212
Enable/Disable the Option 82 feature.
Select the operation for the Option 82 field of the DHCP request
packets from the Host.
Keep: Indicates to keep the Option 82 field of the packets.
Replace:
Indicates to replace the Option 82 field of the
packets with the switch defined one.
Drop:
Indicates to discard the packets including the Option
82 field.
Enter the sub-option Circuit ID for the customized Option 82.
Enter the sub-option Remote ID for the customized Option 82.
Option 82 Config List
Displays the option 82 configuration of the ports.
13.3 ARP Inspection
According to the ARP Implementation Procedure stated in 13.1.3 ARP Scanning, it can be found
that ARP protocol can facilitate the Hosts in the same network segment to communicate with one
another or access to external network via Gateway. However, since ARP protocol is implemented
with the premise that all the Hosts and Gateways are trusted, there are high security risks during
ARP Implementation Procedure in the actual complex network. Thus, the cheating attacks against
ARP, such as imitating Gateway, cheating Gateway, cheating terminal Hosts and ARP Flooding
Attack, frequently occur to the network, especially to the large network such as campus network
and so on. The following part will simply introduce these ARP attacks.
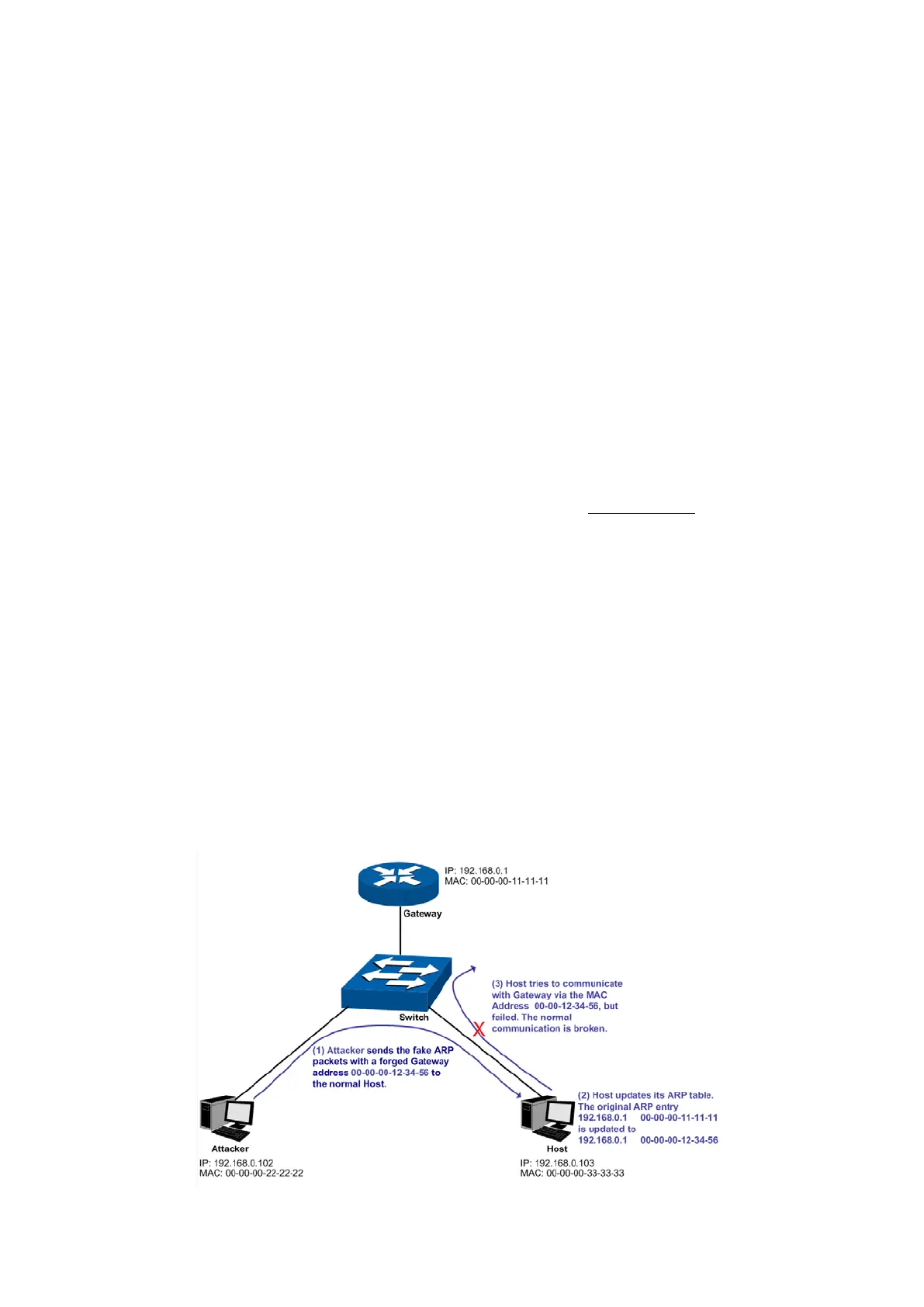
Imitating Gateway
The attacker sends the MAC address of a forged Gateway to Host, and then the Host will
automatically update the ARP table after receiving the ARP response packets, which causes that
the Host cannot access the network normally. The ARP Attack implemented by imitating Gateway
is illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 13-10 ARP Attack - Imitating Gateway
 Loading...
Loading...











