PBB Features
Page 778 7750 SR OS Services Guide
IEEE 802.1ak MMRP for Service Aggregation and Zero Touch
Provisioning
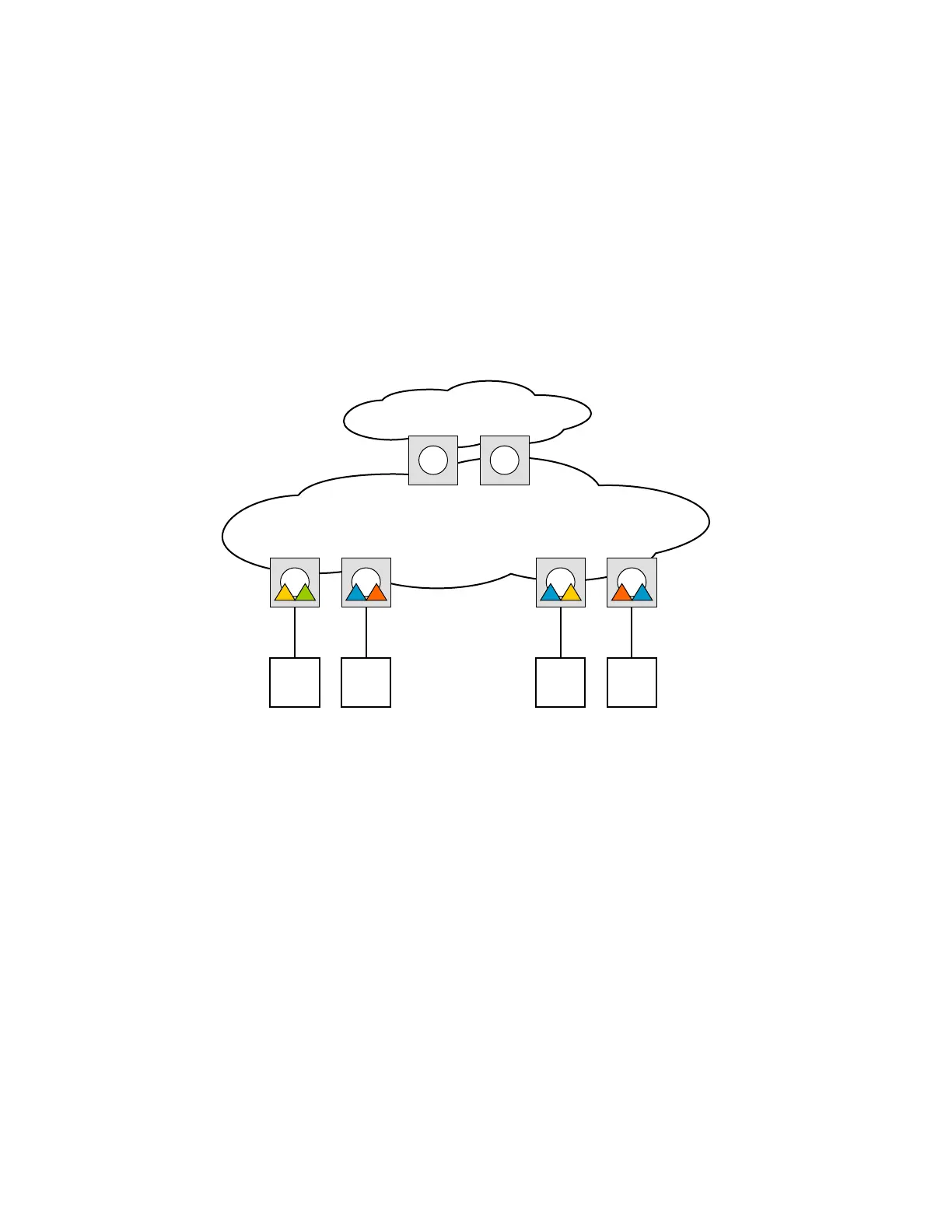
IEEE 802.1ah supports an M:1 model where multiple customer services, represented by ISIDs, are
transported through a common infrastructure (B-component). Alcatel-Lucent’s PBB
implementation supports the M:1 model allowing for a service architecture where multiple
customer services (I-VPLS or Epipe) can be transported through a common B-VPLS infrastructure
as depicted in Figure 104.
Figure 104: Customer Services Transported in 1 B-VPLS (M:1 Model)
The B-VPLS infrastructure represented by the white circles is used to transport multiple customer
services represented by the triangles of different colors. This service architecture minimizes the
number of provisioning touches and reduces the load in the core PEs: for example, G and H use
less VPLS instances and pseudowire.
In a real life deployment, different customer VPNs do not share the same community of interest –
for example, VPN instances may be located on different PBB PEs. The M:1 model depicted in
Figure 105 requires a per VPN flood containment mechanism so that VPN traffic is distributed just
to the B-VPLS locations that have customer VPN sites: for example, flooded traffic originated in
the blue I-VPLS should be distributed just to the PBB PEs where blue I-VPLS instances are
present – PBB PE B, E and F.
OSSG195
E
QinQ
Switch
B-VPLS Metro Infrastructure
Native Ethernet or PWs (Mesh/Spoke)
B-VPLS Core Mesh
F
GH
QinQ
Switch
A
QinQ
Switch
B
QinQ
Switch

 Loading...
Loading...











