Page 458 7750 SR OS Services Guide
Inter-Domain VPLS Resiliency Using Multi-Chassis Endpoints
Inter-domain VPLS refers to a VPLS deployment where sites may be located in different domains.
An example of inter-domain deployment can be where different Metro domains are interconnected
over a Wide Area Network (Metro1-WAN-Metro2) or where sites are located in different
autonomous systems (AS1-ASBRs-AS2).
Multi-chassis endpoint (MC-EP) provides an alternate solution that does not require RSTP at the
gateway VPLS PEs while still using pseudowires to interconnect the VPLS instances located in
the two domains. It is supported in both VPLS and PBB-VPLS on the B-VPLS side.
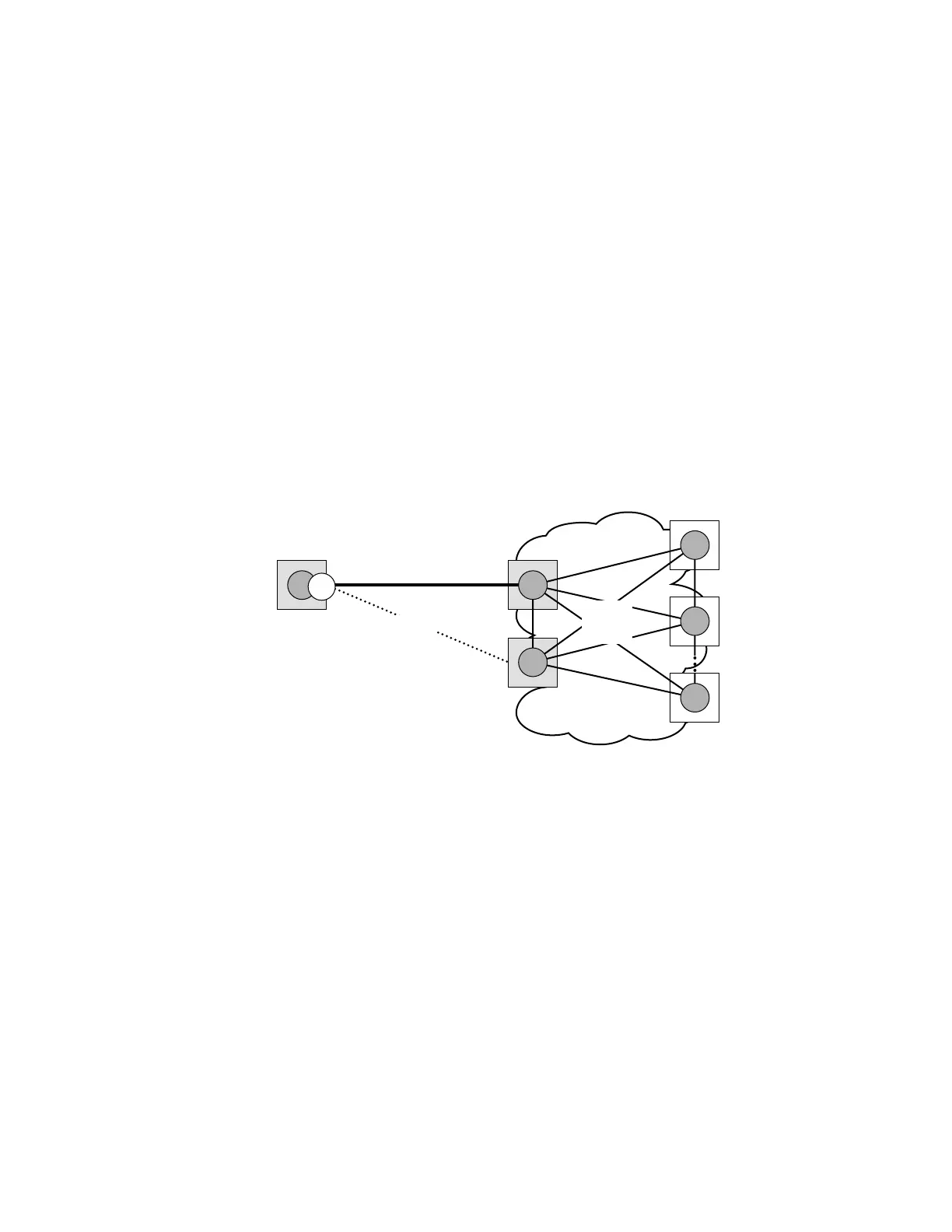
MC-EP expands the single chassis endpoint based on active-standby pseudowires for VPLS
shown in Figure 65.
Figure 65: HVPLS Resiliency Based on AS Pseudowires
The active-standby pseudowire solution is appropriate for the scenario when only one VPLS PE
(MTU-s) needs to be dual-homed to two core PEs (PE1 and PE2). When multiple VPLS domains
need to be interconnected the above solution provides a single point of failure at the MTU-s. The
example depicted in Figure 66 can be used.
OSSG249
HVPLS Resiliency
VPLS
(Mesh)
MTUs
PE1
PE2
EP
Active PW
Standby PW

 Loading...
Loading...











