84
RM2612 Resistance Calculation Software
Comparison of potential values for the nite volume model and an analytical
solution
The following table compares calculated potential values from an analytical solution and calculated potential values
from the nite volume model for a single-layer substance:
Parameters of the electrode sheet used as a model
Single-layer substance
NORMAL: 3.1%
FINE: 2.0%
SUPER FINE: 1.0%
Volume resistivity: 0.1
Ω
cm
Thickness: 100 μm
Analytical solution: Solution obtained by solving the Poisson equation for potential algebraically
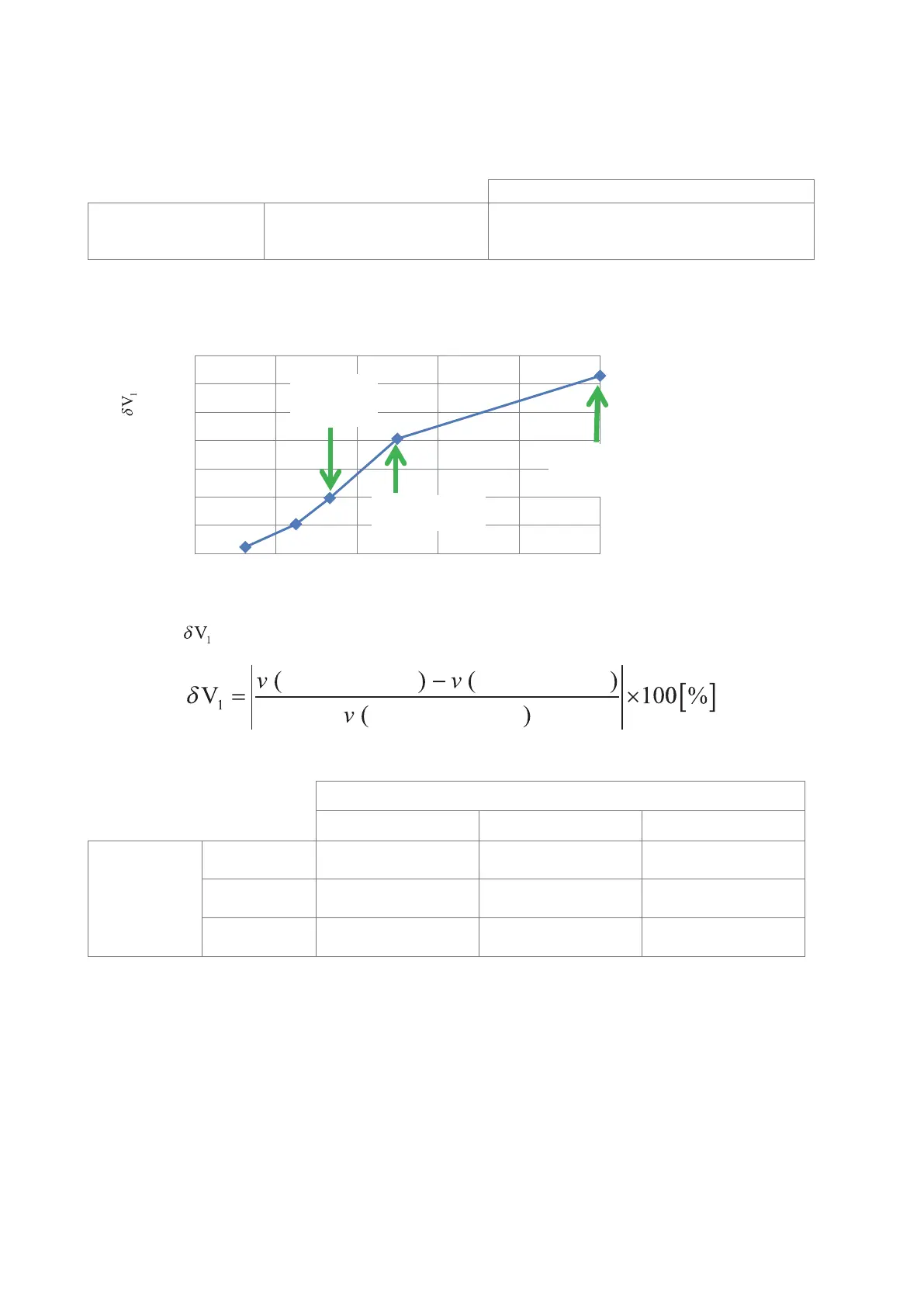
Comparison of potential values for the nite volume model
and an analytical solution
(Potential 120 μm from the probe applying the current)
Potential difference [%]
0 0.2
2.00
2.50
3.00
Element size
equivalent to
SUPER FINE
Element size (where NORMAL = 1)
3.50
0.00
0.50
0.4 0.6 1
1.00
1.50
0.8
Element size
equivalent to FINE
Element size
equivalent to
NORMAL
The difference
relative to the analytical solution is dened as follows:
Analytical solution
Finite volume model
solution
Analytical solution
Calculation time based on element size and nite volume model area (reference values) [typ. min.]
Element size
NORMAL FINE SUPER FINE
Finite volume
model area
NORMAL 0.3 3 6
MEDIUM 0.8 11 18
WIDE 2 12 33
• Figures in the table are reference values. Actual times will vary with the electrode sheet’s resistance values and
potential state.
• In actual usage, calculation times are augmented by contact check times and potential measurement times.
 Loading...
Loading...