HT2000H_en_n.doc Page 135 of 167
8.18 Analytical troubleshooting
The indications given below are for gas chromatography applications and may not be suitable for
other analysis techniques for which this autosampler could be used.
When troubleshooting chromatographic symptoms, always remember that the headspace sampler
is only part of the system. Evaluate the whole system in order to isolate the problem. Often, issues
that appear in the chromatography can be caused by a problem in one or more of the following, in
order:
• The sample;
• The sample preparation (inlcuding the consumable hardware, such as vials, septa, syringe,
solvent and so forth);
• The Data system (acquisition setpoints, integration parameters, peak identification settings,
quantitation settings and reporting);
• The GC (method or hardware);
• The headspace autosampler (method or hardware).
To troubleshoot chromatographic symptoms, begin troubleshooting with the sample and sample
preparation.
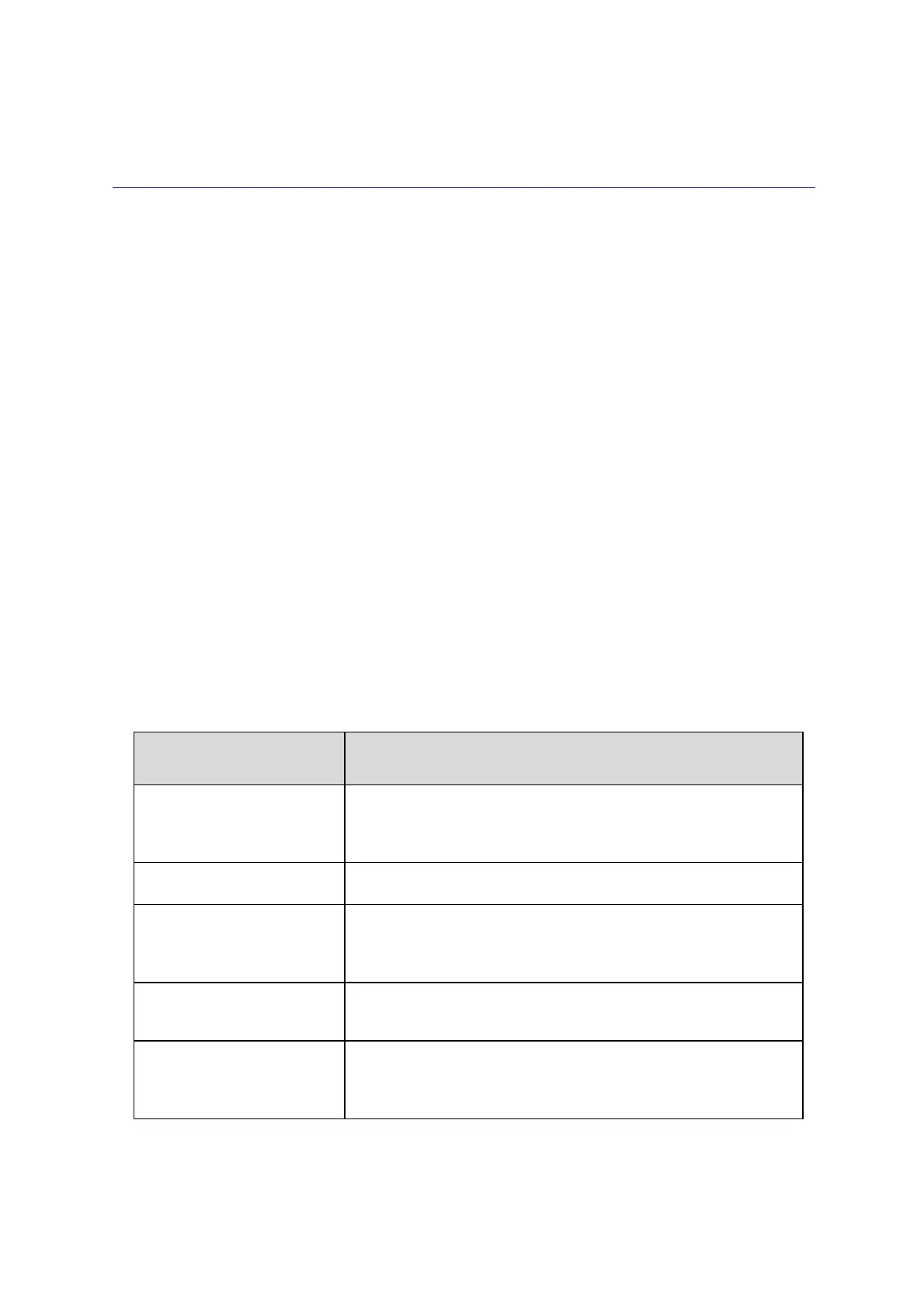
8.18.1 Reproducibility issue
Sample peaks or responses are not reproducibile.
Possible causes
Solutions
Syringe is dirty
Increase the syringe purge time in the method (see paragraph 5.2.2.5).
Set the syringe temperature 10°C above the oven temperature (see
paragraph 5.2.2.3).
Vacuum created in sample vial Reduce sample volume (see paragraph 5.2.2.4).
Improperly crimped vials
Check vial cap by attempting to rotate manually. Loose caps may cause
selective loss of more volatile components from sample. Adjust crimping
tool correctly (see paragraph 3.7.1).
None or too low Syringe flush
gas pressure
Check pressure at External pressure regulator during the syringe purge.
Check gas flow at syringe needle tip.
Method parameters
Check all the method parameters, in particular the sample speed, the pull
up strokes (see paragraph 5.2.2.4), the injection speed and the post in-
jection dwell (see paragraph 5.2.2.5).
 Loading...
Loading...