Administrator’s Guide for SIP-T5 Series Smart Media Phones
552
equivalent capability call server take over from the one that has gone down/off-line. This
mode of operation should be done using the DNS mechanism from the primary to the
secondary server. Therefore, if you want to use this mode, the server must be configured
with a domain name.
Fallback: In this mode, a second less featured call server with SIP capability takes over call
control to provide basic calling capability, but without some advanced features (for
example, shared line and MWI) offered by the working server. IP phones support
configuration of two servers per SIP registration for fallback purpose.
Note
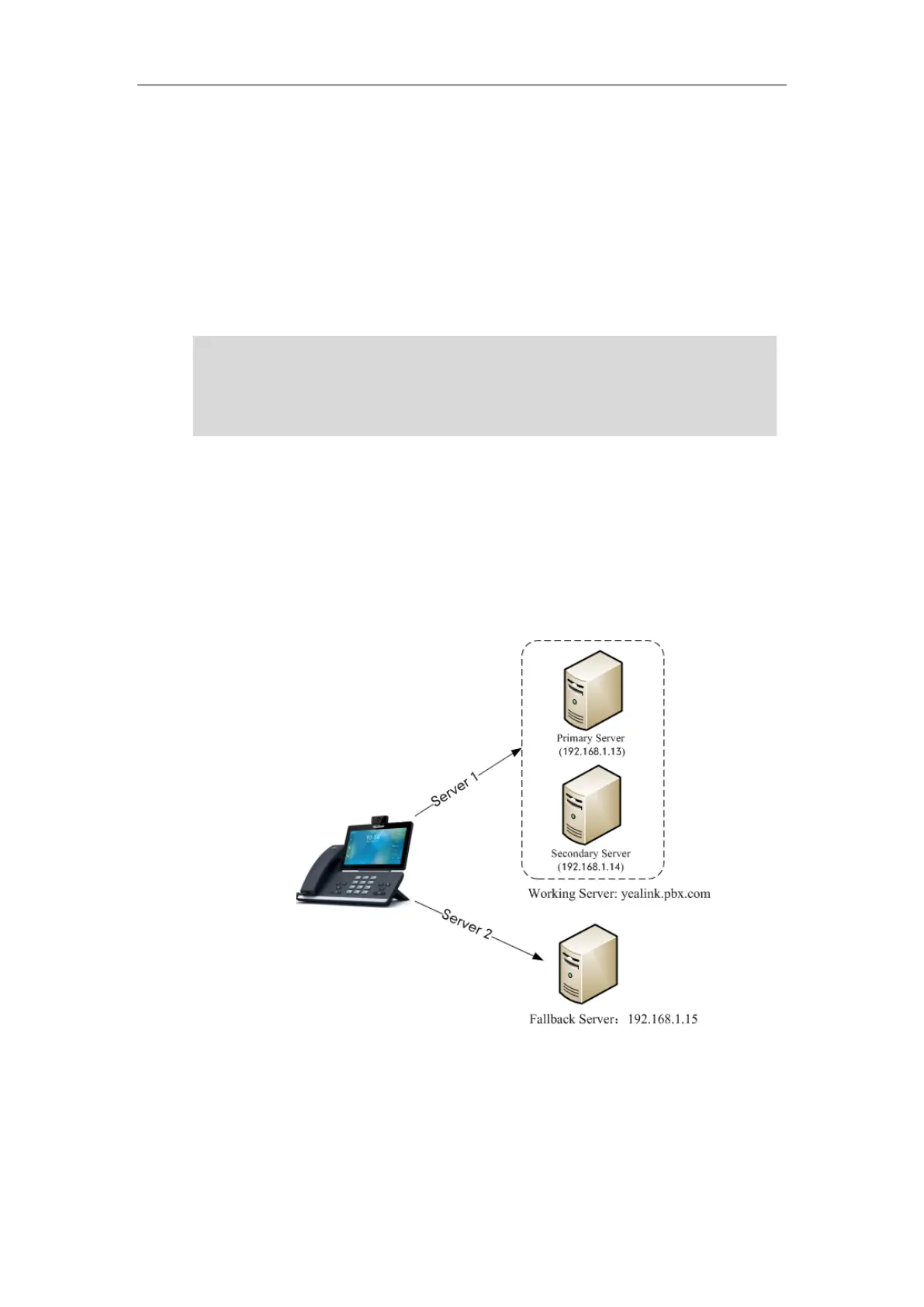
Phone Configuration for Redundancy Implementation
To assist in explaining the redundancy behavior, an illustrative example of how an IP phone may
be configured is shown as below. In the example, server redundancy for fallback and failover
purposes is deployed. Two separate servers (a working server and a fallback server) are
configured for per line registration.
Working Server: Server 1 is configured with the domain name of the working server. For
example: yealink.pbx.com. DNS mechanism is used such that the working server is resolved
to multiple servers with different IP addresses for failover purpose. The working server is
deployed in redundant pairs, designated as primary and secondary servers. The primary
server (e.g., 192.168.1.13) has the highest priority server in a cluster of servers resolved by
the DNS server. The secondary server (e.g., 192.168.1.14) backs up a primary server when
For concurrent registration mode, it has certain limitation when using some advanced features,
and for successive registration mode, the phone service may have a brief interrupt while the
server fails. So we recommend you to use the failover mode for server redundancy because this
mode can ensure the continuity of the phone service and you can use all the call features while

 Loading...
Loading...