One important parameter set by this procedure is the maximum W-CDMA
span. This parameter allocates memory for W-CDMA measurements. Since
W-CDMA measurements require large amounts of memory, set this
parameter to the smallest frequency span that you will measure.
If the analyzer is unable to lock to your signal, verify that you are using
the correct chip rate, scramble code, and center frequency. Also, verify
that [freq spectrum
mirror] is selected if the spectrum of your signal is flipped
(mirrored). The analyzer’s chip rate and scramble code must match that of
your signal. The analyzer’s center frequency must be within 500 Hz. of
your signal’s center frequency.
By default, the analyzer displays the composite code-domain power display,
which shows all layers simultaneously. So you can differentiate between
active layers, the analyzer uses a different color for each code layer. In
some measurements, you may have to use x-scale markers to see the color.
This is because individual channels at the slower layers are represented by
a single line in the code-domain power display.
Tip Code-domain power is relative to the total signal power in the code domain. To
display absolute power, press [
Instrument Mode], [demodulation setup], [normalize off].
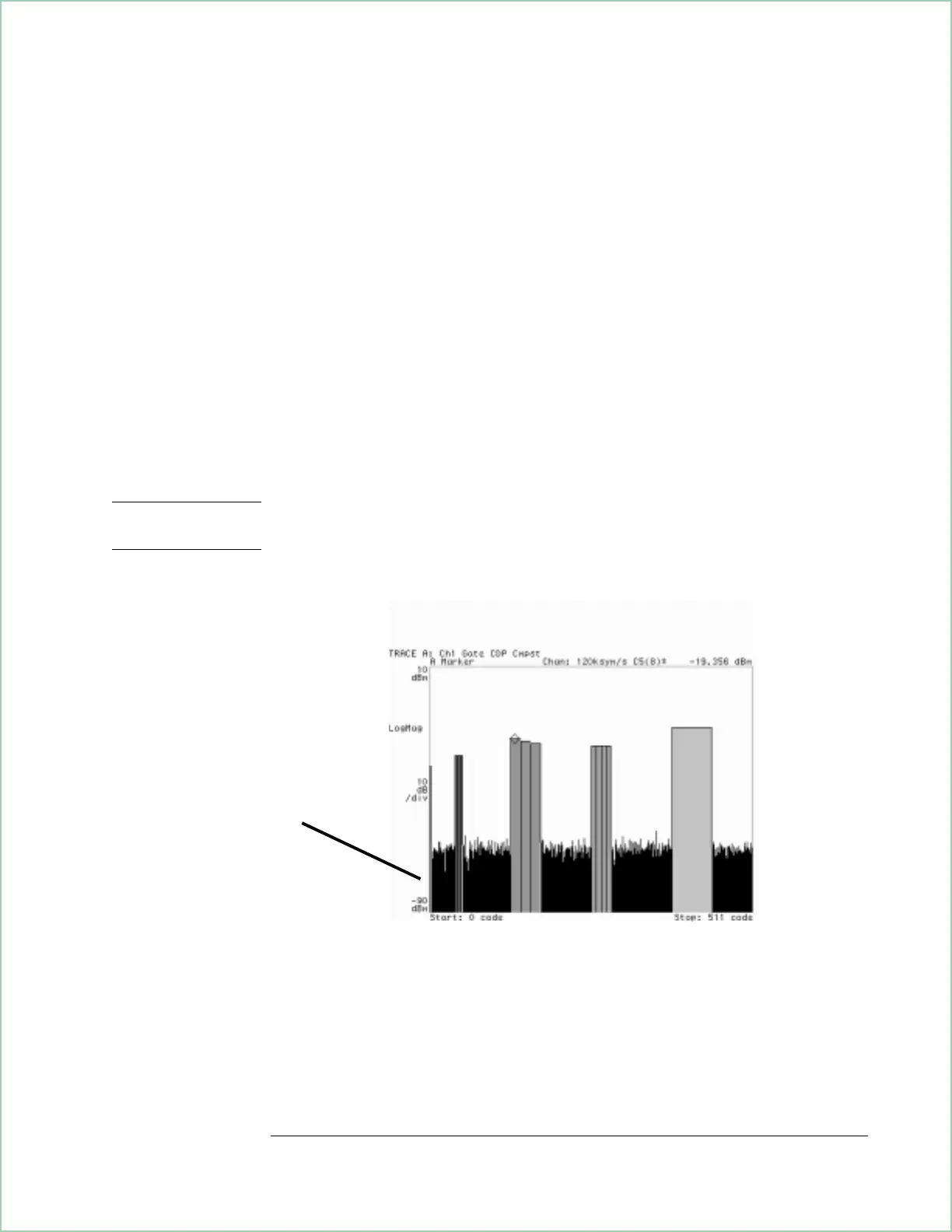
Composite Code-Domain Power Display
X-axis annotation is based on the
slowest code layer. For 3GPP
1999 forward-link signals, the
slowest code layer is code layer 9,
also known as code layer 7.5
ksym/s.
Each code layer uses a different
color. The marker in this
illustration is on channel 8 in
code layer 5 (120 ksym/s).
Using Wideband CDMA (Options B73, B79, and 080)
13 - 5

 Loading...
Loading...