Chapter 7 Service Configuration
Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION 83
zte(cfg)#set vlan 2 add port 16 tag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 2 add port 1 untag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 3 add port 16 tag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 3 add port 3 untag
zte(cfg)#set port 1 pvid 2
zte(cfg)#set port 3 pvid 3
zte(cfg)#set vlan 2-3 enable
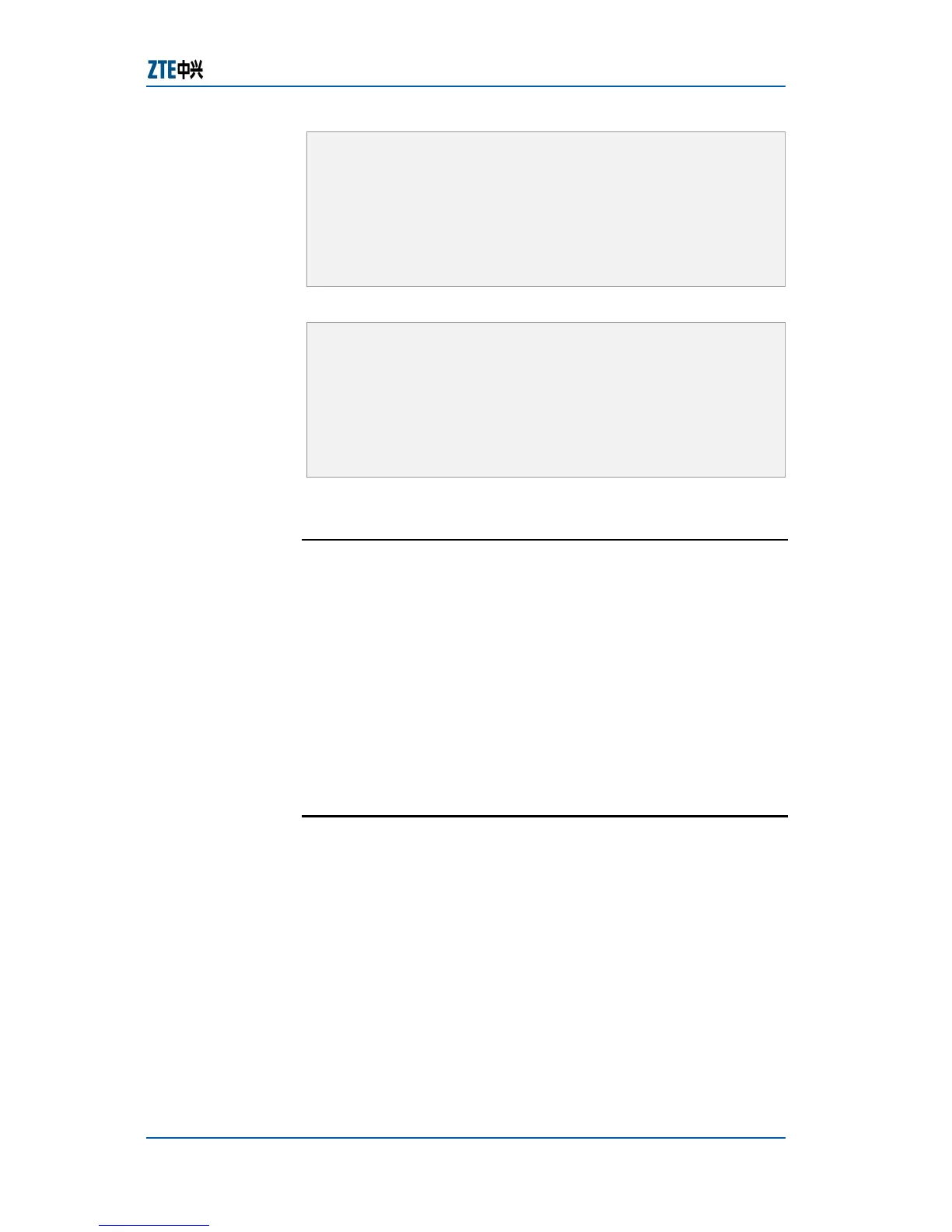
Switch B configuration
zte(cfg)#set vlan 2 add port 16 tag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 2 add port 2 untag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 3 add port 16 tag
zte(cfg)#set vlan 3 add port 4 untag
zte(cfg)#set port 2 pvid 2
zte(cfg)#set port 4 pvid 3
zte(cfg)#set vlan 2-3 enable
Introduction to FDB
Media Access Control (MAC) address is the hardware
identification of a network device, based on which the switch
forwards packets. MAC address is unique, ensuring accurate
packet forwarding.
Each switch maintains a MAC address table called forwarding
database (FDB). FDB records one-to-one mapping relationship
between MAC addresses and switch ports. Upon receiving a
data frame, the switch decides whether to drop it or forward it
to the proper port based on this table. The FDB is the basis
and prerequisite for fast forwarding.
MAC Table Operations
MAC table operations include the configuration of MAC filter
function, static address binding function, and MAC table aging
time.
MAC filter function is to enable the switch to discard the received
data packets whose source or destination MAC address is the
specified MAC address. There are 3 filter mode:according to
source mac address filter, destination mac addressfilter & both
of them.
Static address binding function is to bind the specified MAC
address with the switch port. After the binding, this MAC is
kept away from the dynamic study.
MAC Address
Table
MAC filter
function
Static address
binding
function

 Loading...
Loading...











