Chapter 5 Parameter Introductions
133
Note:
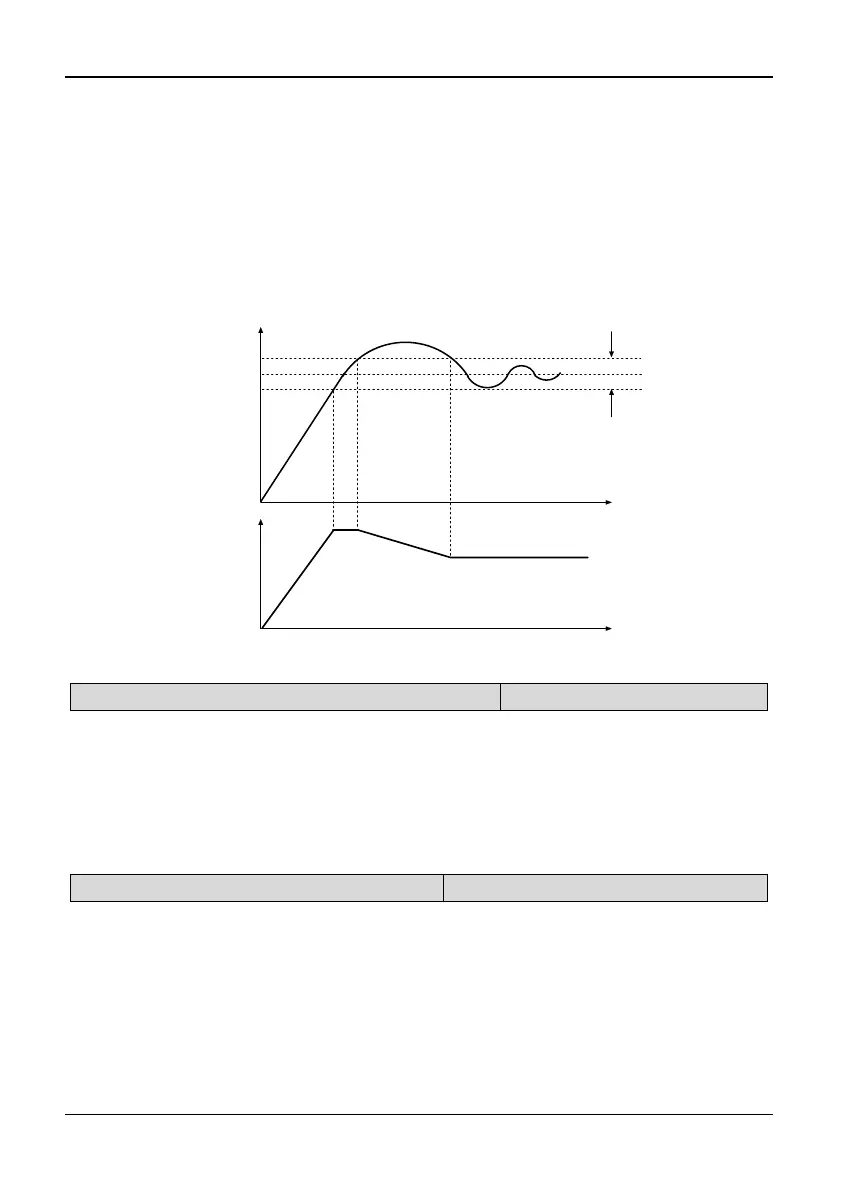
If the residual between feed and feedback value is smaller than residual margin,
PID regulation will stop and the PID output maintain constant. As shown in Fig.
5-7-1.
Setting this parameter correctly is helpful to balance the system output accuracy
and stability. The residual margin reduces the regulation accuracy of the system,
but improves the system stability, to avoid unnecessary fluctuations of output.
If analog PID is selected, the setting of residual margin (P7.09) is the absolute value
of physical value, and it must match the measuring range. If speed PID is selected,
the setting of P7.09 is speed. As shown in Fig.5-7-1:
Time
Time
Reference
Feedback
Residual margin
Opereation Freq.
Fig. 5-7-1 Residual margin diagram
P7.10 PID adjust characteristics
Range: 0,1【0】
0: Positive 1: Negative
Note:
Positive: When the PID output increases, the output frequency will increase and
the controlled physical value will increase, such as waterworks.
Negative: When the PID output increases, the output frequency will increase, but
the controlled physical value will decrease, such as refrigeration system.
P7.11 Integration adjust selection
Range: 0,1【0】
0: Stop Integration Adjust when frequency arrive at limit;
1: Continue Integration Adjust when frequency arrive at limit
Tips:
For the system that needs fast response, “stop integration adjust when frequency arrives
at limit” is recommended.
 Loading...
Loading...