E-bit
The type of external metric. If the E-bit is set, the metric specified is a Type 2 external
metric. This means the metric is considered larger than any link state path. If the E-bit is
zero, the specified metric is a Type 1 external metric. This means that is comparable
Forwarding Address
Data traffic for the advertised destination will be forwarded to this address. If the
Forwarding Address is set to 0.0.0.0, data traffic will be forwarded instead to the
Including the NSSA
The NSSA or Not So Stubby Area is a feature that has been added to OSPF so external routes from ASs
(Autonomous Systems) can be imported into the OSPF area. As an extension of stub areas, the NSSA feature
uses a packet translation system used by BRs (Border Routers) to translate outside routes into the OSPF area.
Consider the following example:
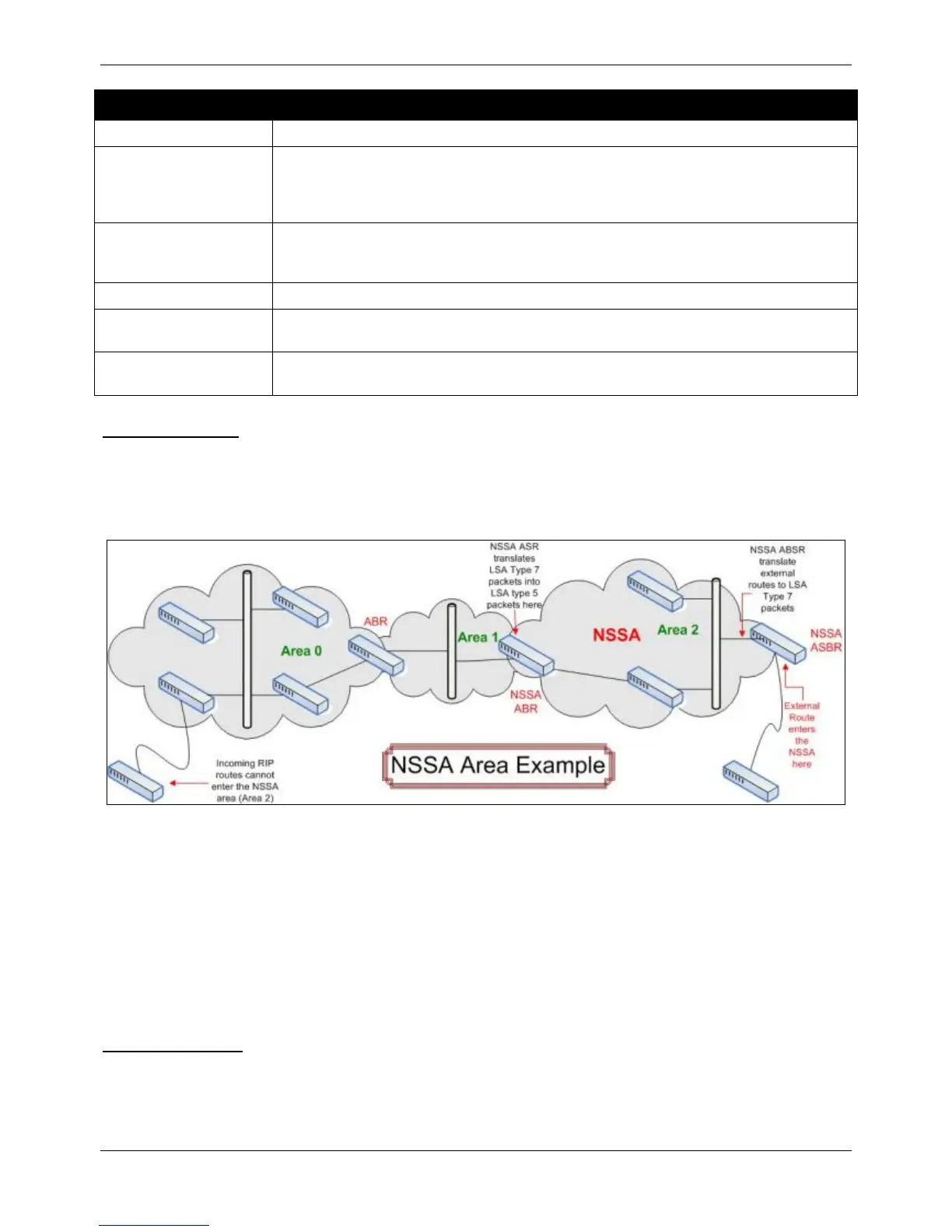
Figure 5-42 NSSA Area example
The NSSA ASBR (Not So Stubby Area Autonomous System Border Router) is receiving External Route information
and translating it as an LSA Type-7 packet that will be distributed ONLY to switches within the NSSA (Area 2 in the
example above). For this route’s information to enter another area, the LSA Type-7 packet has to be translated into
an LSA Type-5 packet by the NSSA ABR (Area Border Router) and then is distributed to other switches within the
other OSPF areas (Area 1 and 2 in the example above). Once completed, new routes are learned and new
shortest routes will be determined.
To alleviate any problems with OSPF summary routing due to new routes and packets, all NSSA area border
routers (ABR) must support optional importing of LSA type-3 summary packets into the NSSA.
Type-7 LSA Packets

 Loading...
Loading...











