103
What is measurement reliability?
8.9 What is measurement reliability?
Measurement reliability provides an indicator of whether potential measurement has been
performed correctly. It allows you to check the status of potential measurement. Measurement
reliability is indicated by three values.
Consistency [PASS/FAIL]
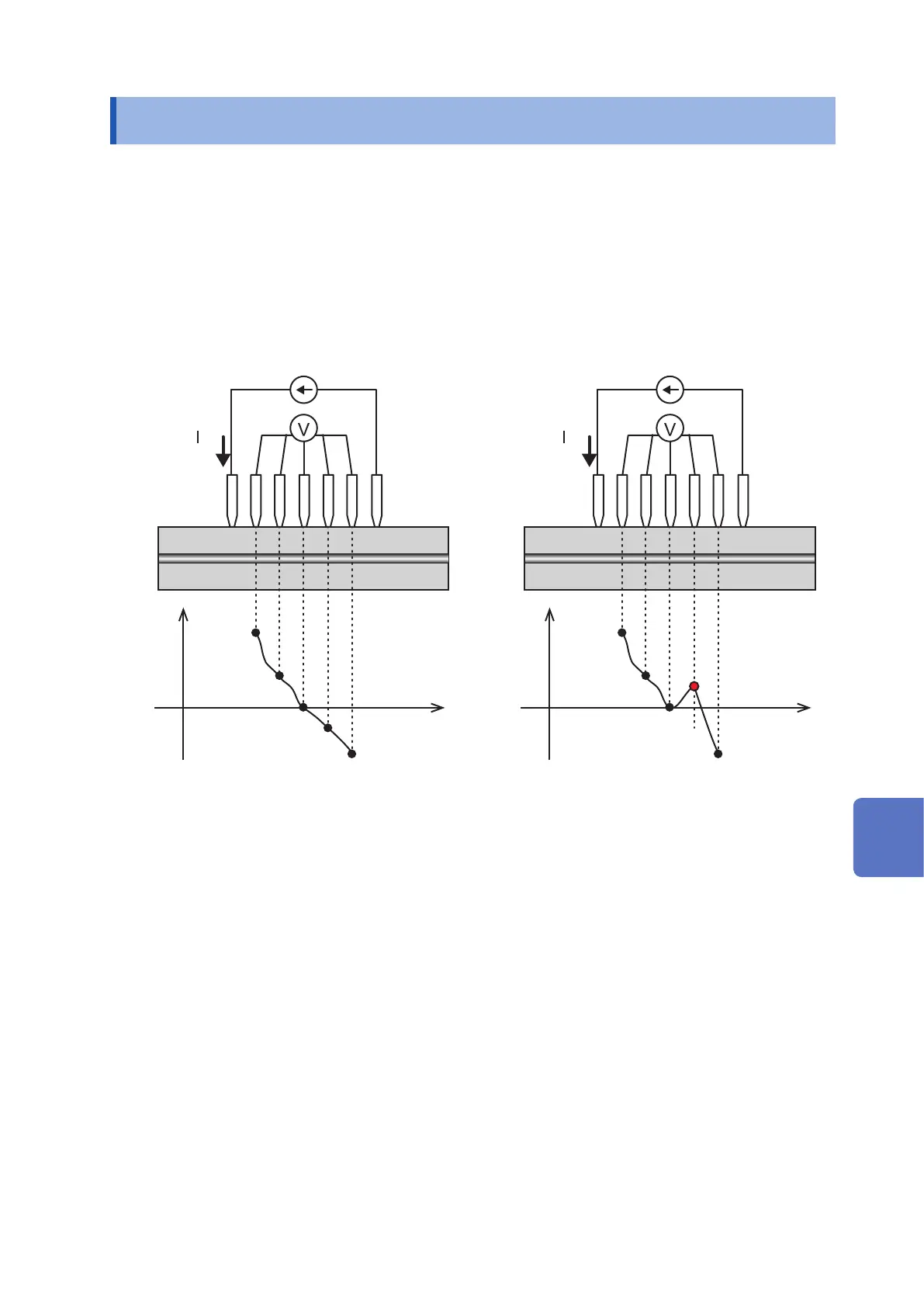
Consistency provides a judgment of whether the magnitude of the gradient in the potential
distribution accords with the theoretical result that would be expected. Potential increases near the
current source probe and decreases near the current drain probe, and consistency checks for the
relationship that would be expected in theory and expresses the result as a PASS or FAIL value.
Potential Potential
Measurement
position
Measurement
position
Figure: Illustration of consistency (left: PASS consistency; right: FAIL consistency)
Error rate [%]
The error rate expresses the number of measurements with a incomplete contact as a percentage
of all measurements obtained during multipoint measurement of potential distribution. The error
rejection function rejects error data with an error rate that falls below a certain threshold and
performs analysis using only normal measurement data.
Coefcient of variability [%]
The coefcient of variability indicates the largest value of the coefcient of variability for equivalent
potential measurements. The coefcient of variability is dened as the result of dividing the standard
deviation by the average value. The instrument performs numerous equivalent measurements and
averages them, and the coefcient of variability for those measurements indicates the amount of
variation.
8
FAQ
 Loading...
Loading...