PBB Features
Page 804 7750 SR OS Services Guide
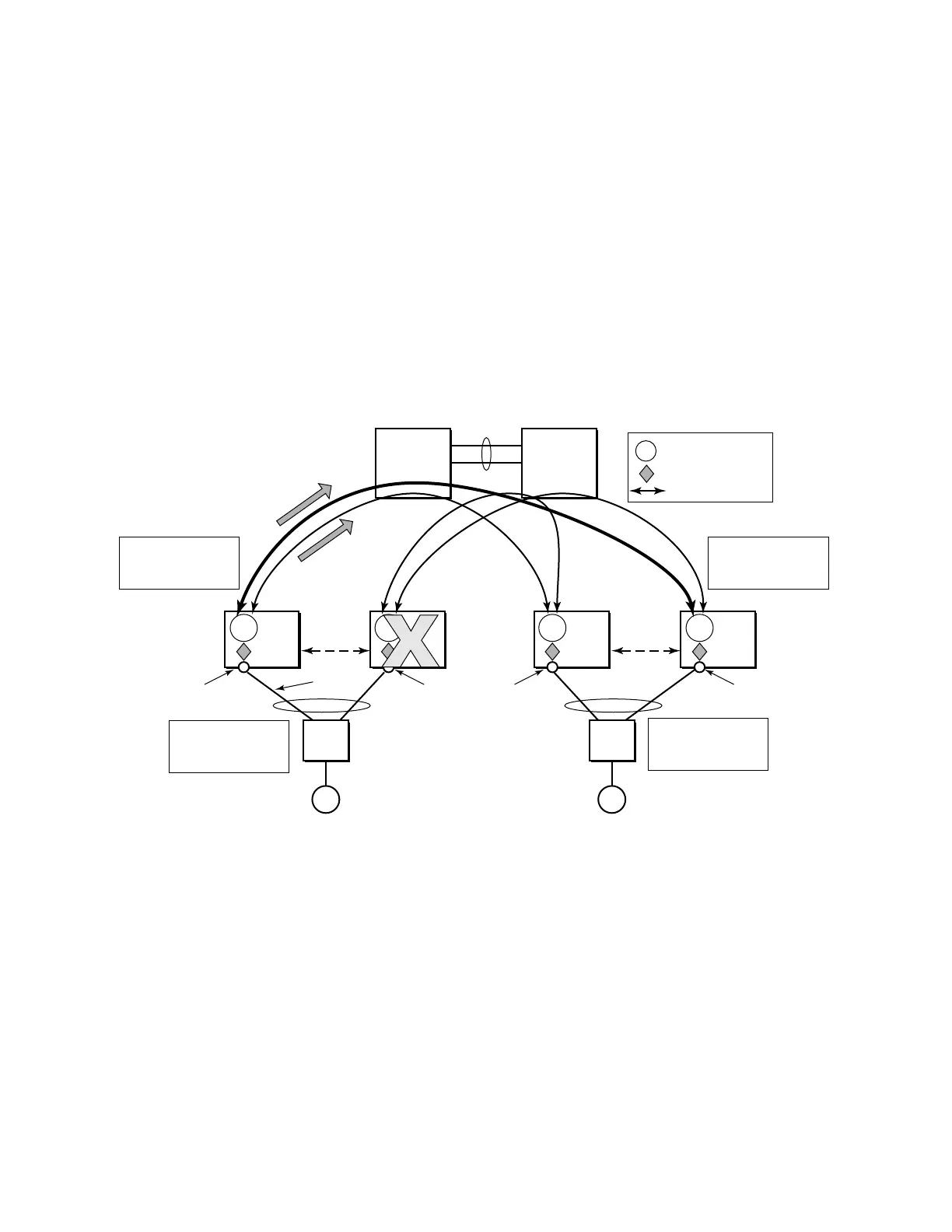
associated with the active MC-LAG are actively used for forwarding into B-VPLS the traffic
ingressing related EPIPE SAPs.
MC-LAG protocol keeps track of which side is active and which is standby for a given MC-LAG
grouping and activates the standby link in a failure scenario. The source BMACs C1 and A1 are
used for PBB encapsulation as traffic arrives at the EPIPE SAPs on P11 and P9, respectively.
MAC Learning in the B-VPLS instances installs MAC FIB entries in BEB C and BEB A as
depicted in Figure 117. The highlighted Ethernet tunnel (EPS) will be used to forward the traffic
between BEB A and BEB C.
Active link (P11) or access node (BEB C) failures are activating through MC-LAG protocol, the
standby link (P12) participating in the MC-LAG on the pair MC-LAG device (BEB D). The
failure of BEB C is depicted in Figure 118. The same procedure applies for the link failure case.
Figure 118: Access Dual-Homing for PBB ELINE - BEB Failure
The following process steps apply:
• BEB D will lose MC-LAG communication with its peer BEB C - no more keep-alives
from BEB C or next-hop tracking may kick in.
• BEB D assumes BEB C is down and activates all shared MC-LAG links, including P12.
OSSG354
BCB-E BCB-F
MC-LAG
P12
Active
P11
Standby
P10
Standby
P9
Active
BMAC
A1
Bridge Table on
BEB D
BMAC A1 EP8
Bridge Table on
BEB C
BMAC A1 EP6
Bridge Table on
BEB A
BMAC C1 EP2
Bridge Table on
BEB B
BMAC C1 EP4
BMAC
D
BMAC
C
C-MAC-1 C-MAC-2
ES1 ES2
BEB
D
BEB
C
IP6EP8 EP2
BVPLS Instance
EPIPE Instance
EPS Tunnel
EP4EP5EP7 EP1EP3
BEB
B
BEB
A
MC-LAG
BMAC
B
BMAC
A
BMAC
C1
BMAC
A1
BMAC
C1
CFM Message - New Opcode
Sorce: CC1 Dest: CFM-Mcast

 Loading...
Loading...











