Time record length limitations
The maximum time record size (the number of points of time data) is limited by the
number of frequency points. As noted earlier, the sample rate (the rate at which
data is digitized and entered into the time record) is determined by span.
Therefore, the maximum time record length for a given span is determined by the
number of frequency points. Because of this we can see that for a given window
type, the minimum resolution bandwidth, while not directly affected by span and
number of frequency points, may be limited by these parameters.
Time record size (also called block size or number of time points) is determined by
window, span, and resolution bandwidth. But maximum and minimum time record
sizes are determined by memory and FFT constraints:
Maximum time record length
The time record length is limited by the number of frequency points.
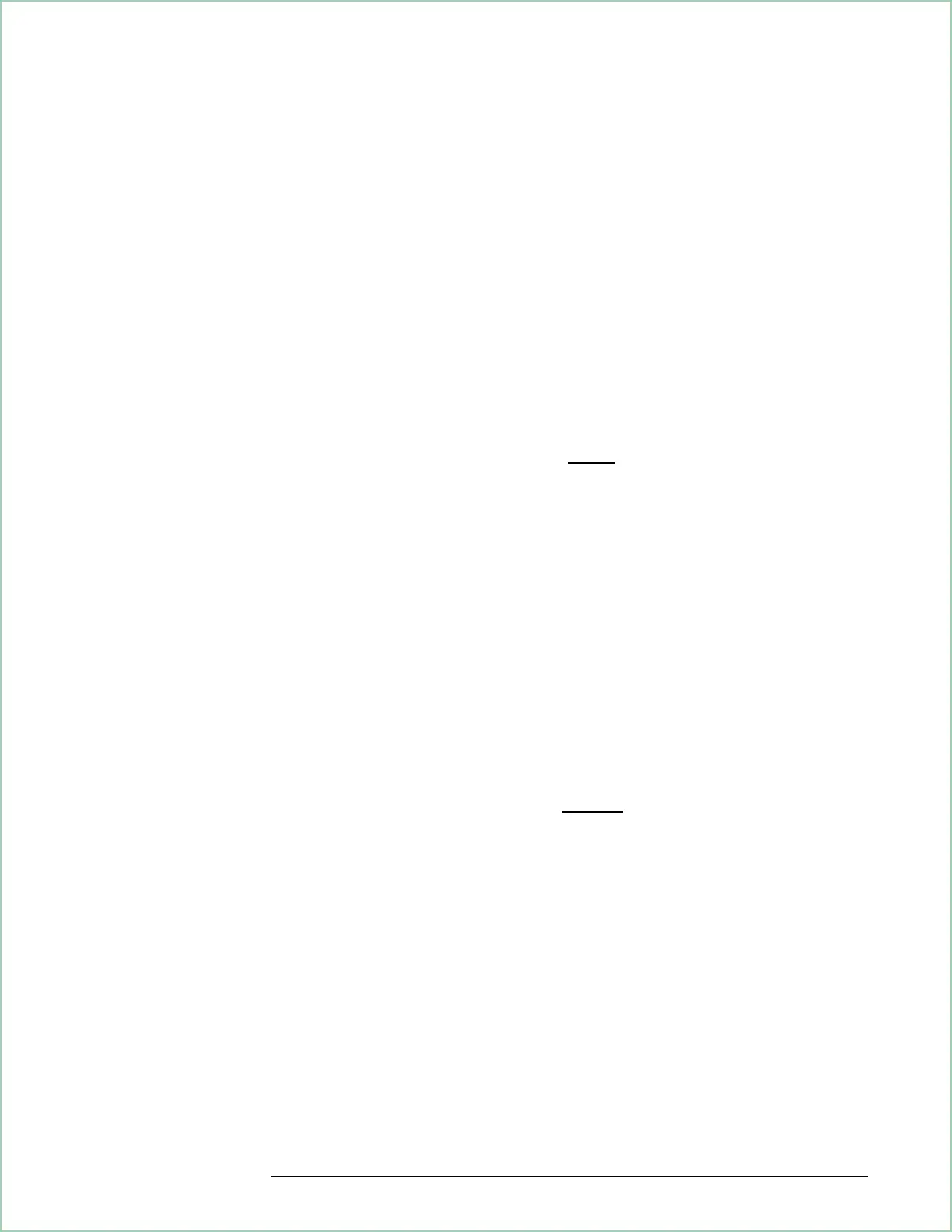
T
max=
(FP−1)
span
Where:
FP = number of frequency points
Maximum time record size
The time record size is also limited by the number of frequency points.
TP
max
= 2.56 ×(FP−1) (In baseband mode, real data)
TP
max
= 1.28 ×(FP−1) (In zoom mode, complex data)
Therefore:
T
max
= TP
max
×∆T
Minimum time record length
Minimum time record length is dependant on the resolution bandwidth to span
ratio:
T
min
=
WBW
RBW
max
RBW
max
= .3 × span
Time record length and memory
To increase the time record length you can increase the number of frequency
points until you reach the maximum number of frequency points allocated in
memory (up to a maximum of 3201). To increase time record length you may have
to reallocate memory space under the [
System Utility
] key.
Fundamental Measurement Interactions
19 - 19
 Loading...
Loading...











