CPU Registers
2-8
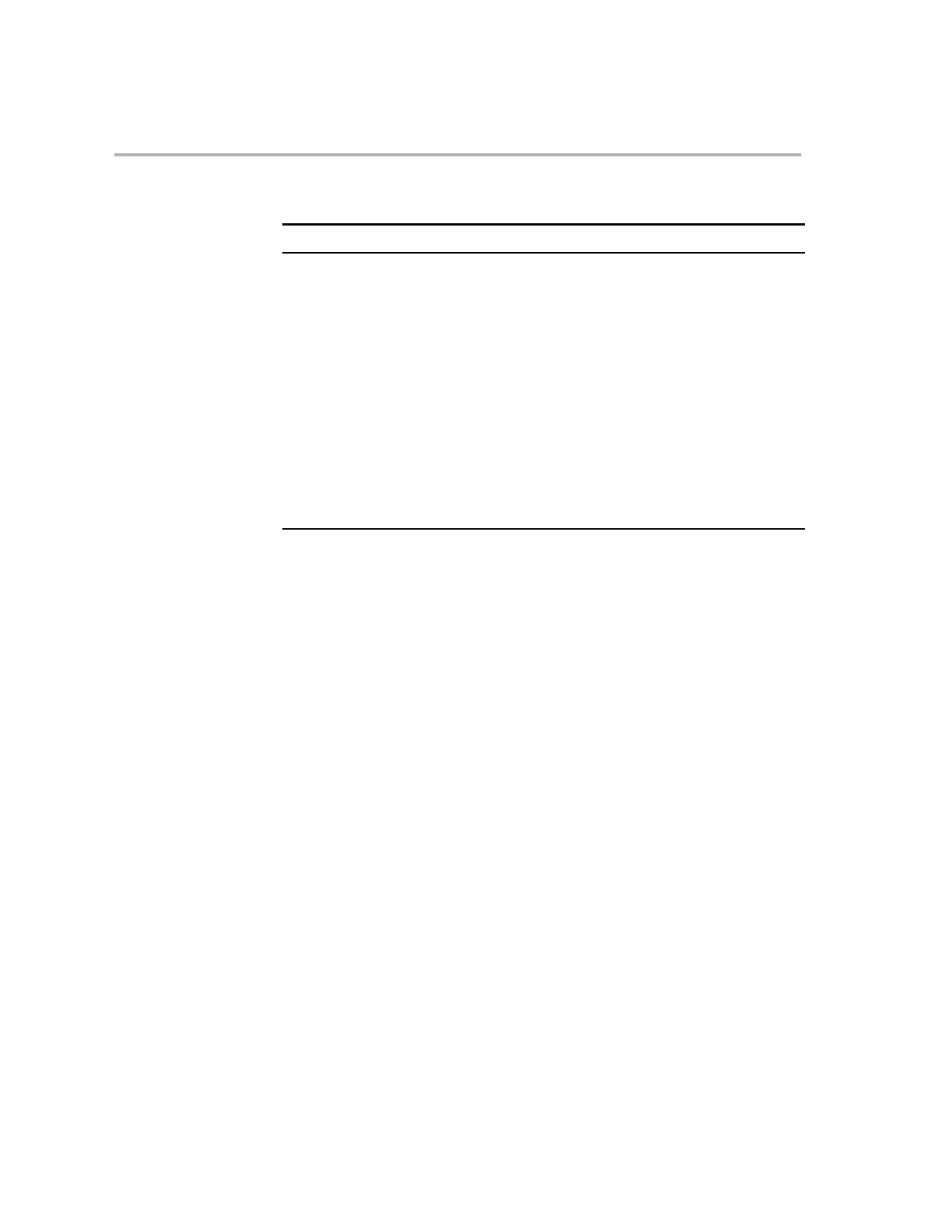
Table 2−2. Available Operations for Shifting Values in the Accumulator
Register Shift Direction Shift Type Instruction
ACC Left Logical LSL or LSLL
Rotation ROL
Right Arithmetic SFR with SXM = 1
or ASRL
Logical SFR with SXM = 0
or LSRL
Rotation ROR
AH or AL Left Logical LSL
Right Arithmetic ASR
Logical LSR
2.2.2 Multiplicand Register (XT)
The multiplicand register (XT register) is used primarily to store a 32-bit signed
integer value prior to a 32-bit multiply operation.
The lower 16-bit portion of the XT register is referred to as the TL register. This
register can be loaded with a signed 16-bit value that is automatically sign-ex-
tended to fill the 32-bit XT register.
The upper 16-bit portion of the XT register is referred to as the T register. The
T register is mainly used to store a 16-bit integer value prior to a 16-bit multiply
operation.
The T register is also used to specify the shift value for some shift operations.
In this case, only a portion of the T register is used, depending on the instruc-
tion.
For example:
ASR AX, T performs an arithmetic shift right
based on the four least significant bits
of T: T(3:0) = 0...15
ASRL ACC, T performs an arithmetic shift right by
the five least significant bits of T:
T(4:0) 0...31
For these operations, the most significant bits of T are ignored.

 Loading...
Loading...