CPU Registers
2-11Central Processing Unit
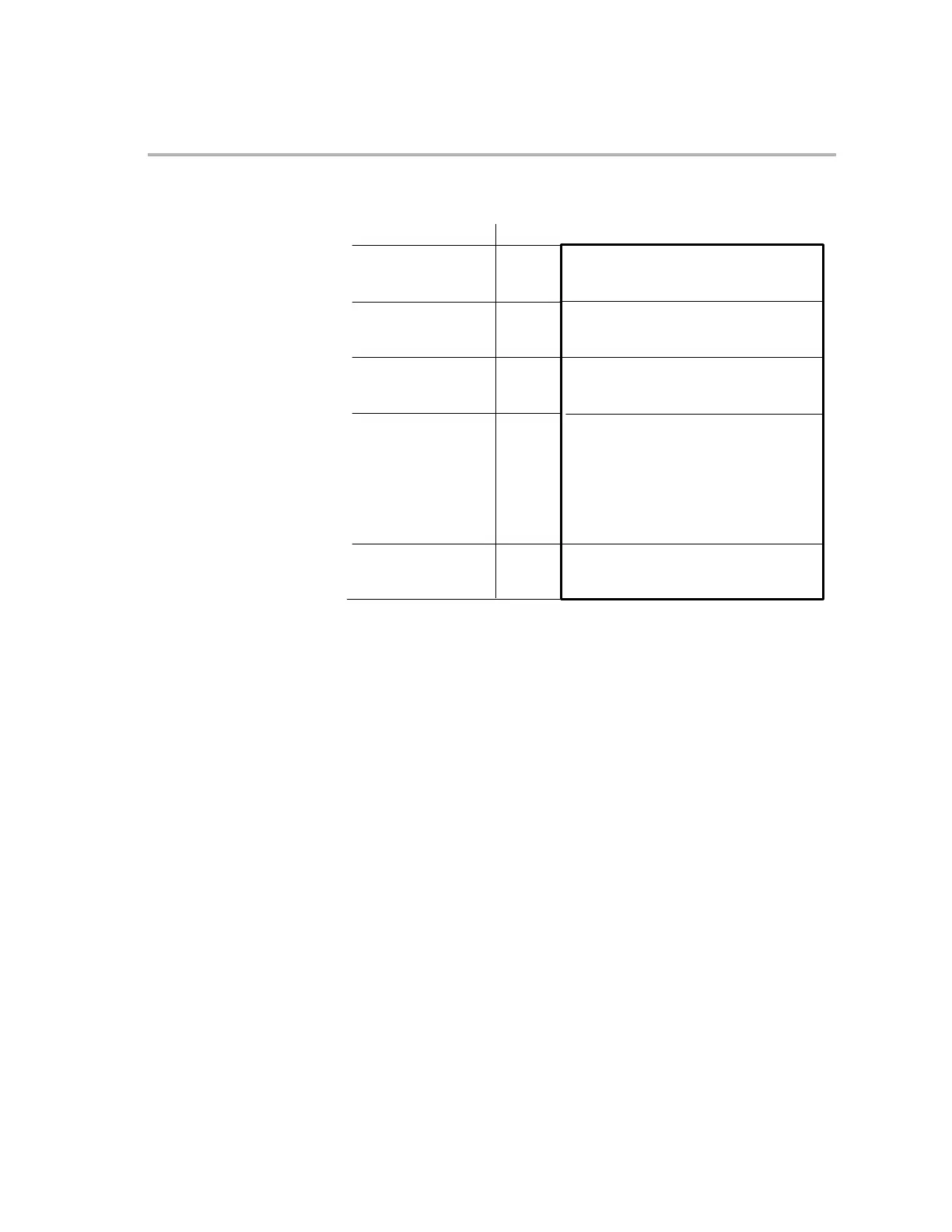
Figure 2−6. Pages of Data Memory
11 1111 1111 1111 11
11 1111
11 1111
00 0000 0000 0000 10
00 0000 0000 0000 01
00 0000 0000 0000 10
00 0000 0000 0000 00
Data memory
Page 0:
Page 1:
Page 2:
Page 65535:
00 0000
OffsetData page
00 0000 0000 0000 00
11 1111
00 0000 0000 0000 01
11 1111 1111 1111 11
00 0000
00 0000
11 1111
00 0000
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
00000000−0000003F
00000040−0000007F
00000080−000000BF
003FFFC0−003FFFFF
.
.
.
.
.
.
Data memory above 4M words is not accessible using the DP.
When operating in C2xLP source-compatible mode, a 7-bit offset is used and
the least significant bit of the DP register is ignored. See Appendix C for more
details.
2.2.5 Stack Pointer (SP)
The stack pointer (SP) enables the use of a software stack in data memory.
The stack pointer has only 16 bits and can only address the low 64K of data
space (see Figure 2−7). When the SP is used, the upper six bits of the 32-bit
address are forced to 0. (For information about addressing modes that use the
SP, see section 5.5 on page 5-9.). After reset, SP points to address
00000400
16
.
 Loading...
Loading...