207
network configuration protocol optimized and developed basing on the BOOTP, functions to solve
the above mentioned problems.
DHCP Working Principle
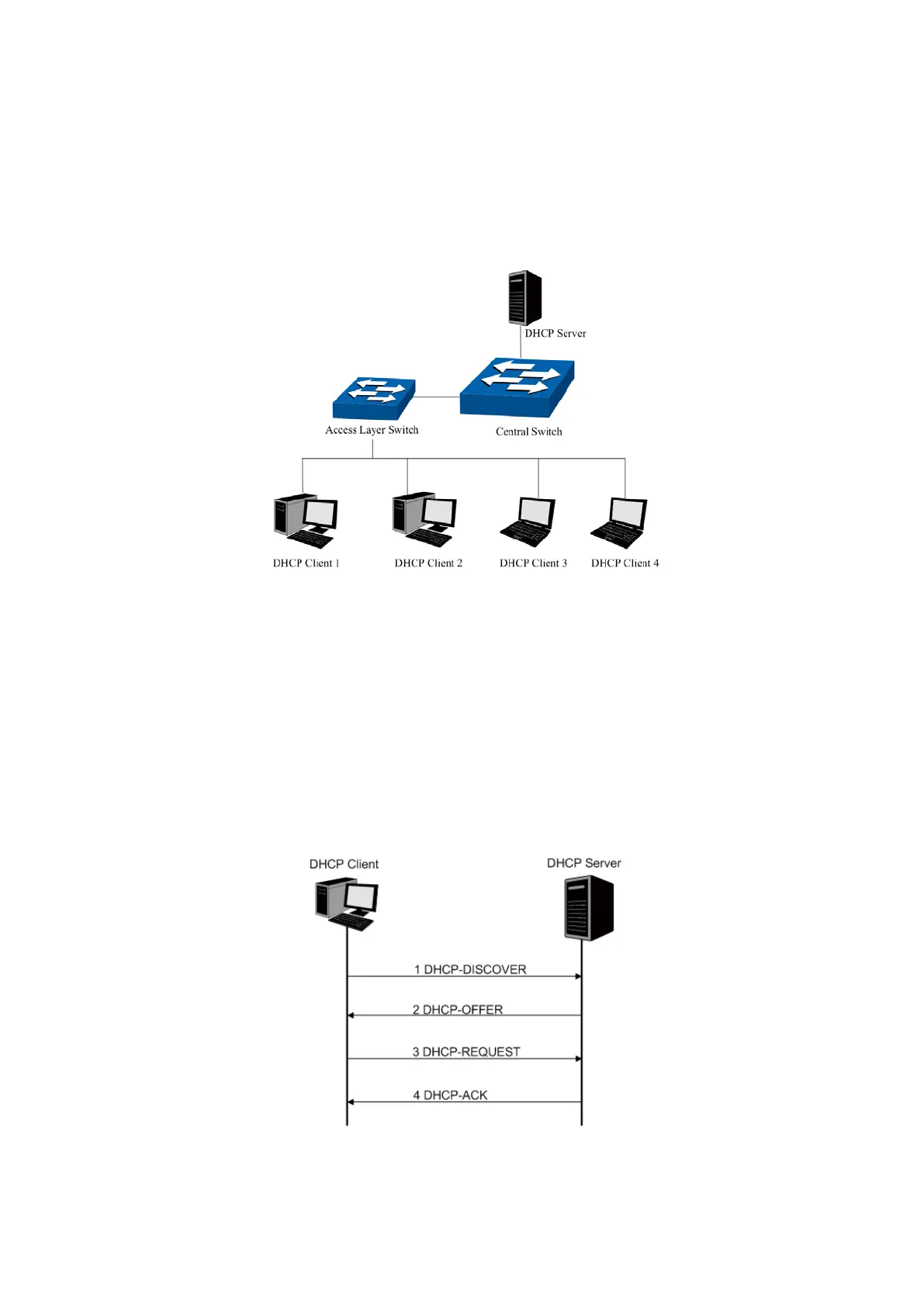
DHCP works via the “Client/Server” communication mode. The Client applies to the Server for
configuration. The Server assigns the configuration information, such as the IP address, to the
Client, so as to reach a dynamic employ of the network source. A Server can assign the IP
address for several Clients, which is illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 13-5 Network diagram for DHCP-snooping implementation
For different DHCP Clients, DHCP Server provides three IP address assigning methods:
1. Manually assign the IP address: Allows the administrator to bind the static IP address to the
specific Client (e.g.: WWW Server) via the DHCP Server.
2. Automatically assign the IP address: DHCP Server assigns the IP address without an
expiration time limitation to the Clients.
3. Dynamically assign the IP address: DHCP Server assigns the IP address with an expiration
time. When the time for the IP address expired, the Client should apply for a new one.
The most Clients obtain the IP addresses dynamically, which is illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 13-6 Interaction between a DHCP client and a DHCP server
1. DHCP-DISCOVER Stage: The Client broadcasts the DHCP-DISCOVER packet to find the
DHCP Server.
 Loading...
Loading...











