14 - 7
14.2 Event Notification
14
COMMUNICATIONS BETWEEN CPU MODULES
[Error details]
In any of the following cases, an operation error occurs, the error flag (SM0) of the
programmable controller CPU turns ON, and the error code is stored into SD0.
* 1: 0000H (Normal)
[Program example]
Sequence program that will cause an interrupt for the C Controller module of CPU No. 2
(5) Precautions
(a) When interrupt event has already been notified at execution of
QBF_WaitEvent function
When an interrupt event has already been notified from the programmable
controller CPU or C Controller module (another CPU) at execution of the
QBF_WaitEvent function, the user program is restored from the interrupt event
waiting status as soon as the QBF_WaitEvent function is executed.
When multiple interrupt events have been notified with the same interrupt event
number at execution of the QBF_WaitEvent function, the user program processes
them as a single interrupt event notification.
(b) When event notification is used by multiple user programs
Do not set the same CPU No. and same interrupt event No. in multiple user
programs.
If such setting is made, it will be uncertain which user program will receive the
interrupt event.
Table14.7 Error codes related to S(P).GINT instruction
Error code
*1
Error factor
Corrective
action
2110
The target CPU start I/O No. 16(n1) specified a reserved
(CPU "Empty" setting) CPU or a CPU module not mounted.
Check and
correct the
sequence
program.
2114
The target CPU start I/O No. 16(n1) specified the host CPU.
2117
The target CPU start I/O No. 16(n1) specified a module not
supported by the S(P).GINT instruction.
4100
The target CPU start I/O No. 16(n1) specified any of 0 to
3DF
H or 3E4H.
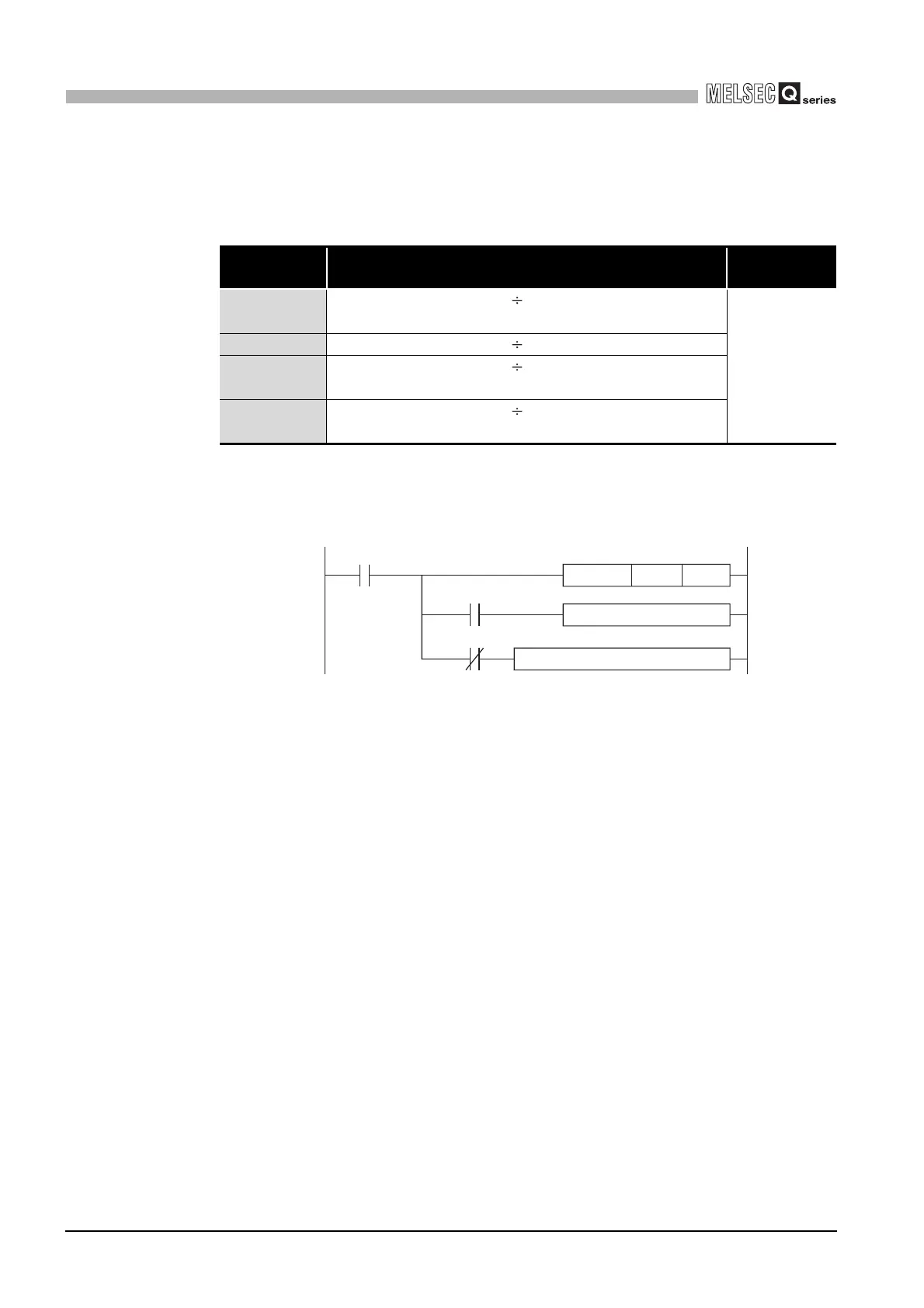
Figure 14.5 Program example using S(P).GINT instruction
S.GINT H3E1 K0
Normally completed program
Program that will cause interrupt again
SM391
SM391
X0

 Loading...
Loading...











