100
What is surface resistivity? How do composite layer volume resistivity and composite layer surface resistivity differ?
8.6 What is surface resistivity? How do composite
layer volume resistivity and composite layer
surface resistivity differ?
Surface resistivity indicates the difculty with which electricity ows perpendicularly to a surface that
has no thickness or that is thin enough that its thickness can be ignored. The property is converted
expressed per unit area and measured in [
Ω
m
2
]. The value is unique and does not depend on the
sheet’s area.
The instrument denes the resistance of the contact surface between the composite and collector
as the interface resistance and expresses it in surface resistivity units. The interface resistance is
the contact resistance between both surfaces, and since no substance actually exists there, the
concept of thickness does not apply. (Another valid approach would be to assume the existence of
an extremely thin non-conductive coating.) In such circumstances, surface resistivity is the most
appropriate indicator of resistance to the ow of electricity.
Composite layer volume resistivity and composite layer surface resistivity are related by unit
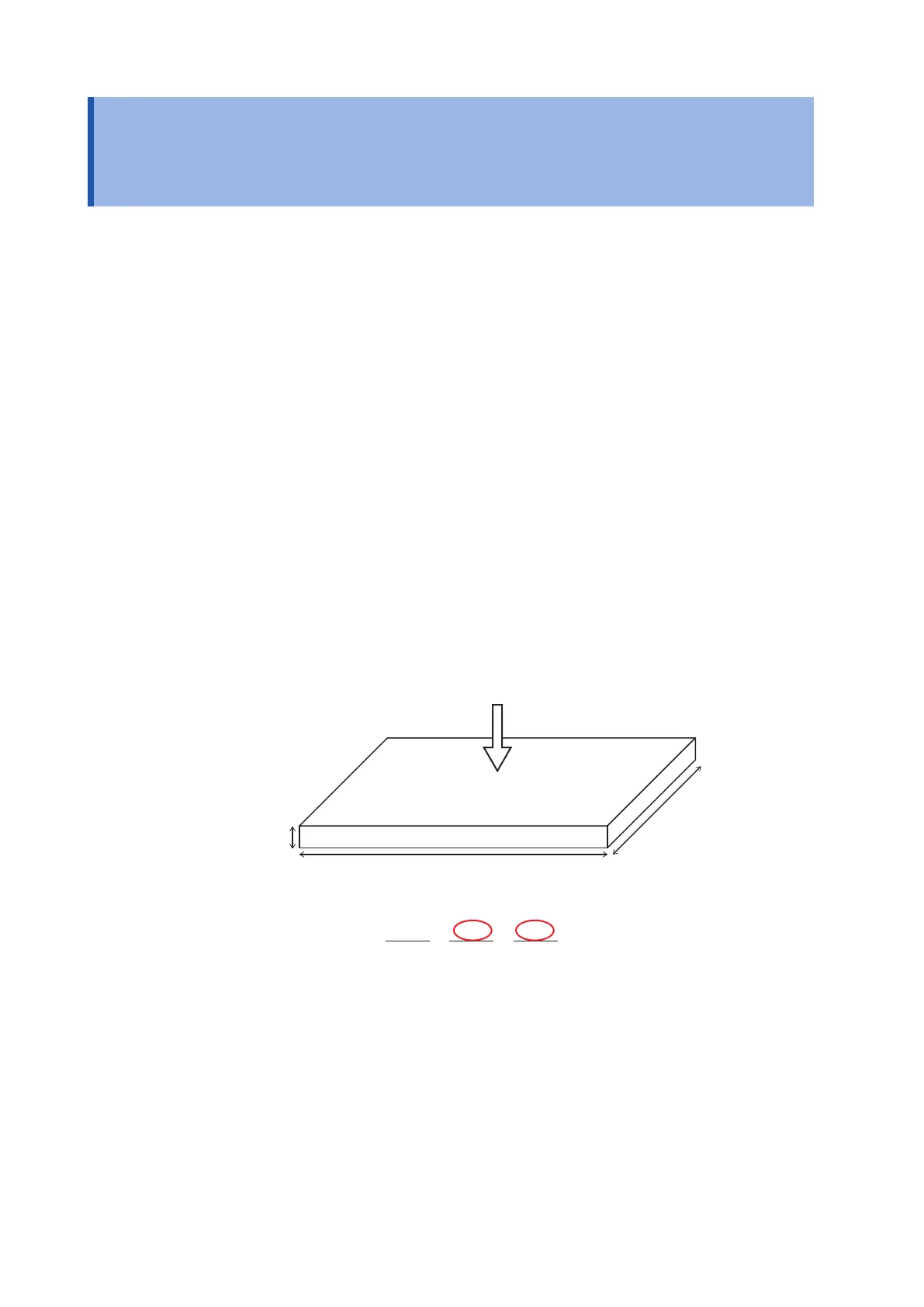
conversion. The gure below provides a diagram that denes surface resistivity. Composite layer
surface resistivity is calculated by multiplying the composite layer volume resistivity by the thickness
of the composite layer. In other words, the relationship can be expressed as follows:
Composite layer surface resistivity = Composite layer volume resistivity × composite layer thickness
Surface resistivity removes the concept of thickness from volume resistivity. It is necessary to
exercise caution as the surface resistivity of the electrode composite may behave slightly differently
since the electrode composite does in fact have thickness.
Current
Resistance R [
Ω
]
Thickness t [m] (
≈
0)
Width W [m]
Length L [m]
Volume resistivity
ρ
[
Ω
m]
Figure: Denition of surface resistivity
R
t
WL
t
WL
R
WL
=
×
=
×
=
×
ρ
ρ
1
1
≡×
ρ
[
Ω
m
2
] Surface resistivity

 Loading...
Loading...