BANZ 16bitOffset,ARn−−
6-59
BANZ 16bitOffset,ARn−− Branch if Auxiliary Register Not Equal to Zero
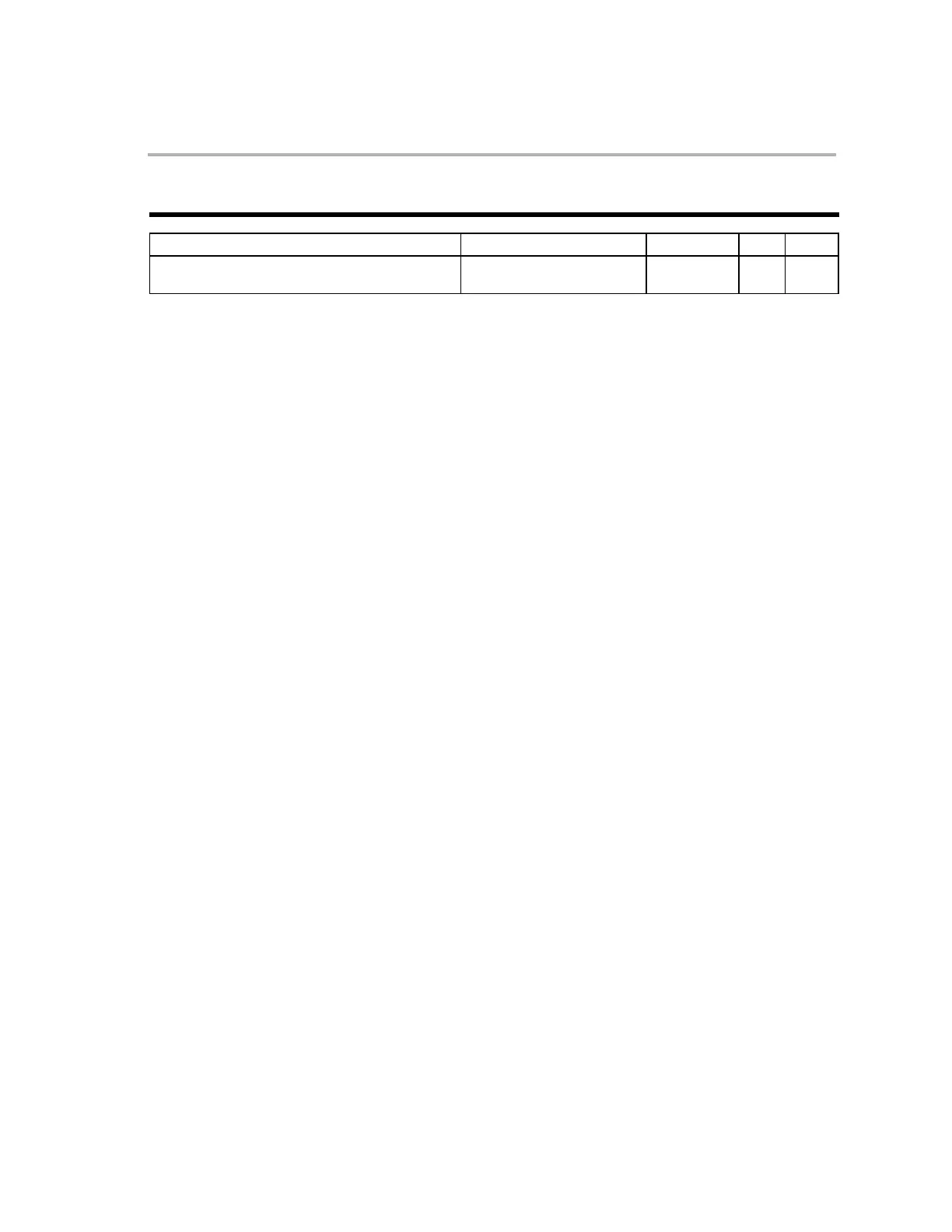
SYNTAX OPTIONS OPCODE OBJMODE RPT CYC
BANZ 16bitOffset,ARn−− 0000 0000 0000 1nnn
CCCC CCCC CCCC CCCC
X − 4/2
Operands 16bit-
Offset
16-bit signed immediate constant value
ARn Lower 16 bits of auxiliary registers XAR0 to XAR7
Description If the 16-bit content of the specified auxiliary register is not equal to 0, then the
16-bit sign offset is added to the PC value. This forces program control to the
new address (PC + 16bitOffset). The 16-bit offset is sign extended to 22 bits
before the addition. Then, the content of the auxiliary register is decremented
by 1. The upper 16 bits of the auxiliary register (ARnH) is not used in the
comparison and is not affected by the post decrement:
if( ARn != 0 )
PC = PC + signed 16-bit offset;
ARn = ARn – 1;
ARnH = unchanged;
Note: If branch is taken, then the instruction takes 4 cycles
If branch is not taken, then the instruction takes 2 cycles
Flags and
Modes
None
Repeat This instruction is not repeatable. If this instruction follows the RPT
instruction, it resets the repeat counter (RPTC) and executes only once.
Example
; Copy the contents of Array1 to Array2:
; int32 Array1[N];
; int32 Array2[N];
; for(i=0; i < N; i++)
; Array2[i] = Array1[i];
MOVL XAR2,#Array1 ; XAR2 = pointer to Array1
MOVL XAR3,#Array2 ; XAR3 = pointer to Array2
MOV @AR0,#(N−1) ; Repeat loop N times
Loop:
MOVL ACC,*XAR2++ ; ACC = Array1[i]
MOVL *XAR3++,ACC ; Array2[i] = ACC
BANZ Loop,AR0−− ; Loop if AR0 != 0, AR0−−
 Loading...
Loading...