10 - 45
10.3 Programming Using MELSEC Data Link Functions
10.3.11 Device types for MELSEC data link functions
10
FUNCTIONS AND PROGRAMMING
(3) Device types for CC-Link module access
* 1 Device name specification (macro) is defined in the included file "MdFunc.h" of the MELSEC data
link functions. ( Section 10.2.3 (1) )
* 2 Not usable for the mdRandR, mdRandW, mdDevSet and mdDevRst functions.
* 3 The link special relay for CC-Link (own station SB) has two different device type definitions
(DevSM and DevQSB), and either of them may be specified.
* 4 The link special register for CC-Link (own station SW) has two different device type definitions
(DevSD and DevQSW), and either of them may be specified.
* 5 Continuous access to link devices of a CC-Link module (with mdSend, mdReceive, mdRandR,
mdRandW, mdDevSet, or mdDevRst function), for which Block guarantee of cyclic data per
station is enabled, may result in a delay of up to one link scan time. (This is the same as the case
where the QBF_ToBuf or QBF_FromBuf function is used with "automatic" set for the CC-Link
refresh method. ( Section 4.3.1))
Moreover, please note that the function of block guarantee of cyclic data per station cannot be
used in mdRandR and mdRandW function.
Refer to the following for details.
( mdReadR and mdReadW functions in MELSEC data link function HELP)
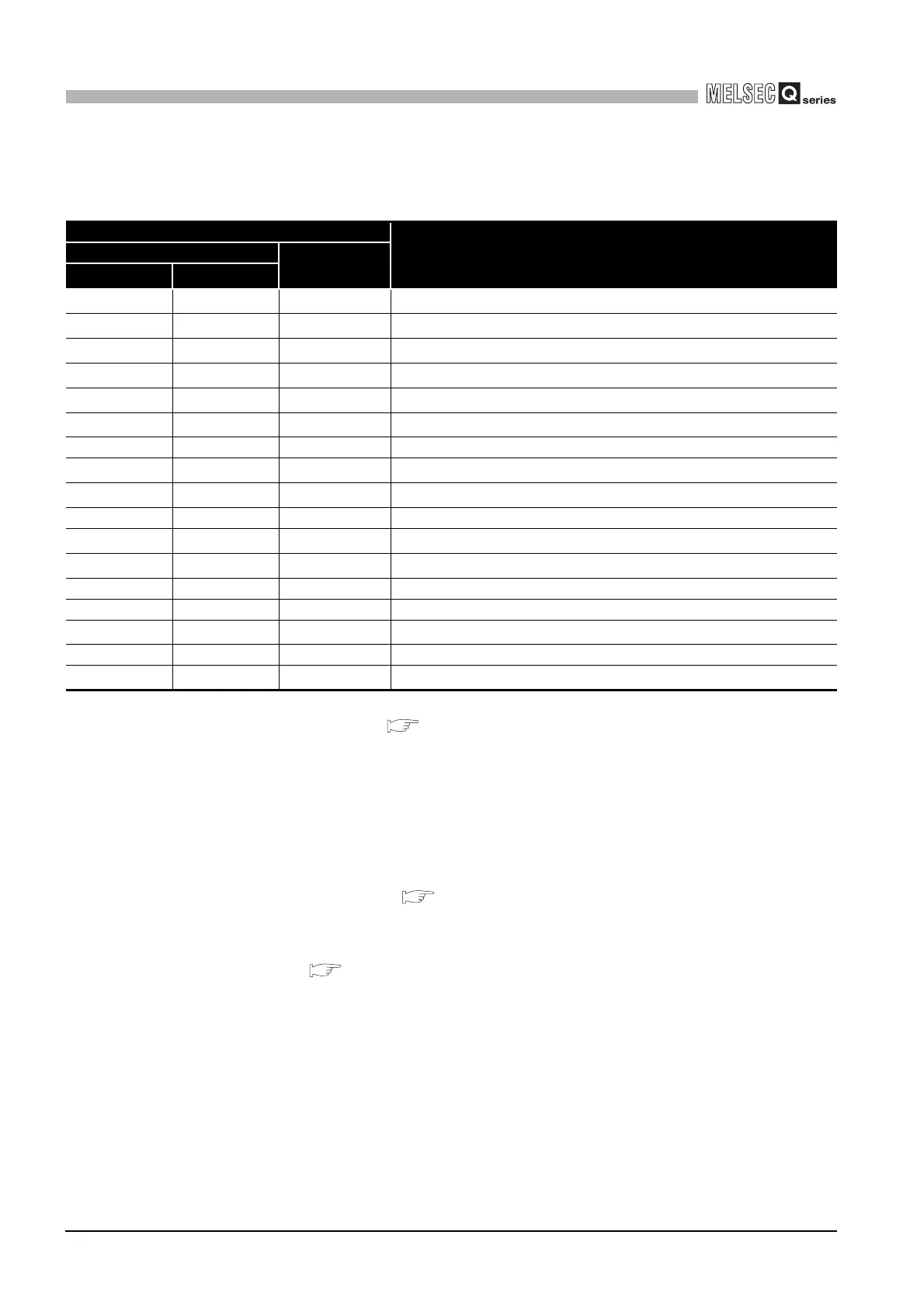
Table10.16 Device types for CC-Link module access
Device type
Device
Code specification Device name
specification
*1
DEC. HEX.
11H DevX
Own station RX
*5
22H DevY
Own station RY
*5
55H DevSM
Own station SB (link special relay for CC-Link)
*3
14 EH DevSD
Own station SW (link special register for CC-Link)
*4
25 19H DevQSB
Own station SB (link special relay for CC-Link)
*3
28 1CH DevQSW
Own station SW (link special register for CC-Link)
*4
33 21H DevMRB Own station random access buffer
36 24
H DevWw
Own station link register (for sending)
*5
37 25H DevWr
Own station link register (for receiving)
*5
50 32H DevSPB Own station buffer memory
-32768 8000
H DevRBM
Other station buffer memory
*2
-32736 8020H DevRAB
Other station random access buffer
*2
-32735 8021H DevRX Other station RX
-32734 8022H DevRY Other station RY
-32732 8024
H DevRW
Other station link register
*2
-32669 8063H DevSB Other station SB (link special relay for CC-Link)
-32668 8064
H DevSW
Other station SW (link special register for CC-Link)
*2

 Loading...
Loading...











