CPU Registers
2-7Central Processing Unit
compare operations from 32-bit-wide data memory. It can also accept the
32-bit result of a multiplication operation.
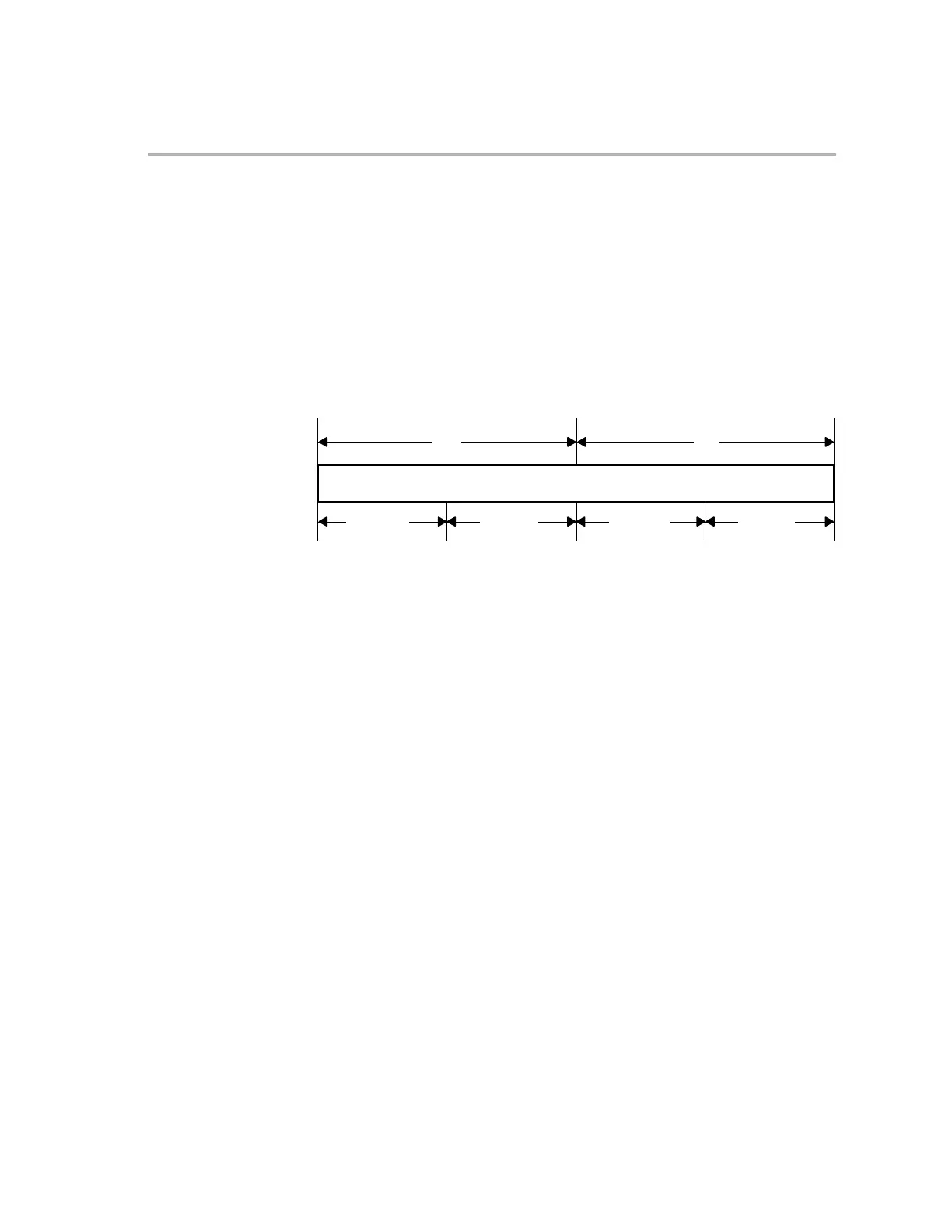
The halves and quarters of the ACC can also be accessed (see Figure 2−3).
ACC can be treated as two independent 16-bit registers: AH (high 16 bits) and
AL (low 16 bits). The bytes within AH and AL can also be accessed
independently. Special byte-move instructions load and store the most signifi-
cant byte or least significant byte of AH or AL. This enables efficient byte pack-
ing and unpacking.
Figure 2−3. Individually Accessible Portions of the Accumulator
ACC
AH AL
AH.MSB
AH = ACC (31:16)
AH.MSB = ACC (31:24)
AH.LSB = ACC (23:16)
AH.LSB AL.MSB AL.LSB
AL = ACC (15:0)
AL.MSB = ACC (15:8)
AL.LSB = ACC (7:0)
The accumulator has the following associated status bits. For the details on
these bits, see section 2.3, Status Register ST0.
- Overflow mode bit (OVM)
- Sign-extension mode bit (SXM)
- Test/control flag bit (TC)
- Carry bit (C)
- Zero flag bit (Z)
- Negative flag bit (N)
- Latched overflow flag bit (V)
- Overflow counter bits (OVC)
Table 2−2 shows the ways to shift the content of AH, AL, or ACC.

 Loading...
Loading...