Operation
0590−1/A1
Winterthur Gas & Diesel Ltd.
1/ 2
Defective Turbocharger
1. General
If a turbocharger becomes defective, you must shut down the engine as quickly as
possible to prevent damage.
If repair or replacement of a turbocharger is not immediately possible, the engine can
operate in Emergency Operation at decreased load after the procedure below is
completed.
In Emergency Operation, you must operate the engine only for as long as necessary
(see 0500−1, paragraph 2 Decreased Power Output).
The loads (outputs) given are guidance values, which are related to the condition of
the engine. It is possible that these values will be decreased.
2. Defective Conditions
2.1 Condition One
One turbocharger is defective.
2.1.1 Procedure
The engine load output is approximately
50% of the CMCR. This is related to the
output of the auxiliary blowers.
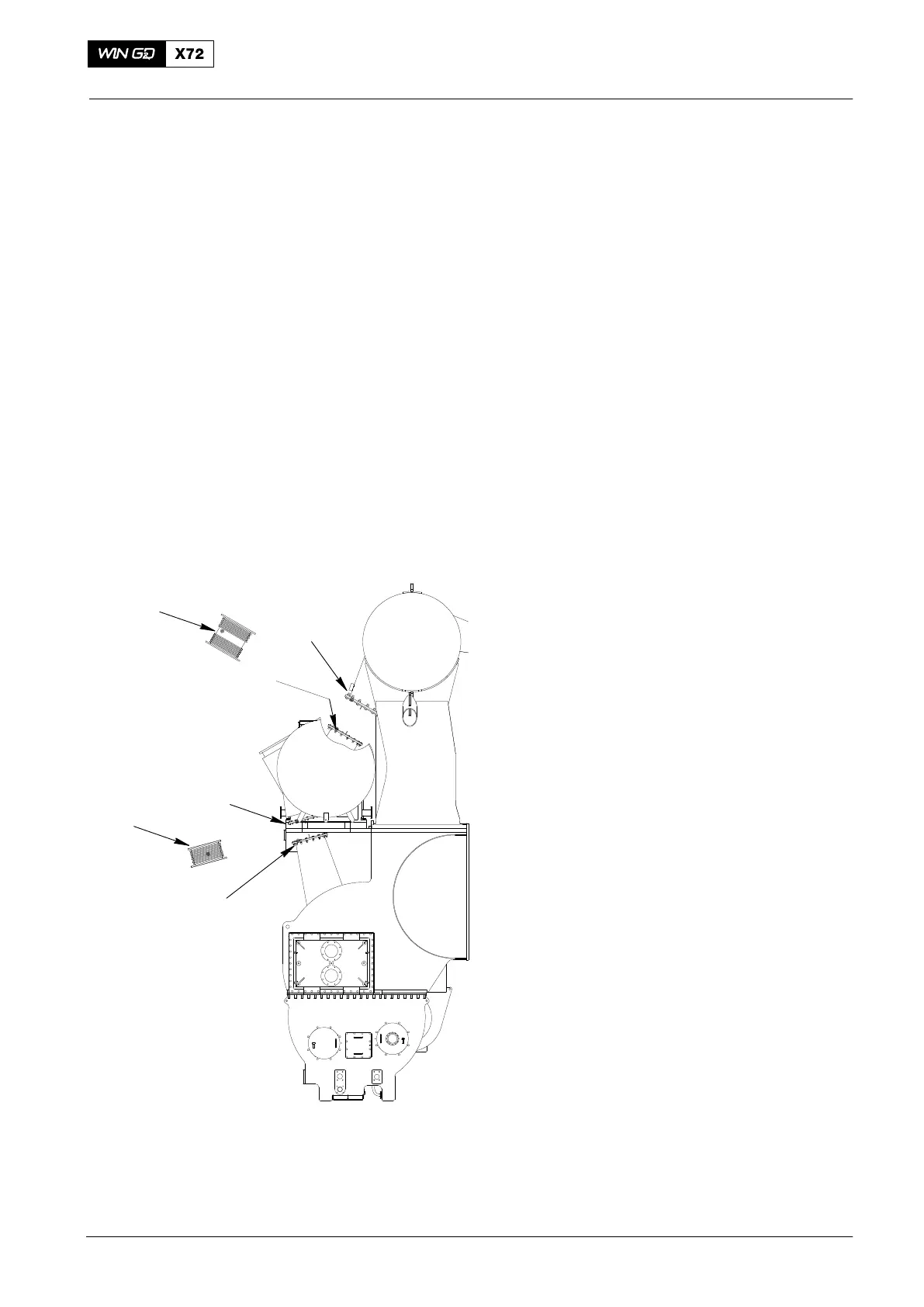
1) Lock the rotor of the turbocharger (see
the turbocharger manual).
2) Remove the expansion joint (6, Fig. 1)
from the defective turbocharger and the
exhaust manifold.
3) Install the blind flanges (1) and (2, tool
94653).
4) Remove the expansion joint (5) from
the defective turbocharger air outlet
and the diffusor.
Note: Install the blind flange (3) only if
air flows in through a suction duct.
5) Install the blind flanges (3, tool 94655)
and (4, tool 94653).
The scavenge air pressure, turbocharger
speed and firing pressures must not be
higher than during usual operation.
Note: Before you start the turbocharger,
make sure that you remove the
plugs from the oil supply pipes.
2014
Operation during Unusual Conditions
1
2
3
4
6
5
Fig. 1: Defective Condition One
 Loading...
Loading...