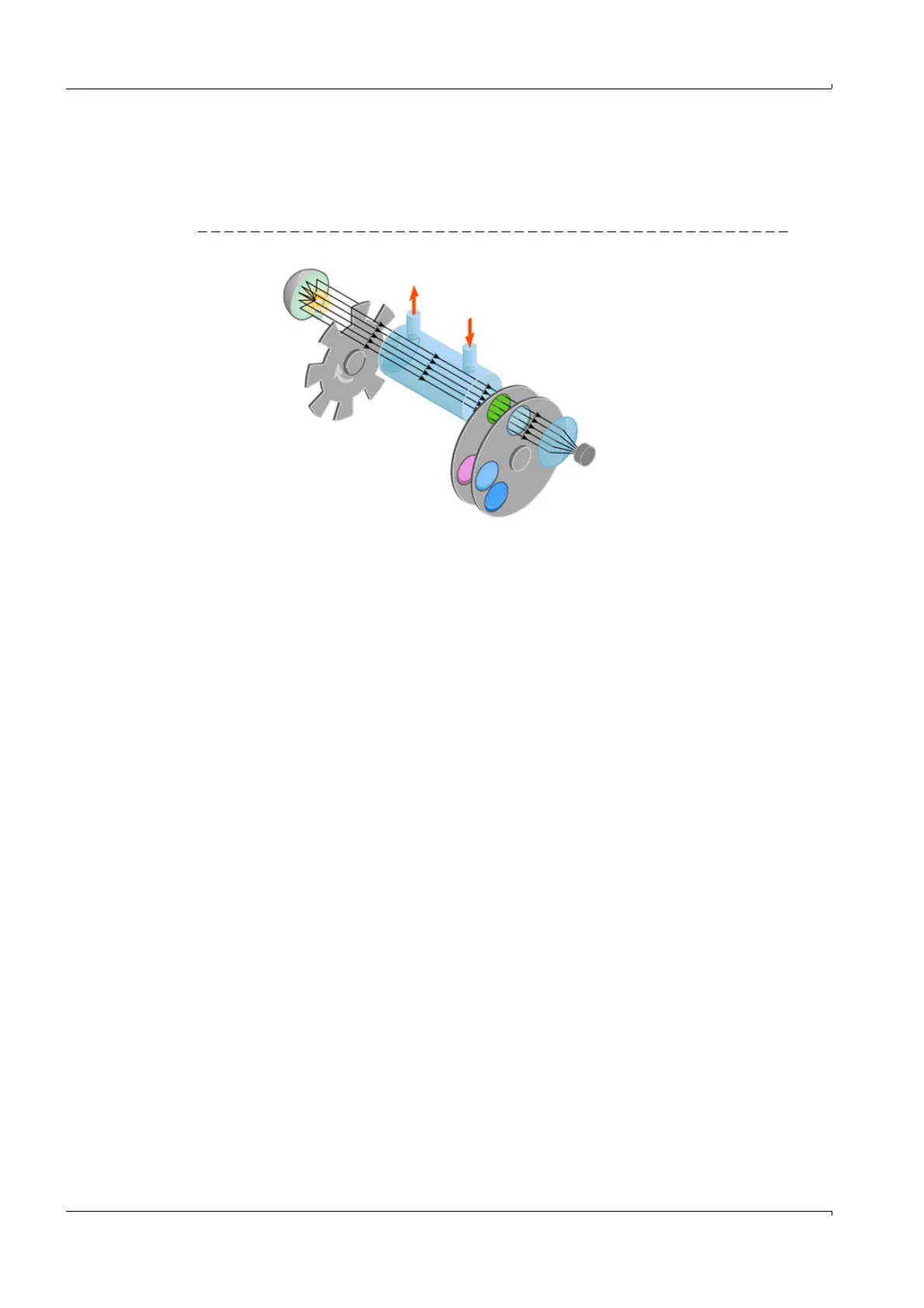
2.2.2 Measuring principle
MCS100E is a single-beam infrared photometer that works on the basis of the transmitted
light measuring technique applying the single-beam dual-wavelength method and the gas
filter correlation method.
Figure 3 Measuring principle
2.2.2.1
Correction of spectral interferences
In order to achieve greater measuring accuracy, interference sensitivities can be detected
and compensated (depending on application).
Additive (spectral superposition) and multiplicative (dilution effects) effects are considered.
Moreover, external digital and analog signals can be read in and processed (option).
2.2.3 Thermostatic control
MCS100E is equipped with a self-resetting thermal circuit breaker that protects the
instrument against thermal damage.
2.2.4 Cell
Sample gas filter
A sintered metal filter in the gas inlet of the cell serves as protective filter.
Beam path
The beam path corresponds to the principle of the White Cell with the beam being folded by
mirrors. The mirrors are mill-cut in the end plates. Thus the optical path length of the cell is
invariable (depending on the application).
Thermostatic control
The cell is thermostatic-controlled (temperature control
→
p. 83, §5.7.11.12).
2.2.5 Flow meter
The flow meter functions on the resistance anemometer principle. It comprises two
temperature-dependent, heated resistors, one of which is positioned in the gas stream
begin measured while the other does not have gas flowing over it. The difference in the
resistances is a measure of the flow rate.
Light source
Cell
Interference filter
Detector

 Loading...
Loading...











