99
What is volume resistivity?
8.5 What is volume resistivity?
Volume resistivity is a physical property that indicates the comparative difculty with which
electricity passes through a material. It is also known as resistivity, specic resistance, and
electrical resistivity. Volume resistivity is measured in [
Ω
m].
Each material has a characteristic volume resistivity that does not depend on its shape or size. As
a result, the characteristic offers a convenient means of comparing the electrical conductivity of
different materials.
The relationship between the volume resistivity
ρ
and the electrical resistance R is shown below.
[R = (V: Voltage drop) / (I: Current)]
(
V
)·····(Equation 1)
Here
(V) is a correction coefcient that corrects for the effects of the material’s shape, size,
and measurement position.
and
vary with the shape, size, and measurement position of
the material.
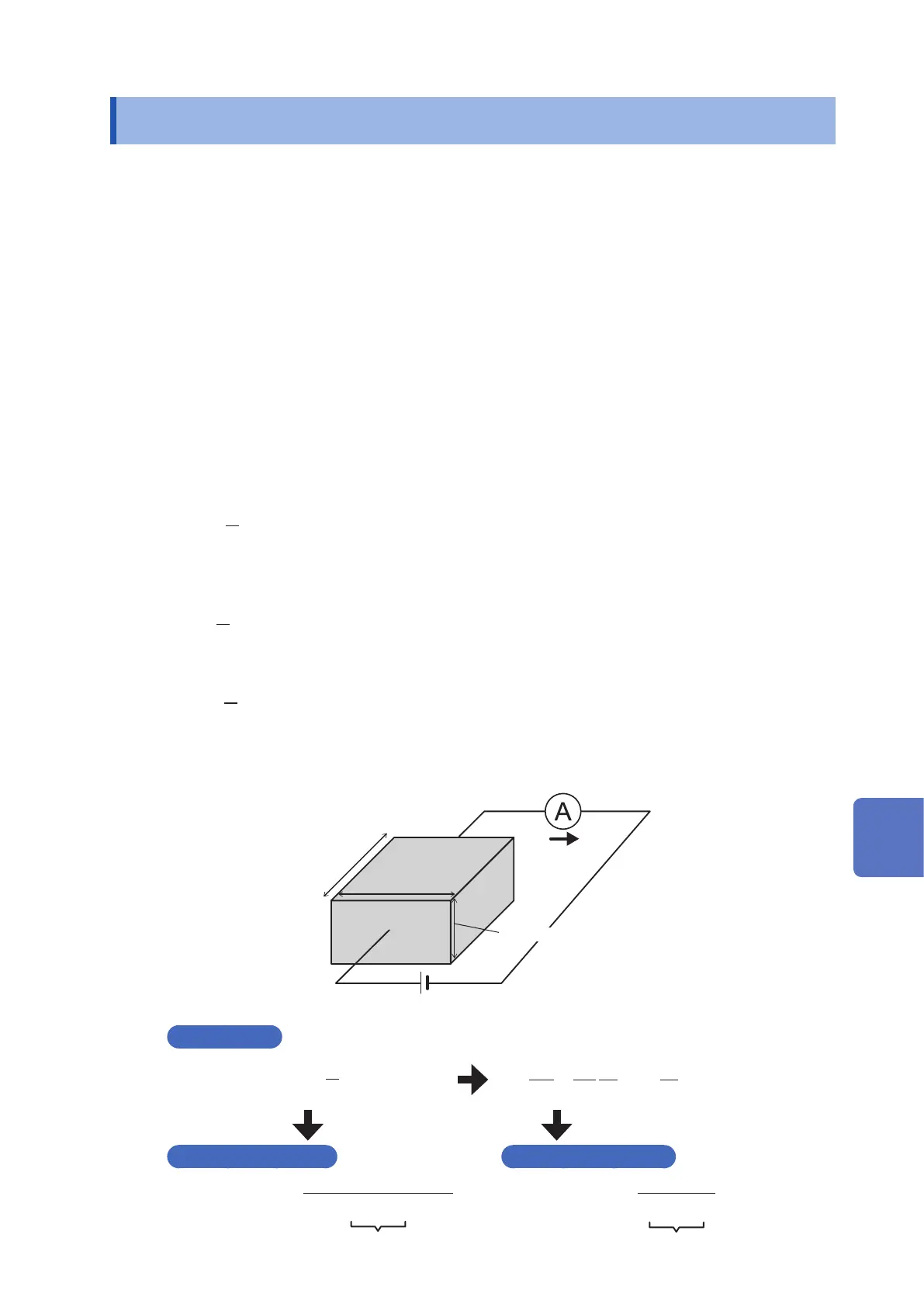
For example, for a columnar object with length L and cross-sectional area S, electrical resistance is
proportional to the length L and inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area S.
R
= ×
ρ
·····(Equation 2)
The proportionality coefcient here is the volume resistivity, and the equation can be changed as
shown below so that it can be compared with Equation 1.
ρ
= ×R
·····(Equation 3)
Consequently, the object’s RCF can be expressed as follows:
RCF
=
·····(Equation 4)
Methods for measuring the volume resistivity of a conductor include that described in JIS K 7194,
“Testing method for resistivity of conductive plastics with four-point probe array.”
Length (L)
Width (W)
Cross-sectional
area (S)
Current (I)
DC power supply (V)
Thickness (t)
Resistance
R
Rv
=
ρ
ρ
ρ
ρ
v
tW
t
W
s
W
= =
Volume resistivity
ρν
Surface resistance
ρ
s
= Resistance
R
×
Cross-sectional area
S
=
Resistance
R
×
Width
W
Length
L
Length
L
(
V
)
(
S
)
8
FAQ
 Loading...
Loading...